1 public class test2 { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 4 // 字符串和字符数组互相转换 5 // 字符串转字符数组 6 String str1 = "hiuzb12316"; 7 char[] cs1 = str1.toCharArray(); 8 System.out.println(cs1);// 字符串转字符数组:toCharArray() 9 10 // 字符数组转字符串 11 String str2 = ""; 12 for (int i = 0; i < cs1.length; i++) { 13 str2 += cs1[i]; 14 } 15 System.out.println(str2);// 字符数组转字符串:遍历,拼接即可 16 17 // ASCII和字符互相转换 18 // 0~9:48~57 19 // A~Z:65~90 20 // a~z:97~122 21 22 char a = 'a'; 23 int numOfa = (int) a;// 强制转换即可,下面同理 24 25 int x = 100; 26 char chOfx = (char) x; 27 System.out.println(numOfa); 28 System.out.println(chOfx); 29 30 // 数字和字符互相转换(不能强制转换!) 31 // 数字转字符串 32 int i = 12345; 33 // System.out.println((char) i);// 结果出错,因为ASCII没有12345这么多!!! 34 String str_1 = String.valueOf(i);// 办法一:String.valueOf(要转的数字对象) 35 System.out.println(str_1); 36 Integer it = i;// 办法二:先”装箱“ 37 String str_2 = it.toString();// 再调用toSting()即可 38 System.out.println(str_2); 39 40 // 字符串转数字 41 int res = Integer.parseInt(str_1);// Integer.parseInt(要转的字符串对象) 42 System.out.println(res); 43 } 44 }
进阶运用:创建一个长度是5的随机字符串,随机字符有可能是数字,大写字母或者小写字母
运用知识点:ASCII与数字的互相转换,随机数
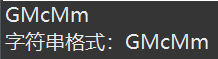
8 public static char rand() { 9 int a1 = (int) (Math.round(Math.random() * (122 - 97)) + 97);// a-z 10 int a2 = (int) (Math.round(Math.random() * (90 - 65)) + 65);// A-Z 11 int a3 = (int) (Math.round(Math.random() * (57 - 48)) + 48);// 0-9 12 int oneOfThem = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 2);// 随机决定a1,a2,a3中的一个 13 14 if (oneOfThem == 0) { 15 return (char) a1; 16 } else if (oneOfThem == 1) { 17 return (char) a2; 18 } else { 19 return (char) a3; 20 } 21 } 22 23 public static void main(String[] args) { 24 char cs[] = new char[5]; 25 for (int i = 0; i < cs.length; i++) { 26 cs[i] = rand(); 27 } 28 System.out.println(cs); 29 // 若要字符串格式,把字符数组转换成字符串即可 30 String str = ""; 31 for (int i = 0; i < cs.length; i++) { 32 str += cs[i]; 33 } 34 System.out.println("字符串格式:" + str); 35 } 36 }
运行结果:
进阶运用2:
创建一个长度是8的字符串数组
使用8个长度是5的随机字符串初始化这个数组
对这个数组进行排序,按照每个字符串的首字母排序(无视大小写)
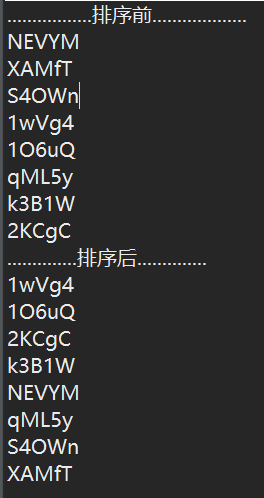
1 public class test { 2 3 public static char rand() { 4 int a1 = (int) (Math.round(Math.random() * (122 - 97)) + 97);// a-z 5 int a2 = (int) (Math.round(Math.random() * (90 - 65)) + 65);// A-Z 6 int a3 = (int) (Math.round(Math.random() * (57 - 48)) + 48);// 0-9 7 int oneOfThem = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 2);// 随机决定a1,a2,a3中的一个 8 9 if (oneOfThem == 0) { 10 return (char) a1; 11 } else if (oneOfThem == 1) { 12 return (char) a2; 13 } else { 14 return (char) a3; 15 } 16 } 17 18 public static String randString() { 19 char cs[] = new char[5]; 20 String str = ""; 21 for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { 22 cs[i] = rand(); 23 str += cs[i]; 24 } 25 return str; 26 } 27 28 public static void StringArraySort(String str[]) {//采用简单选择排序 29 int i, j, min; 30 String tmp; 31 for (i = 0; i < str.length; i++) 32 { 33 min = i; 34 for (j = i + 1; j < str.length; j++) 35 { 36 if (Character.toLowerCase(str[min].charAt(0)) > Character.toLowerCase(str[j].charAt(0))) 37 { 38 min = j; 39 } 40 } 41 tmp=str[i]; 42 str[i]=str[min]; 43 str[min]=tmp; 44 } 45 } 46 47 public static void main(String[] args) { 48 49 String str[] = new String[8]; 50 for (int i = 0; i < str.length; i++) 51 { 52 str[i] = randString();//生成随机字符串 53 } 54 System.out.println(".................排序前..................."); 55 for (String each : str) 56 { 57 System.out.println(each); 58 } 59 StringArraySort(str);//对随机字符串按首字母进行排序 60 System.out.println("..............排序后.............."); 61 for (String each : str) 62 { 63 System.out.println(each); 64 } 65 } 66 }
运行结果:
进阶运用:穷举法破解密码
1. 生成一个长度是3的随机字符串,把这个字符串作为当做密码
2. 使用穷举法生成长度是3个字符串,匹配上述生成的密码
要求: 分别使用多层for循环 和 递归解决上述问题
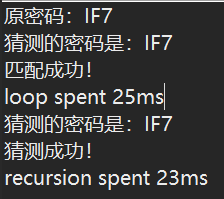
1 public class test2 { 2 public static char randChar() { 3 return (char) ((int) Math.round(Math.random() * (126 - 33) + 33)); 4 } 5 6 public static String qiongJuFa(String passWord) { 7 8 String tryPassWord = ""; 9 for (int i = 33; i <= 126; i++) { 10 for (int j = 33; j <= 126; j++) { 11 for (int k = 33; k <= 126; k++) { 12 char t1 = (char) i; 13 char t2 = (char) j; 14 char t3 = (char) k; 15 tryPassWord = "" + t1 + t2 + t3;// 前面必须加 "" 16 if (t1 == passWord.charAt(0) && t2 == passWord.charAt(1) && t3 == passWord.charAt(2)) { 17 System.out.println("猜测的密码是:" + tryPassWord); 18 System.out.println("匹配成功!"); 19 20 return tryPassWord; 21 } else { 22 tryPassWord = ""; 23 } 24 } 25 } 26 } 27 return ""; 28 } 29 30 public static void recursion(String psw, char[] tpsw, int num) {// num是tpsw第几位 31 if (num < 3) { 32 int i; 33 for (i = 33; i <= 126; i++) {// 取的ASCII范围是33-126 34 tpsw[num] = (char) i; 35 if (psw.charAt(num) == tpsw[num]) { 36 recursion(psw, tpsw, ++num);// 第一位匹配成功,递归调用去判断下一位 37 break;// 递归的“归”的时候,因为已经匹配成功了,无须再次循环,所以直接break 38 } 39 } 40 } else { 41 System.out.printf("猜测的密码是:%s%n", String.valueOf(tpsw)); 42 System.out.println("猜测成功!"); 43 } 44 45 } 46 47 public static void main(String[] args) { 48 49 String passWord = ""; 50 for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) { 51 passWord += randChar(); 52 } 53 System.out.println("原密码:" + passWord); 54 55 // 穷举法 56 long st1 = System.currentTimeMillis(); 57 String tpsw = qiongJuFa(passWord); 58 long et1 = System.currentTimeMillis(); 59 System.out.println("loop spent " + (et1 - st1) + "ms"); 60 // 递归法 61 char tryPassWord[] = new char[3]; 62 long st = System.currentTimeMillis(); 63 recursion(passWord, tryPassWord, 0); 64 long et = System.currentTimeMillis(); 65 System.out.println("recursion spent " + (et - st) + "ms"); 66 } 67 }
运行结果: