介绍
Runtime简称运行时,是使用C和汇编写的,其中包含了很多C语言的API。它的作用主要是提供系统在运行时的一些操作,其中最主要的是消息机制。学习 Runtime 会让我们更好的掌握 Objective-C 语言的工作机制和内存管理。
对于 Objective-C 程序员来说我们都知道,它的函数调用使用的是消息发送,属于动态调用过程。在编译过程中并不能决定调用哪个函数(在编译阶段OC可以调用任何一个声明过的函数而不报错,即使这个函数没有实现),只有在真正运行的时候才会决定调用哪个函数。
Objective-C 代码在运行的时候是转换成 Runtime 方式运行的,每一句 Objective-C 代码底层必然会有与之相应的 Runtime 方法。
例如我们写这样一行代码:
[LTTableViewCell cellWithTableView:tableView];
在运行时会被转化为:
objc_msgSend(LTTableViewCell, @selector(cellWithTableView:), tableView);
其中 LTTableViewCell 是消息的接收者,cellWithTableView: 称为 选择子,tableView 是参数,选择子 与 参数 合起来称为 消息 。
当编译器看到消息后会将其转换为标准的 C 语言函数调用,它的原型为:
void objc_msgSend(id self, SEL cmd, ...)
这是一个参数可变的 C 语言函数,其中第一个参数是接收者,第二个参数是 选择子 ,后续参数为消息的其他参数。在执行过程中 objc_msgSend 会以 选择子 作为 key 搜索接收者的 函数列表,找到名称相符的方法就会跳转到方法的实现代码,没有找到就会向上执行 消息转发,直至抛出异常。
常用方法
-
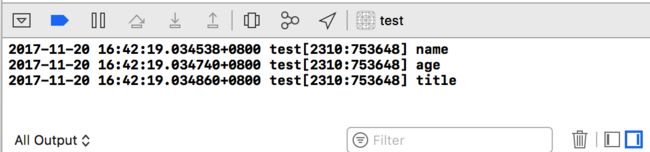
获取属性列表
- (void)printPropertyList { // 1. 获取属性列表,返回值为 typedef struct objc_property *objc_property_t 结构体 unsigned int count; objc_property_t *propertyListC = class_copyPropertyList([self class], &count); // 2. 遍历这个 “结构体” 类型 for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) { // 2.1 通过 property_getName 方法 从 propertyListC 中获取单个属性名称,返回值为 const char * const char *propertyCName = property_getName(propertyListC[i]); // 3.2 将 C语言 字符串转为 OC 字符串并输出 NSLog(@"%@", [NSString stringWithUTF8String:propertyCName]); } }输出结果:
-
获取方法列表
- (void)printMethodList { unsigned int count; Method *methodList = class_copyMethodList([self class], &count); for (unsigned int i = 0; i < count; i++) { Method method = methodList[i]; NSLog(@"method------->%@", NSStringFromSelector(method_getName(method))); } }输出结果:
-
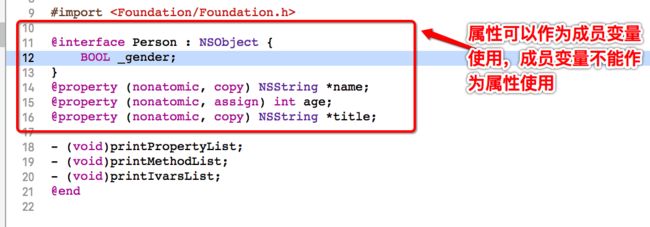
获取成员变量(
ivar)列表- (void)printIvarsList { Ivar *ivarList = class_copyIvarList([self class], &count); for (unsigned int i = 0; i < count; i++) { Ivar ivar = ivarList[i]; NSString *ivarName = [NSString stringWithUTF8String:ivar_getName(ivar)]; NSLog(@"%@", ivarName); } }
输出结果:
-
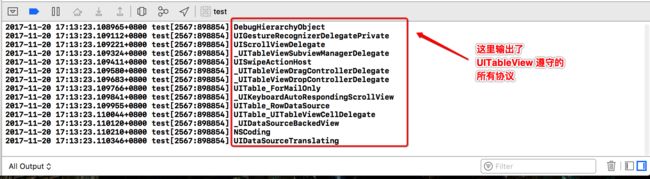
获取协议列表
- (void)printProtocolList { __unsafe_unretained Protocol **protocolList = class_copyProtocolList([UITableView class], &count); for (unsigned int i = 0; i < count; i++) { Protocol *tableViewProtocol = protocolList[i]; NSLog(@"%@", [NSString stringWithUTF8String:protocol_getName(tableViewProtocol)]); } }输出结果:
-
在运行时动态的为类添加一个方法
- (void)runtimeAddMethod { Person *p = [[Person alloc] init]; BOOL addSuccess = class_addMethod([Person class], @selector(testAddMethod), class_getMethodImplmentation([self class], @selector(test)), "v@:"); if (addSuccess) { [p performSelector:@selector(testAddMethod)]; } } - (void)test { NSLog("代码能运行到这里代表方法添加成功"); }BOOL class_addMethod(Class cls, SEL name, IMP imp, const char * types)
