全局事务如何运作,只针对AT模式。(源码持续更新,本文仅供参考)
- Fescar源码阅读-解决分布式事务的利器
- Fescar源码阅读-RPC和消息
- Fescar源码阅读-全自动的分布式事务AT
- Fescar源码阅读-神奇的UndoLog(一)
前文大致了解了Fescar系统总体架构、消息定义和交互方式,现在来看看Fescar如何通过这些消息的交互,最终转换为对分布式事务的管控。
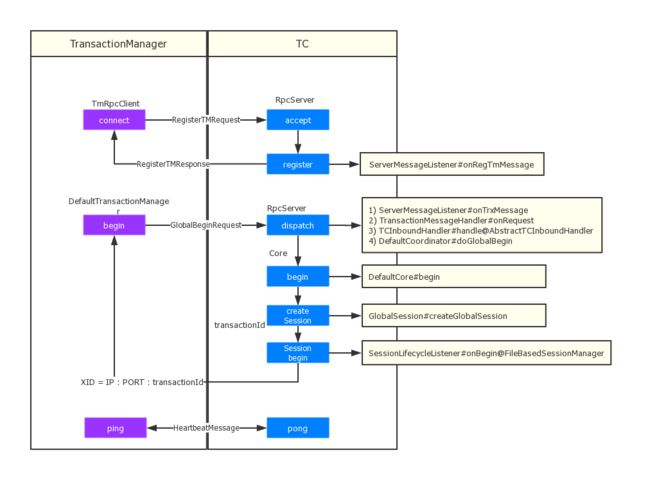
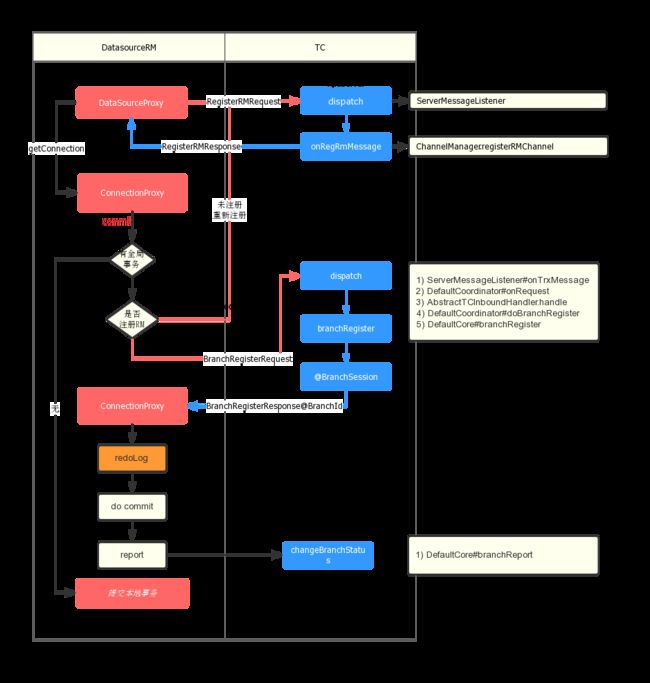
再看一次这张图:
首先Fescar中,分布式事务的生命周期是交给TC来协调管理的,对于一个全局事务,TC需要管理全局事务以及全局事务下包含的所有branch分支事务(已注册的)。
全局事务生命周期(begin, commit, rollback)可以用以下代码来体现:
在 2.1部分,可开启一个或者多个本地事务,同时本地事务加入全局事务, 被TM和TC管理。
// 1. get or create a transaction
GlobalTransaction tx = GlobalTransactionContext.getCurrentOrCreate();
// 2. begin transaction
try {
tx.begin(business.timeout(), business.name());
} catch (TransactionException txe) {
}
Object rs = null;
try {
// 2.1 自己的业务逻辑
rs = business.execute();
} catch (Throwable ex) {
// 3. any business exception, rollback.
try {
tx.rollback();
}
}
// 4. everything is fine, commit.
try {
tx.commit();
} catch (TransactionException txe) {
}
return rs;
在了解Fescar如何管理事务之前,需要想看看关键的两个类GlobalSession和BranchSession,顾名思义,这两个类分别定义、维护了全局事务和branch分支事务的信息和状态。
public class GlobalSession implements SessionLifecycle, SessionStorable {
// 全局事务ID
private long transactionId;
// 全局事务状态
private GlobalStatus status;
// 应用ID 标识发起全局事务的服务
private String applicationId;
//全局事务分组 默认default
private String transactionServiceGroup;
//全局事务名称
private String transactionName;
private int timeout;
private long beginTime;
private boolean active;
//branch事务Session
private ArrayList branchSessions = new ArrayList<>();
// 省略...
}
public class BranchSession implements Lockable, Comparable, SessionStorable {
// 全局事务ID
private long transactionId;
// branch事务ID
private long branchId;
// 忽略,暂未使用
private String resourceGroupId;
// 资源ID
private String resourceId;
// 锁 key
private String lockKey;
// AT, MT
private BranchType branchType;
private BranchStatus status = BranchStatus.Unknown;
private String applicationId;
private String txServiceGroup;
// 标识具体client applicationID + client_ip + client_port
private String clientId;
// 忽略,暂未使用
private String applicationData;
private ConcurrentHashMap, Set> lockHolder = new ConcurrentHashMap, Set>();
// 省略...
