1. 在某些特殊的linux机器上面, 比如龙芯后者是飞腾服务器,部分工具不太好用, 需要使用x86弄好之后进行同步过去, 这个时候scp 最简单但是网络流量非常大, 不如使用rsync, rsync 一开始不知道能够实现source文件夹的删除操作, destation文件夹也可以重演.
2. rsync的两种模式
ssh模式和daemon模式.
简单起见 可以使用ssh-copy-id 实现无密码登录的话 可以使用 ssh 模式 更加方便一些.
关于rsync的两种模式: 该部分额外的内容来自IBM官方网站上的一篇文章。该文章把rsync的运行模式扩展成了四种,但我认为rsync官方文档的两种模式的划分更加合理一些。 所谓rsync daemon,就是在一台机器上永久运行的rsync进程。在任何一台安装rsync的机器上运行rsync --daemon,则这台机器上运行的rsync就是rsync daemon。我们可以把文件发送给daemon,也可以向daemon请求文件。 daemon模式非常适合创建中心备份服务器,或项目存储库。 两种模式的区别前面已经说过,shell模式在源路径和目的路径中使用一个冒号,而daemon模式使用两个冒号。 关于rsync命令的语法: 本地拷贝: rsync [选项] SRC… DEST,在本地进行复制操作 shell模式: rsync [选项] [user@]Host:SRC… [DEST],拉动作,从远程主机拉文件到本地 rsync [选项] SRC… [user@]Host:DEST,推动作,把本地文件推送到远程主机 daemon模式: rsync [选项] [user@]Host::SRC… [DEST],拉动作 rsync [选项] rsync://[user@]Host [:port]/SRC… [DEST],仍然是拉动作 rsync [选项] SRC... [user@]Host::DEST,推动作 rsync [选项] SRC...rsync://[user@]Host [:port]/DEST,仍然是推动作
来源: https://blog.csdn.net/s1070/article/details/77978907
3. 简单测试验证:
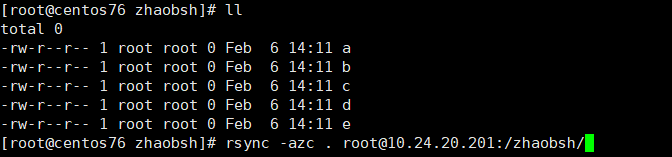
host01 mkdir /zhaobsh touch a b c d e host02 mkdir /zhaobsh touch b c d e f
然后在源文件的host01 机器上面执行命令
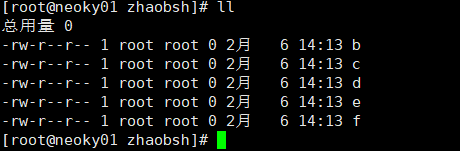
rsync -azc . root@10.24.20.201:/zhaobsh/
host02 机器 执行命令之前的文件为:
执行命令之后的文件为:
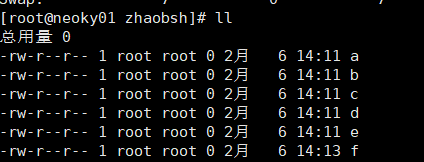
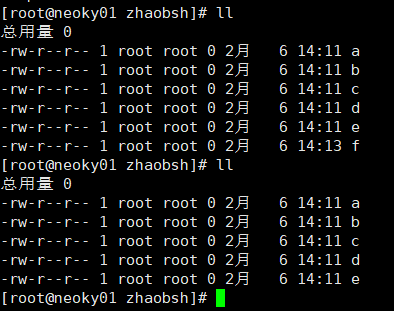
4. 如果想验证能够删除 source 里面不存在的文件 那么需要添加参数
rsync -azc . --delete root@10.24.20.201:/zhaobsh/
就会发现 source 里面没有的文件 f 就会在destination
5. 其实GNU工具链非常好 里面的东西非常实用 直接看help的话 就能学到很多东西(就是自己的耐心不够)
[root@centos76 zhaobsh]# rsync --help rsync version 3.1.2 protocol version 31 Copyright (C) 1996-2015 by Andrew Tridgell, Wayne Davison, and others. Web site: http://rsync.samba.org/ Capabilities: 64-bit files, 64-bit inums, 64-bit timestamps, 64-bit long ints, socketpairs, hardlinks, symlinks, IPv6, batchfiles, inplace, append, ACLs, xattrs, iconv, symtimes, prealloc rsync comes with ABSOLUTELY NO WARRANTY. This is free software, and you are welcome to redistribute it under certain conditions. See the GNU General Public Licence for details. rsync is a file transfer program capable of efficient remote update via a fast differencing algorithm. Usage: rsync [OPTION]... SRC [SRC]... DEST or rsync [OPTION]... SRC [SRC]... [USER@]HOST:DEST or rsync [OPTION]... SRC [SRC]... [USER@]HOST::DEST or rsync [OPTION]... SRC [SRC]... rsync://[USER@]HOST[:PORT]/DEST or rsync [OPTION]... [USER@]HOST:SRC [DEST] or rsync [OPTION]... [USER@]HOST::SRC [DEST] or rsync [OPTION]... rsync://[USER@]HOST[:PORT]/SRC [DEST] The ':' usages connect via remote shell, while '::' & 'rsync://' usages connect to an rsync daemon, and require SRC or DEST to start with a module name. Options -v, --verbose increase verbosity --info=FLAGS fine-grained informational verbosity --debug=FLAGS fine-grained debug verbosity --msgs2stderr special output handling for debugging -q, --quiet suppress non-error messages --no-motd suppress daemon-mode MOTD (see manpage caveat) -c, --checksum skip based on checksum, not mod-time & size -a, --archive archive mode; equals -rlptgoD (no -H,-A,-X) --no-OPTION turn off an implied OPTION (e.g. --no-D) -r, --recursive recurse into directories -R, --relative use relative path names --no-implied-dirs don't send implied dirs with --relative -b, --backup make backups (see --suffix & --backup-dir) --backup-dir=DIR make backups into hierarchy based in DIR --suffix=SUFFIX set backup suffix (default ~ w/o --backup-dir) -u, --update skip files that are newer on the receiver --inplace update destination files in-place (SEE MAN PAGE) --append append data onto shorter files --append-verify like --append, but with old data in file checksum -d, --dirs transfer directories without recursing -l, --links copy symlinks as symlinks -L, --copy-links transform symlink into referent file/dir --copy-unsafe-links only "unsafe" symlinks are transformed --safe-links ignore symlinks that point outside the source tree --munge-links munge symlinks to make them safer (but unusable) -k, --copy-dirlinks transform symlink to a dir into referent dir -K, --keep-dirlinks treat symlinked dir on receiver as dir -H, --hard-links preserve hard links -p, --perms preserve permissions -E, --executability preserve the file's executability --chmod=CHMOD affect file and/or directory permissions -A, --acls preserve ACLs (implies --perms) -X, --xattrs preserve extended attributes -o, --owner preserve owner (super-user only) -g, --group preserve group --devices preserve device files (super-user only) --copy-devices copy device contents as regular file --specials preserve special files -D same as --devices --specials -t, --times preserve modification times -O, --omit-dir-times omit directories from --times -J, --omit-link-times omit symlinks from --times --super receiver attempts super-user activities --fake-super store/recover privileged attrs using xattrs -S, --sparse handle sparse files efficiently --preallocate allocate dest files before writing them -n, --dry-run perform a trial run with no changes made -W, --whole-file copy files whole (without delta-xfer algorithm) -x, --one-file-system don't cross filesystem boundaries -B, --block-size=SIZE force a fixed checksum block-size -e, --rsh=COMMAND specify the remote shell to use --rsync-path=PROGRAM specify the rsync to run on the remote machine --existing skip creating new files on receiver --ignore-existing skip updating files that already exist on receiver --remove-source-files sender removes synchronized files (non-dirs) --del an alias for --delete-during --delete delete extraneous files from destination dirs --delete-before receiver deletes before transfer, not during --delete-during receiver deletes during the transfer --delete-delay find deletions during, delete after --delete-after receiver deletes after transfer, not during --delete-excluded also delete excluded files from destination dirs --ignore-missing-args ignore missing source args without error --delete-missing-args delete missing source args from destination --ignore-errors delete even if there are I/O errors --force force deletion of directories even if not empty --max-delete=NUM don't delete more than NUM files --max-size=SIZE don't transfer any file larger than SIZE --min-size=SIZE don't transfer any file smaller than SIZE --partial keep partially transferred files --partial-dir=DIR put a partially transferred file into DIR --delay-updates put all updated files into place at transfer's end -m, --prune-empty-dirs prune empty directory chains from the file-list --numeric-ids don't map uid/gid values by user/group name --usermap=STRING custom username mapping --groupmap=STRING custom groupname mapping --chown=USER:GROUP simple username/groupname mapping --timeout=SECONDS set I/O timeout in seconds --contimeout=SECONDS set daemon connection timeout in seconds -I, --ignore-times don't skip files that match in size and mod-time -M, --remote-option=OPTION send OPTION to the remote side only --size-only skip files that match in size --modify-window=NUM compare mod-times with reduced accuracy -T, --temp-dir=DIR create temporary files in directory DIR -y, --fuzzy find similar file for basis if no dest file --compare-dest=DIR also compare destination files relative to DIR --copy-dest=DIR ... and include copies of unchanged files --link-dest=DIR hardlink to files in DIR when unchanged -z, --compress compress file data during the transfer --compress-level=NUM explicitly set compression level --skip-compress=LIST skip compressing files with a suffix in LIST -C, --cvs-exclude auto-ignore files the same way CVS does -f, --filter=RULE add a file-filtering RULE -F same as --filter='dir-merge /.rsync-filter' repeated: --filter='- .rsync-filter' --exclude=PATTERN exclude files matching PATTERN --exclude-from=FILE read exclude patterns from FILE --include=PATTERN don't exclude files matching PATTERN --include-from=FILE read include patterns from FILE --files-from=FILE read list of source-file names from FILE -0, --from0 all *-from/filter files are delimited by 0s -s, --protect-args no space-splitting; only wildcard special-chars --address=ADDRESS bind address for outgoing socket to daemon --port=PORT specify double-colon alternate port number --sockopts=OPTIONS specify custom TCP options --blocking-io use blocking I/O for the remote shell --stats give some file-transfer stats -8, --8-bit-output leave high-bit chars unescaped in output -h, --human-readable output numbers in a human-readable format --progress show progress during transfer -P same as --partial --progress -i, --itemize-changes output a change-summary for all updates --out-format=FORMAT output updates using the specified FORMAT --log-file=FILE log what we're doing to the specified FILE --log-file-format=FMT log updates using the specified FMT --password-file=FILE read daemon-access password from FILE --list-only list the files instead of copying them --bwlimit=RATE limit socket I/O bandwidth --outbuf=N|L|B set output buffering to None, Line, or Block --write-batch=FILE write a batched update to FILE --only-write-batch=FILE like --write-batch but w/o updating destination --read-batch=FILE read a batched update from FILE --protocol=NUM force an older protocol version to be used --iconv=CONVERT_SPEC request charset conversion of filenames --checksum-seed=NUM set block/file checksum seed (advanced) -4, --ipv4 prefer IPv4 -6, --ipv6 prefer IPv6 --version print version number (-h) --help show this help (-h is --help only if used alone) Use "rsync --daemon --help" to see the daemon-mode command-line options. Please see the rsync(1) and rsyncd.conf(5) man pages for full documentation. See http://rsync.samba.org/ for updates, bug reports, and answers