在FPGA设计开发中,很多场合会遇到同一根信号既可以是输入信号,又可以是输出信号,即IO类型(Verilog定义成inout)。
对于inout型的信号,我们既可以使用FPGA原语来实现,也可以使用Verilog代码来实现。下面将介绍在Xilinx 7系列FPGA上两种实现方式的差别和注意点。
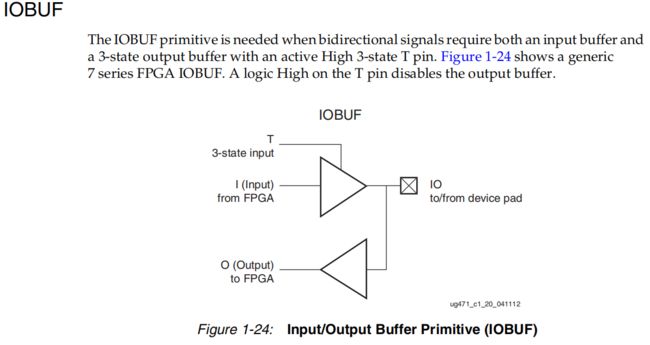
不管哪种方式实现IO功能,从编译结果看都会调用IOBUF原语,为此,我们先来看一下IOBUF的结构,如下图所示。
1.FPGA原语实现
首先,我们编写的代码如下:
1`define PRIMITIVE 2 3 module io_buf( 4 input T , 5 input I , 6 output O , 7 inout IO 8 ); 9 10 `ifdef PRIMITIVE 11 IOBUF #( 12 .DRIVE (12 ), // Specify the output drive strength 13 .IBUF_LOW_PWR ("TRUE" ), // Low Power - "TRUE", High Performance = "FALSE" 14 .IOSTANDARD ("DEFAULT" ), // Specify the I/O standard 15 .SLEW ("SLOW" ) // Specify the output slew rate 16 ) IOBUF_INST ( 17 .O (O ), // Buffer output 18 .IO (IO ), // Buffer inout port (connect directly to top-level port) 19 .I (I ), // Buffer input 20 .T (T ) // 3-state enable input, high=input, low=output 21 ); 22 `else 23 assign IO = T? I:1'bz; 24 assign O = IO; 25 `endif 26 27 endmodule
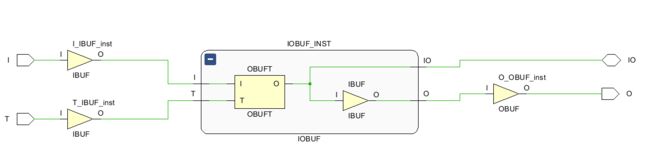
该代码通过原语IOBUF实现IO功能,使用Vivado编译后的原理图如下图所示。可以看到IOBUF内部由OBUFT和IBUF原语构成。
2.使用Verilog实现
把`define PRIMITIVE注释掉,则为通过Verilog的实现方式,如下图:
//`define PRIMITIVE module io_iobuf( input T , input I , output O , inout IO ); `ifdef PRIMITIVE IOBUF #( .DRIVE (12 ), // Specify the output drive strength .IBUF_LOW_PWR ("TRUE" ), // Low Power - "TRUE", High Performance = "FALSE" .IOSTANDARD ("DEFAULT" ), // Specify the I/O standard .SLEW ("SLOW" ) // Specify the output slew rate ) IOBUF_INST ( .O (O ), // Buffer output .IO (IO ), // Buffer inout port (connect directly to top-level port) .I (I ), // Buffer input .T (T ) // 3-state enable input, high=input, low=output ); `else assign IO = T? I:1'bz; assign O = IO; `endif endmodule
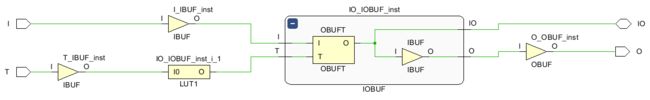
该代码使用Vivado编译后的原理图如下图所示。该实现方式也会调用IOBUF原语,但多消耗了一个LUT资源。
通过Verilog实现时,我们在把IO信号当成输入时给赋值高阻态(1‘bz)。假如我们把此时的IO信号赋值1‘b0或者1‘b1,会出现什么情况呢?我们把1‘bz写成1‘b1,如下所示:
1 //`define PRIMITIVE 2 3 module io_iobuf( 4 input T , 5 input I , 6 output O , 7 inout IO 8 ); 9 10 `ifdef PRIMITIVE 11 IOBUF #( 12 .DRIVE (12 ), // Specify the output drive strength 13 .IBUF_LOW_PWR ("TRUE" ), // Low Power - "TRUE", High Performance = "FALSE" 14 .IOSTANDARD ("DEFAULT" ), // Specify the I/O standard 15 .SLEW ("SLOW" ) // Specify the output slew rate 16 ) IOBUF_INST ( 17 .O (O ), // Buffer output 18 .IO (IO ), // Buffer inout port (connect directly to top-level port) 19 .I (I ), // Buffer input 20 .T (T ) // 3-state enable input, high=input, low=output 21 ); 22 `else 23 assign IO = T? I:1'b1; 24 assign O = IO; 25 `endif 26 27 endmodule
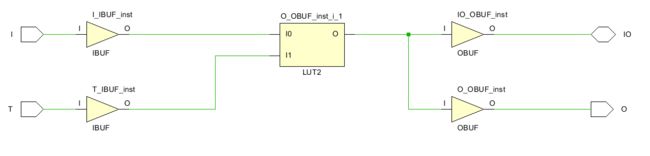
编译后的原理图如下,可以看到并不会调用IOBUF原语,IO的不能实现输入功能,这就是解释了为什么在使用Verilog实现一根信号的IO功能时需要赋值1‘bz。