collectionView没有类似于tableView的Plain效果(即sectionHeader悬浮),不过可以通过自定义flowLayout实现,因此它比tableView拥有更强大的扩展性,这点是毋庸置疑的。
在项目中相关列表页的实现,我更倾向于使用UIColletionView,这个因人而异。
下面的代码是我参考XLPlainFlowLayout转换成Swift来的(就是copy+学习),在此感谢源代码的分享。
MTPlainFlowLayout.swift
import UIKit
class MTPlainFlowLayout: UICollectionViewFlowLayout {
// 设置停留位置,默认为64(没有导航栏同样设置有效)
var naviHeight: CGFloat = 64
override func layoutAttributesForElementsInRect(rect: CGRect) -> [UICollectionViewLayoutAttributes]? {
// UICollectionViewLayoutAttributes:称它为collectionView中的item(包括cell和header、footer这些)的《结构信息》
var attributesArray: [UICollectionViewLayoutAttributes] = []
if let superAttributesArray = super.layoutAttributesForElementsInRect(rect) {
attributesArray = superAttributesArray
}
// 创建存索引的数组,无符号(正整数),无序(不能通过下标取值),不可重复(重复的话会自动过滤)
let noneHeaderSections = NSMutableIndexSet()
// 遍历superArray,得到一个当前屏幕中所有的section数组
for attributes in attributesArray {
// 如果当前的元素分类是一个cell,将cell所在的分区section加入数组,重复的话会自动过滤
if attributes.representedElementCategory == .Cell {
noneHeaderSections.addIndex(attributes.indexPath.section)
}
}
// 遍历superArray,将当前屏幕中拥有的header的section从数组中移除,得到一个当前屏幕中没有header的section数组
// 正常情况下,随着手指往上移,header脱离屏幕会被系统回收而cell尚在,也会触发该方法
for attributes in attributesArray {
if let kind = attributes.representedElementKind {
//如果当前的元素是一个header,将header所在的section从数组中移除
if kind == UICollectionElementKindSectionHeader {
noneHeaderSections.removeIndex(attributes.indexPath.section)
}
}
}
// 遍历当前屏幕中没有header的section数组
noneHeaderSections.enumerateIndexesUsingBlock { (index, stop) in
// 取到当前section中第一个item的indexPath
let indexPath = NSIndexPath(forRow: 0, inSection: index)
// 获取当前section在正常情况下已经离开屏幕的header结构信息
if let attributes = self.layoutAttributesForSupplementaryViewOfKind(UICollectionElementKindSectionHeader, atIndexPath: indexPath) {
// 如果当前分区确实有因为离开屏幕而被系统回收的header,将该header结构信息重新加入到superArray中去
attributesArray.append(attributes)
}
}
// 遍历superArray,改变header结构信息中的参数,使它可以在当前section还没完全离开屏幕的时候一直显示
for attributes in attributesArray {
if attributes.representedElementKind == UICollectionElementKindSectionHeader {
let section = attributes.indexPath.section
let firstItemIndexPath = NSIndexPath(forRow: 0, inSection: section)
var numberOfItemsInSection = 0
// 得到当前header所在分区的cell的数量
if let number = self.collectionView?.numberOfItemsInSection(section) {
numberOfItemsInSection = number
}
// 得到最后一个item的indexPath
let lastItemIndexPath = NSIndexPath(forRow: max(0, numberOfItemsInSection-1), inSection: section)
// 得到第一个item和最后一个item的结构信息
let firstItemAttributes: UICollectionViewLayoutAttributes!
let lastItemAttributes: UICollectionViewLayoutAttributes!