}
开启全局事务(TM连接和注册)
- TM发送GlobalBeginRequest到TC,请求开启全局事务
- TC处理请求,生成GlobalSession,生成TransacntionId,xid,并返回给TM,全局事务开启成功
提交本地事务(RM连接和注册)
以DataSourceRM为例:
- RM的操作从DataSourceProxxy和ConnectionProxy发起,代理了真正的DataSource和Connection
- 本地数据库事务提交时,RM判断是否存在全局事务,如果是这注册branchTransaction(注册时将会携带lockkey,TC加锁,后续再看这些细节~)
- TC生成BranchSession 并返回。
- RM注册完成后其实并不会阻塞等待全局事务的提交(fescar最新实现有全局锁模式,但已经不属于当前流程,暂时先不管),而是先生成
redoLog(划重点,redolog是Fescar可以放心的提交本地事务的关键,我们下一章在看),然后直接提交本地事务,最后向TC报告。
commit部分代码如下:
public void commit() throws SQLException {
try {
register();
} catch (TransactionException e) {
recognizeLockKeyConflictException(e);
}
try {
if (context.hasUndoLog()) {
UndoLogManager.flushUndoLogs(this);
}
targetConnection.commit();
} catch (Throwable ex) {
report(false);
if (ex instanceof SQLException) {
throw new SQLException(ex);
}
}
report(true);
context.reset();
}
提交/回滚全局事务
全局事务的提交、回滚都由TM控制,发起,TC协调。
- 全局事务提交
TM发起提交,TC负责校验各个branch session的状态,是否正常提交,如果失败可发起重试。 - TC通知RM提交branch事务,此时DataSourceRM将会删除undolog。
TC核心接口:com.alibaba.fescar.server.coordinator.Core
void doGlobalCommit(GlobalSession globalSession, boolean retrying) throws TransactionException;
void doGlobalRollback(GlobalSession globalSession, boolean retrying) throws TransactionException;
部分代码如下:
// 通知RM执行commit,DataSourceRM将会删除undolog
BranchStatus branchStatus = resourceManagerInbound.branchCommit(branchSession.getBranchType(), XID.generateXID(branchSession.getTransactionId()), branchSession.getBranchId(),
branchSession.getResourceId(), branchSession.getApplicationData());
witch (branchStatus) {
case PhaseTwo_Committed:
globalSession.removeBranch(branchSession);
continue;
case PhaseTwo_CommitFailed_Unretryable:
if (globalSession.canBeCommittedAsync()) {
LOGGER.error("By [{}], failed to commit branch {}", branchStatus, branchSession);
continue;
} else {
SessionHelper.endCommitFailed(globalSession);
LOGGER.error("Finally, failed to commit global[{}] since branch[{}] commit failed",
globalSession.getTransactionId(), branchSession.getBranchId());
return;
}
default:
if (!retrying) {
//转入重试队列
queueToRetryCommit(globalSession);
return;
}
- 全局事务回滚
TM发起回滚,TC通知RM回滚。
BranchStatus branchStatus = resourceManagerInbound.branchRollback(branchSession.getBranchType(), XID.generateXID(branchSession.getTransactionId()), branchSession.getBranchId(),
branchSession.getResourceId(), branchSession.getApplicationData());
switch (branchStatus) {
case PhaseTwo_Rollbacked:
globalSession.removeBranch(branchSession);
LOGGER.error("Successfully rolled back branch " + branchSession);
continue;
case PhaseTwo_RollbackFailed_Unretryable:
SessionHelper.endRollbackFailed(globalSession);
LOGGER.error("Failed to rollback global[" + globalSession.getTransactionId() + "] since branch["
+ branchSession.getBranchId() + "] rollback failed");
return;
default:
LOGGER.info("Failed to rollback branch " + branchSession);
if (!retrying) {
queueToRetryRollback(globalSession);
}
看看DataSrouceRM如何rollback
DataSourceProxy dataSourceProxy = get(resourceId);
try {
UndoLogManager.undo(dataSourceProxy, xid, branchId);
} catch (TransactionException te) {
if (te.getCode() == TransactionExceptionCode.BranchRollbackFailed_Unretriable) {
return BranchStatus.PhaseTwo_RollbackFailed_Unretryable;
} else {
return BranchStatus.PhaseTwo_RollbackFailed_Retryable;
}
}
return BranchStatus.PhaseTwo_Rollbacked;
很明显,对于已经提交的本地事务,DataSourceRM直接使用commit时生成的undolog进行数据回滚!
完整的分布式事务完成!
很明显,undolog就是Fescar可以打破二段提交的机制,允许本地事务在第一阶段就提交的基础,也是Fescar自信拥有高性能和高吞吐量的底气所在。
那么undolog道理是如何形成,里面内容是什么呢?Fescar如何利用undolog进行回滚呢?下一章继续