解释一下函数里的几个参数:
Class cls : 需要一个class对象,可以理解成接收所添加方法的类,比如上面代码中的[Person class]。
SEL name : 为你添加的方法起个名字,可以随意填写,但调用的时候必须使用相同的名字,否则会崩溃。可以理解为目标位置的方法名。
IMP imp : implementation 的缩写,它是一个指向实现方法的指针。每一个方法都有一个对应的 IMP。注意方法里需要的是 IMP,所以不能直接写方法,需要使用class_getMethodImplmentation获取对应方法的指针。
const char * types : 返回值与参数,光看提示很难理解。上面代码中"v@:"是Runtime中Types类型编码,表示该方法无返回值和传参。感兴趣的朋友可以看一下 苹果官方文档,这里就不一一介绍了。有一点非常值得注意,我们使用运行时添加的方法必须使用
performSelector调用,因为编译的时候不存在此方法。performSelector方法的运行机制是在运行时匹配方法,不需要在编译的时候自动校验。 -
获取类方法
Method classMethod = class_getClassMethod([Person class], @selector(classMethodIMP)); -
获取实例方法
Method instanceMethod = class_getInstanceMethod([Person class], @selector(instanceMethodIMP)); -
交换两个方法的实现
在实际工作中,系统提供的方法往往无法完全达到我们想要的效果。举个例子,在iOS6项目适配iOS7的时候,我们需要同时兼容拟物化设计和扁平化设计,这个时候需要做系统版本判断来添加图片,如果我们在项目中每个添加图片的操作前都要加一句版本判断会出现大量的重复代码而且工作量也很大,如果项目比较大出错的几率会很高。当然很多人会通过继承重写来解决,这也不失为一种方式,只是我们今天讨论的是Runtime下更简洁更轻松的解决方式。啰嗦了这么多,直接上代码吧。import "UIImage + extension.h" import@implementation UIImage(extension) + (void) load { static dispatch_once_t onceToken; dispatch_once(&onceToken, ^{ // 获取当前类(需要明确操作的方法的类型是实例方法还是类方法) // 操作实例方法的时候 // Class selfCls = [self class]; // 操作类方法的时候 Class selfCls = objct_getClass((id)self); // 获取原始方法和替换方法 Method originalMethod = class_getClassMethod(selfCls, @selector(imageNamed:)); Method customMethod = class_getClassMethod(selfCls, @selector(custom_imageNamed:)); // 替换两个方法 method_exchangeMethod(originalMethod, customMethod); } } + (UIImage *)custom_imageNamed:(NSString *)imageName { // 动态获取设备版本号 double versionNum = [[UIDevice currentDevice] systemVersion].doubleValue; // 判断版本是否大于 7.0,如果大于7.0将图片名更换 if (versionNum >= 7.0) { imageName = [imageName stringByAppendingString:@"_os7"]; } /* * 调用原来方法使我们自己写的方法具备系统功能 * 这里不是递归,因为上面已经通过 method_exchangeMethod 函数 将两个方法做了替换 * 这里调用 custom_imageNamed:imageName 相当于调用系统的原始方法 imageNamed */ return [UIImage custom_imageNamed:imageName]; } @end 我们只需要在项目中添加以上代码就可以解决
iOS6项目快速适配iOS7。原项目中只需要添加相应图片名的图片资源就可以了,项目内部并不需要做代码的更改。
以上代码是替换系统原方法,在实际开发中除不得已情况外并不推荐破坏原系统的结构,所以一般情况下为防止需求更改我们都会子类化系统的类,在子类的基础上做更改,需求变更的时候我们只需要修改子类的方法保证系统结构的完整性。举例说明:我们项目中使用的是一个继承自UIImage的子类(LTImage)做操作,这个子类并没有重写任何方法,这个时候我们如何修改子类达到上面代码的同样功能呢?上代码#import "LTImage+extension.h" #import@implementation LTImage (extension) + (void)load { static dispatch_once_t onceToken; dispatch_once(&onceToken, ^{ // 1. 获取类 Class selfCls = object_getClass((id)self); // 2. 获取父类方法 SEL originalSEL = @selector(imageNamed:); Method originalMethod = class_getClassMethod(selfCls, originalSEL); // 3. 获取新创建的方法 SEL customSEL = @selector(override_imageNamed:); Method customMethod = class_getClassMethod(selfCls, customSEL); // 4. 将方法添加到子类中 BOOL success = class_addMethod(selfCls, originalSEL, method_getImplementation(customMethod), method_getTypeEncoding(customMethod)); // 5. 目标类(LTImage)中不存在这个方法(添加成功):替换方法实现,反之(添加失败):交换两个方法 if (success) { class_replaceMethod(selfCls, customSEL, method_getImplementation(originalMethod), method_getTypeEncoding(originalMethod)); } else { method_exchangeImplementations(originalMethod, customMethod); } }); } + (UIImage *)override_imageNamed:(NSString *)imageName { if ([UIDevice currentDevice].systemVersion.doubleValue > 9.0) { imageName = [imageName stringByAppendingString:@"_os10"]; } return [self override_imageNamed:imageName]; } 在子类中操作我们必须确保子类中重写过父类的目标方法(这里指
imageNamed:方法),通过class_addMethod添加方法到子类中,如果子类重写过该方法会返回失败,这时候可以使用method_exchangeImplementations直接替换。如果子类没有重写过父类的方法,需要先将该方法添加进子类中然后通过class_replaceMethod来更换两个方法的实现。代码的调用使用[LTImage imageNamed:@"test"];就可以实现版本检测了,使用[UIImage imageNamed:@"test"];依旧会调用系统原方法。
常用功能实现
-
使用
Runtime在Category中添加属性
一般情况下Obejctive-C的Category中只能扩展方法,无法扩展属性(因为在Category中添加完属性后不会生成getter和setter方法也不会生成默认的成员变量),但在有些情况下我们必须要在Category里添加一个或多个属性简化我们的开发过程,这个时候Runtime为我们提供了相应的功能。以下代码为例,为UIViewController添加Category并扩展一个name属性,存储本类的类名。#import@interface UIViewController (extension) @property (nonatomic, copy) NSString *name; @end #import "UIViewController+extension.h" #import @implementation UIViewController (extension) - (void)setName:(NSString *)name { // 为属性绑定关联策略 objc_setAssociatedObject(self, "CLASS_NAME", name, OBJC_ASSOCIATION_COPY_NONATOMIC); } - (NSString *)name { return objc_getAssociatedObject(self, "CLASS_NAME"); } @end void objc_setAssociatedObject(id object, const void * key, id value, objc_AssociationPolicy policy)
id objc_getAssociatedObject(id object, const void * key)
解释一下函数参数:
- id object:源对象,代码中
self表示本类; - const void * key:关键字,一个
void类型的指针,必须唯一。通常使用静态的变量作为关键字。 - id value:关键字对应的值,通常写在
setter方法中。 - objc_AssociationPolicy policy:关联策略,通常使用预编译常量表示,表明相关对象是通过赋值、保留引用还是复制进行关联的,同时说明该对象是否为原子的。跟定义属性很像。
- id object:源对象,代码中
-
使用
Runtime简化NSCoding协议
在开发中经常会用到自定义模型数据持久化的需求,如果某个模型中有成百上千个属性,这时候我们为每个属性都实现一遍encodeObject和decodeObjectForKey显然是不现实的,工作量大不说代码也没什么可读性,接下来我们比较一下普通写法与Runtime的写法。
假设现在有一个LTMusic模型对象,对象中有三个属性,分别为:songName,singer,albumName。
LTMusc.h#import@interface LTMusic : NSObject @property (nonatomic, copy) NSString *songName; @property (nonatomic, copy) NSString *singer; @property (nonatomic, copy) NSString *albumName; @end LTMusic.m