if numberOfItemsInSection > 0 {
// cell有值,则获取第一个cell和最后一个cell的结构信息
firstItemAttributes = self.layoutAttributesForItemAtIndexPath(firstItemIndexPath)
lastItemAttributes = self.layoutAttributesForItemAtIndexPath(lastItemIndexPath)
} else {
// cell没值,就新建一个UICollectionViewLayoutAttributes
firstItemAttributes = UICollectionViewLayoutAttributes()
// 然后模拟出在当前分区中的唯一一个cell,cell在header的下面,高度为0,还与header隔着可能存在的sectionInset的top
let itemY = attributes.frame.maxY + self.sectionInset.top
firstItemAttributes.frame = CGRect(x: 0, y: itemY, width: 0, height: 0)
// 因为只有一个cell,所以最后一个cell等于第一个cell
lastItemAttributes = firstItemAttributes
}
// 获取当前header的frame
var rect = attributes.frame
// 当前的滑动距离 + 因为导航栏产生的偏移量,默认为64(如果app需求不同,需自己设置)
var offset_Y: CGFloat = 0
if let y = self.collectionView?.contentOffset.y {
offset_Y = y
}
offset_Y = offset_Y + naviHeight
// 第一个cell的y值 - 当前header的高度 - 可能存在的sectionInset的top
let headerY = firstItemAttributes.frame.origin.y - rect.size.height - self.sectionInset.top
// 哪个大取哪个,保证header悬停
// 针对当前header基本上都是offset更加大,针对下一个header则会是headerY大,各自处理
let maxY = max(offset_Y, headerY)
// 最后一个cell的y值 + 最后一个cell的高度 + 可能存在的sectionInset的bottom - 当前header的高度
// 当当前section的footer或者下一个section的header接触到当前header的底部,计算出的headerMissingY即为有效值
let headerMissingY = lastItemAttributes.frame.maxY + self.sectionInset.bottom - rect.size.height
// 给rect的y赋新值,因为在最后消失的临界点要跟谁消失,所以取小
rect.origin.y = min(maxY, headerMissingY)
// 给header的结构信息的frame重新赋值
attributes.frame = rect
// 如果按照正常情况下,header离开屏幕被系统回收,而header的层次关系又与cell相等,如果不去理会,会出现cell在header上面的情况
// 通过打印可以知道cell的层次关系zIndex数值为0,我们可以将header的zIndex设置成1,如果不放心,也可以将它设置成非常大
attributes.zIndex = 1024
}
}
return attributesArray
}
override func shouldInvalidateLayoutForBoundsChange(newBounds: CGRect) -> Bool {
return true
}
}
注意:
1.上述自定义flowLayout里存在一个bug,代码里使用的self.sectionInset是初始化UICollectionViewFlowLayout设置的sectionInset,而不会随着代理方法:func collectionView(collectionView: UICollectionView, layout collectionViewLayout: UICollectionViewLayout, insetForSectionAtIndex section: Int) -> UIEdgeInsets返回的sectionInset去更新;
2.如果初始化UICollectionViewFlowLayout并且只有一组section的时候设置sectionInset,是没有上述问题的;
3.如果有多组section,同时需要动态设置每组的sectionInset的话,那么就会sectionHeader与预期效果就会有一定的偏差,这个偏差就是因为上述1的bug所造成的。
4.OC版本也有同样上述问题
···
解决办法:
1.如果只有一组section的话可以选择在初始化flowLayout的时候设置sectionInset;
2.多组section的话就不建议使用上述1的方式,而是选择
UICollectionViewDelegateFlowLayout里的代理方法func collectionView(collectionView: UICollectionView, layout collectionViewLayout: UICollectionViewLayout, insetForSectionAtIndex section: Int) -> UIEdgeInsets去动态设置当前section的sectionInset,这样上面的bug就可以避免了;
3.以上两个方法大家因情况而选择,如果大家有更好的解决方案或者自定义flowLayout请留言或在本文底部评论;
4.OC版同样可使用上面的解决方案。
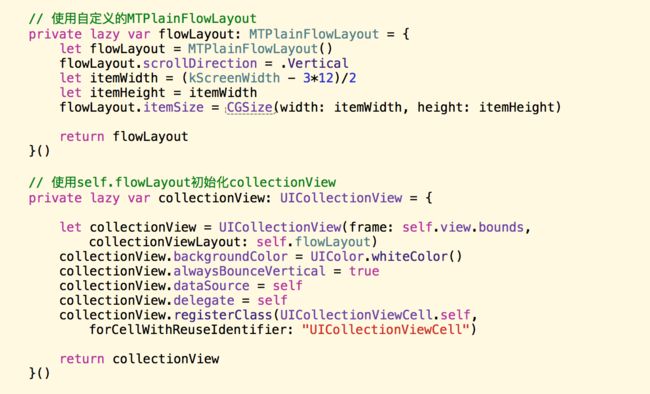
如何使用
上面贴出来的代码就是完整的Swift文件,直接使用
MTPlainFlowLayout创建UICollectionViewFlowLayout对象使用即可。
图片示例: