Hystrix
学习资料:https://github.com/Netflix/Hystrix/wiki
What Is Hystrix For?
Hystrix is designed to do the following:
- Give protection from and control over latency and failure from dependencies accessed (typically over the network) via third-party client libraries. 让程序具有处理调用外部服务失败的能力
- Stop cascading failures in a complex distributed system.
- Fail fast and rapidly recover.
- Fallback and gracefully degrade when possible.
- Enable near real-time monitoring, alerting, and operational control.
Hystrix works by:
- Preventing any single dependency from using up all container (such as Tomcat) user threads.
- Shedding load and failing fast instead of queueing.
- Providing fallbacks wherever feasible to protect users from failure.
- Using isolation techniques (such as bulkhead, swimlane, and circuit breaker patterns) to limit the impact of any one dependency.
- Optimizing for time-to-discovery through near real-time metrics, monitoring, and alerting
- Optimizing for time-to-recovery by means of low latency propagation of configuration changes and support for dynamic property changes in most aspects of Hystrix, which allows you to make real-time operational modifications with low latency feedback loops.
- Protecting against failures in the entire dependency client execution, not just in the network traffic.
Hystrix使用命令模式HystrixCommand(Command)包装依赖调用逻辑,每个命令在单独线程中/信号授权下执行
Hello World
下面是一个HystrixCommand的简单的“hello world”实现
public class CommandHelloWorld extends HystrixCommand {
private final String name;
public CommandHelloWorld(String name) {
super(HystrixCommandGroupKey.Factory.asKey("ExampleGroup"));
this.name = name;
}
@Override
protected String run() {
// a real example would do work like a network call here
return "Hello " + name + "!";
}
}
同步执行
Hystrix commands能通过execute()方法调用被同步的执行
String s = new CommandHelloWorld("World").execute();
异步执行
异步执行通过调用queue()方法实现
Future fs = new CommandHelloWorld("World").queue();
响应式执行
响应式执行(异步回调)通过使用observe() 执行
Observable fs = new CommandHelloWorld("World").observe();
返回值可以通过订阅Observable获得
fs.subscribe(new Action1() {
@Override
public void call(String s) {
// value emitted here
}
});
Fallback
优美的降级可以通过增加一个getFallback()实现来达到。该方法在各种类型的失败后执行。如: run()方
法调用失败,超时,线程池,信号丢弃以及熔断器短路。
@Override
protected String getFallback() {
return "Hello Failure " + name + "!";
}
错误传播
从run()方法中抛出的所以异常(除了HystrixBadRequestException)都被计为异常。将触发getFallback()
和熔断逻辑。在HystrixBadRequestException中抛出的例外,你可以根据你的喜好进行包装,然后通过
getCause()获取。
HystrixBadRequestException设计的使用场景为,报告不合法的参数或非系统性错误。这些都不能计入失
败次数的度量,也不应当触发回退逻辑
Command Name
Command Group
group进行统一管理
command组键名被用于将command分组,如报表,警告,面板或者组包的所以者。
默认情况下,它被用于command的线程池的命名,除非有单独的定义
private static final Setter cachedSetter =
Setter.withGroupKey(HystrixCommandGroupKey.Factory.asKey("ExampleGroup"))
.andCommandKey(HystrixCommandKey.Factory.asKey("HelloWorld"));
public CommandHelloWorld(String name) {
super(cachedSetter);
this.name = name;
}
Command线程池
线程池的键被用于监控HystrixThreadPool时的呈现,度量的发布,缓存等其它应用。一个
HystrixCommand 是和一个单个的HystrixThreadPool相关联,通过注入它的HystrixThreadPoolKey可以取
得HystrixThreadPool 或者它默认情况下用HystrixCommandGroupKey创建一个。
请求缓存
请求缓存通过实现HystrixCommand或者HystrixObservableCommand中的getCacheKey()方法完成:依赖于request context 的某些东西,必须实例化HystrixRequestContext
public class CommandUsingRequestCache extends HystrixCommand {
private final int value;
protected CommandUsingRequestCache(int value) {
super(HystrixCommandGroupKey.Factory.asKey("ExampleGroup"));
this.value = value;
}
@Override
protected Boolean run() {
return value == 0 || value % 2 == 0;
}
@Override
protected String getCacheKey() {
return String.valueOf(value);
}
}
请求合并
请求合并是一个特性,它能自动将一批请求合并到单一的HystrixCommand实例中执行。
可以设定批次的大小和时间作为促发器来执行一个批次
两种style的请求合并
- request-scoped
- globally-scoped.
This is configured at collapser construction, and defaulted to request-scoped.
Request Context Setup
为了能使用request的scoped特性(请求缓存,请求折叠,请求日记)HystrixRequestContext 的生命周期
必须被管理起来。(或者一个替代的HystrixConcurrencyStrategy 实现)
这就意味着下面代码必须在一个请求之前执行
HystrixRequestContext context = HystrixRequestContext.initializeContext();
然后在请求的最后调用
context.shutdown();
常见模式
快速失败 Fail Fast
无声失败 Fail Silent
无声的失败等同于返回一个空的响应或者删除功能,它通过返回null,空的map对象,空的list或者其他类似
的响应实现。 通常通过HystrixCommand实例中的getFallback() 方法实现
回退:静态的 Fallback:Static
一些回退能返回在代码中硬编码的值。它不能引起特性或将被移除服务(如同无声失败经常处理的方
法),但是执行默认的行为逻辑。
Fallback: Stubbed
一个存根回退典型的被用于包含多个字段的一个组合对象被返回时。它们其中的一部分能被其它请求状态
来决定。当其它字段被设置为默认值。
Fallback: Cache via Network
由于回退如果重掉网络可能导致另外的失败,因此需要通过另外的HystrixCommand转换。
另外重要的是,回退command应当在独立的线程池中执行。如果两个command共享相同的线程池,会导
致主command将变的延迟并且占用整个的线程池,从而阻止回退。
主从都失效
通过两个Command进行隔离
Client Doesn't Perform Network Access
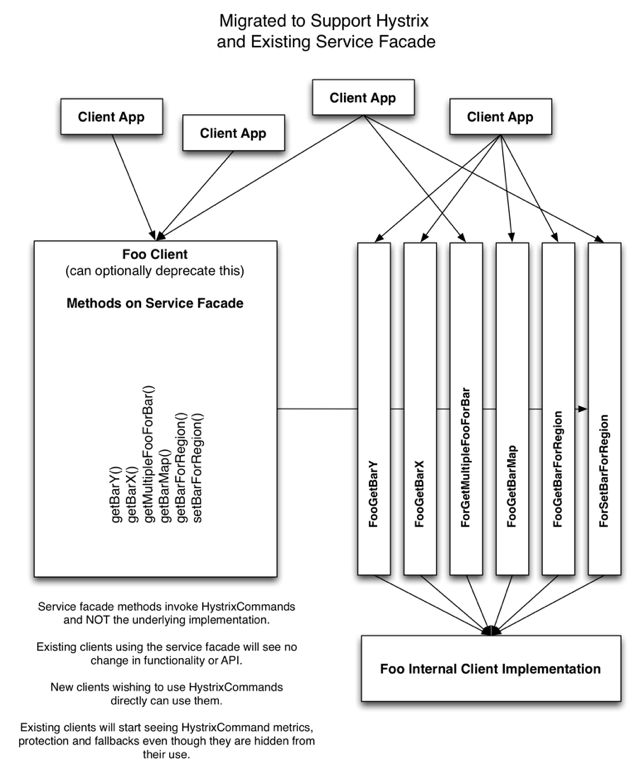
迁移
to