#import "LTMusic.h" @implementation LTMusic // 解档 - (instancetype)initWithCoder:(NSCoder *)aDecoder { if (self = [super init]) { self.songName = [aDecoder decodeObjectForKey:@"songName"]; self.singer = [aDecoder decodeObjectForKey:@"singer"]; self.albumName = [aDecoder decodeObjectForKey:@"albumName"]; } return self; } // 归档 - (void)encodeWithCoder:(NSCoder *)aCoder { [aCoder encodeObject:_songName forKey:@"songName"]; [aCoder encodeObject:_singer forKey:@"singer"]; [aCoder encodeObject:_albumName forKey:@"albumName"]; } @end以上这样的写法并没有错,也算是
NSCoding的标准写法,但它的缺点也很明显,每多一个属性我们都要在编码和解码里各加入一句,随着项目越来越大可能我们模型的属性会与日俱增,如果有一次忘记添加那么我们再用的时候数据就会出现问题,而且在大项目中这样的问题是很难定位的BUG,因为并不会抛出异常。接下来使用
Runtime来对比一下#import "LTMusic.h" #import@implementation LTMusic // 解档 - (instancetype)initWithCoder:(NSCoder *)aDecoder { if (self = [super init]) { // 1. 获取成员变量列表 unsigned int count; Ivar *ivarList = class_copyIvarList([self class], &count);; // 2. 遍历成员变量列表 for (unsigned int i = 0; i < count; i++) { // 2.1 取出 i 位置的成员变量 Ivar ivar = ivarList[i]; // 2.2 获取成员变量的 C 语言名称并转换为 OC 名称 NSString *ivarName = [NSString stringWithUTF8String:ivar_getName(ivar)]; // 2.3 解档 id value = [aDecoder decodeObjectForKey:ivarName]; // 2.4 使用 KVC 为 self 的属性赋值 [self setValue:value forKey:ivarName]; } // 3. 使用 C 语言一定要记得释放内存空间,否则会造成内存泄漏 free(ivarList); } return self; } // 归档 - (void)encodeWithCoder:(NSCoder *)aCoder { // 1. 获取成员变量列表 unsigned int count; Ivar *ivarList = class_copyIvarList([self class], &count); // 2. 遍历成员变量 for (unsigned int i = 0; i < count; i++) { // 2.1 依次取出 i 位置的成员变量 Ivar ivar = ivarList[i]; // 2.2 获取 C 语言变量名称并转换为 OC 变量名 NSString *ivarName = [NSString stringWithUTF8String:ivar_getName(ivar)]; // 2.3 使用 KVC 取出 变量的 value 值并执行归档 id value = [self valueForKey:ivarName]; [aCoder encodeObject:value forKey:ivarName]; } // 3. 使用 C 语言一定要记得释放内存空间,否则会造成内存泄漏 free(ivarList); } @end 可以明显的感觉到,使用
Runtime可以让我们一劳永逸,增加属性只需要在.h文件中增加属性名称就可以了,再也不需要在.m文件中做任何操作了。 字典转模型第三方框架的实现原理
所有的iOS开发者或多或少都接触过字典转模型的第三方框架,用起来非常方便,比较火的有JSONModel、MJExtension、YYModel。这些框架的实现方式虽然有些差别,究其原理其实都是一致的,实现的思路也是一致的:获取模型属性列表->遍历属性列表->使用模型的属性名作为 key 去字典里寻找 value->将获取到的value值赋值给属性。
其实苹果原生也提供了字典转模型的API如果想实现简单的转换还是很好用的。说一下思路,假设我们现在做一个类似于微博的 App,每一条微博内容就是一个模型,使用系统自带的KVC为模型赋值,然后在控制台输出赋值后的模型属性。
-
KVC方式的简单实现
WBMessage.h#import@interface WBMessage : NSObject /** 微博创建时间*/ @property (nonatomic, copy) NSString *created_at; /** 字符串型的微博ID*/ @property (nonatomic, copy) NSString *idstr; /** 微博信息内容*/ @property (nonatomic, copy) NSString *text; /** 微博来源*/ @property (nonatomic, copy) NSString *source; /** 转发数*/ @property (nonatomic, assign) int reposts_count; /** 评论数*/ @property (nonatomic, assign) int comments_count; /** 表态数*/ @property (nonatomic, assign) int attitudes_count; /** 是否为转发微博 */ @property (nonatomic, assign, getter = isRetweetedStatus) BOOL retweetedStatus; @end WBMessage.m
#import "WBMessage.h" @implementation WBMessage - (void)setValue:(id)value forKey:(NSString *)key { if ([key isEqualToString:@"id"]) { _idstr = value; } else { [super setValue:value forKey:key]; } } - (void)setValue:(id)value forUndefinedKey:(NSString *)key { } - (NSString *)description { return [NSString stringWithFormat:@"\ncreated_at = %@,\nidstr = %@,\ntext = %@\nsource = %@,\nreposts_count = %d,\ncomments_count = %d,\nattitudes_count = %d,\nretweetedStatus = %d", self.created_at, self.idstr, self.text, self.source, self.reposts_count, self.comments_count, self.attitudes_count, self.isRetweetedStatus]; } @endViewController.m
#import "ViewController.h" #import "WBMessage.h" @interface ViewController () // 创建一组假数据 @property (nonatomic, strong) NSDictionary *wbInfomation; @end @implementation ViewController - (NSDictionary *)wbInfomation { if (!_wbInfomation) { _wbInfomation = @{ @"id" : @"6733577", @"created_at" : @"2017-11-27", @"text" : @"北京近日进行强拆暴力执法,早上发通知下午提着锤子来拆墙。", @"source" : @"李二蛋的 iPhone X 客户端", @"reposts_count" : @"226", @"comments_count" : @"151", @"attitudes_count" : @"1000", @"retweetedStatus" : @"1", @"pic_urls" : @"https://114.114.114.114/source/images/1128.png" }; } return _wbInfomation; } - (IBAction)outputDictionaryTransfromModel:(id)sender { WBMessage *wbMessage = [[WBMessage alloc] init]; [wbMessage setValuesForKeysWithDictionary:self.wbInfomation]; NSLog(@"%@", wbMessage); }当我们使用
setValuesForKeysWithDictionary:方法的时候,模型类需要重写setValue:forkey:和setValue:forUndefinedKey:这两个方法,目的是为了排除字典中的key与模型中的属性名不一致的情况(比如字典中存在一个id的key)和字典中键值对比模型中属性多的情况。如果不重写这俩方法在运行的时候项目会崩溃。 -
使用
Runtime实现字典转模型
NSObject+Extension#import@protocol NSObjectDelegate @optional /** * 提供一个协议,告诉系统数组中存放的对象类型,当子类实现了该协议方法就可以将数组中的字典转换为模型 * * @return 字典,字典中的 key 是模型中定义的数组名称,value 是所存放的类型,例如 [NSObject class] 或者 字符串 @"NSObject" */ + (NSDictionary *)objectInArray; /** * 处理字典中出现 id 等关键字 * * @return 字典,key 是在模型中定义的属性名,value 是字典中出现的 key */ + (NSDictionary *)replaceKey; @end @interface NSObject (Extension) /** * 字典转模型核心方法,可以继续封装 JSON 字符串转模型 * * @param dict 入参为一个字典类型,字典中存放的 key 为模型的属性,通过KVC将value赋值给属性 * @return 返回一个转化好的模型对象 */ + (instancetype)objectWithDictionary:(NSDictionary *)dict; @end NSObjec+Extension.m
#import "NSObject+Extension.h" #import@implementation NSObject (Extension) + (instancetype)objectWithDictionary:(NSDictionary *)dict { // 1. 实例化操作对象 id modelObjc = [[self alloc] init]; // 2. 获取成员变量列表 unsigned int count; Ivar *ivarList = class_copyIvarList(self, &count); // 3. 遍历成员变量列表并使用成员变量作为 key 在字典中查找 value 再将 value 赋值给成员变量 for (unsigned int i = 0; i < count; i++) { // 3.1 获取 i 位置的 ivar Ivar ivar = ivarList[i]; // 3.2 获取 ivar 的名称,因为每个成员变量前默认会加上一个 “_” 所以需要去掉 NSString *ivarName = [[NSString stringWithUTF8String:ivar_getName(ivar)] substringFromIndex:1]; // 3.3 处理字典中的关键字 NSString *newKey = nil; if ([self respondsToSelector:@selector(replaceKey)]) { newKey = [self replaceKey][ivarName] ? [self replaceKey][ivarName] : ivarName; } else { newKey = ivarName; } // 3.4 去字典中取出成员变量对应的 value 值 id ivarValue = dict[newKey]; // 3.5 获取成员变量的类型 NSString *ivarType = [NSString stringWithUTF8String:ivar_getTypeEncoding(ivar)]; // 3.6 判断成员变量的值是否为字典,如果是字典类型需要继续向内转换 if ([ivarValue isKindOfClass:[NSDictionary class]] && [ivarType containsString:@"NS"]) { // 进入这一层表示位置 i 的成员变量的值是一个字典并且这个对象是个自定义对象 // 3.6.1 处理类型字符串, 通过 ivar_getTypeEncoding(ivar) 的表现形式为 @"\"对象名称\"" ivarType = [ivarType stringByReplacingOccurrencesOfString:@"@" withString:@""]; ivarType = [ivarType stringByReplacingOccurrencesOfString:@"\"" withString:@""]; // 3.6.2 获取自定义模型类对象 Class modelClass = NSClassFromString(ivarType); // 3.6.3 递归调用字典转模型 if (modelClass) { [modelClass objectWithDictionary:ivarValue]; } } // 3.7 value值是数组,数组中又嵌套字典 if ([ivarValue isKindOfClass:[NSArray class]]) { // 3.7.1 判断子类有没有实现协议方法,YES : 将数组中的字典转换模型 // NO : 对数组不操作或者模型类中不存在数组 if ([self respondsToSelector:@selector(objectInArray)]) { // 3.7.2 将 self 的类型转换为 id 类型可以保证该变量可以调用任何对象的方法 id idSelf = self; // 3.7.3 获取数组中存放的字典 id classType = [idSelf objectInArray][ivarName]; Class clazz = nil; // 3.7.4 判断两种情况,1. 字典的 value 是 class 类型,直接获取 2. 字典的 value 是字符串类型,通过字符串获取 if ([classType isKindOfClass:[NSString class]]) { clazz = NSClassFromString(classType); } else { clazz = (Class)classType; } // 3.7.5 遍历 value 并组装成模型数组 NSMutableArray *models = [NSMutableArray array]; for (NSDictionary *dict in ivarValue) { id model = [clazz objectWithDictionary:dict]; [models addObject:model]; } // 3.7.6 将成员变量的值替换为模型数组 ivarValue = [models mutableCopy]; } } // 4. 使用 KVC 将实现字典转模型 if (ivarValue) { [modelObjc setValue:ivarValue forKey:ivarName]; } } // 5. 将转换好的模型对象返回 return modelObjc; } @end 上面代码为
Runtime字典转模型的核心代码,其本质还是使用KVC的底层实现。重点需要讲一下三级转换中使用到的协议方法,这在字典转模型中是个难点。
在实际开发中经常会遇到一个模型的某个属性是数组,数组中又存放了多个模型,这个时候Category无法获取到数组中存放的类型,需要程序员主动告知,协议方法是最合适的书写方式。
本篇文章参考夜千寻墨前辈的runtime详解稍作改动。
本文示例代码已上传到GitHub,点击下载。