本文用于纠正网络中“广为流传”的“涡旋电场不真实存在”的理解谬误,“涡旋电场”是真实存在的。当然下面即将写下的内容并不仅限于此。如何界定“涡旋电场”?又应该如何认识它呢?“涡旋电流”又源于什么,与其相对的概念“径向电流”又是指什么,“涡流”的基本应用原理,以及,“涡旋”这个词语的一些扩展内容,以上。
How to give "Eddy current" a definition? First we should learn something about the "Vortex electric field", as the Maxwell equation hold (Faraday's law, of course, Ampere's Law, but will not be used in the article), the time-varying magnetic field will induce an electric field, which can be expressed as
,
from which we can easily see that the induced electric field is rotational, ie.
.
This kind of induce field is called "Vortex electric field", and its name means the field is different from the electrostatic field, work will be done if a charge go through a loop in it.
After that, we can say the "Eddy current" is current occured in the closed loop in conductor due to the "Vortex electric field", as figure below, Aluminum plate of induction watt-hour meter is an example of the eddy current.
It is also an important thing to referance "The Vortex electric field is provided by both the magnetic field emit by the eddy current and the magnetic field between the magnet and the current loop changes due to the motion of the non-cutting magnetic line", and it is the reason why "Farady's Law" exist.
In a general way, the experiment of "magnetism of rotation" named by François Arago, is the first time "Eddy current" has been discovered as a symbol, but this judgement is, to some extent, inaccurate. From now on, this phenomenon will be called as "Radial electric current".
As shown below, the magnetic field is perpendicular to the page for a half and outside for the other side.
When the copper plate begin to rotate, with , draw out the induceed current gennerated by the law of cutting the magnetic induction line, we can easily get the current, this current, which is due to the motion of cutting the magnetic induction line, is called "Radial electric current", different from "Eddy current" with their different mechanism. (As the graph below)
These knowleges are popular in applications such as solid iron transformer core, (to make the core out of thin laminations parallel to the field to protect Joule heating effect), using the eddy current (the repulsive effects) in levitation, etc.
Finally, I will give out a new senary of the volcabulary "vortex" in Optoelectronics and Laser, which is about "propagation of higher-order coherent vortices and optical vortices".
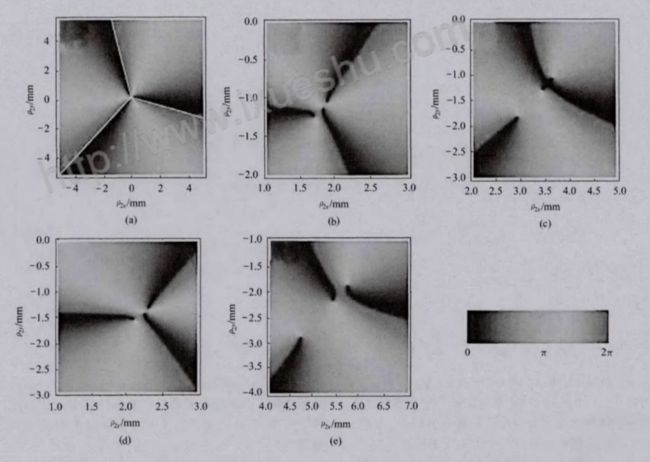
近年,涡旋光束在大气湍流中的传输特性和相干涡旋、光涡旋的动态演化成为光学微操控、光量子计算、光数据存储、量子密码系统和激光通信等领域的研究热点。下面给出的是以“LG光束”为例的理论模型。
在空间域中,LG 光束在入射面 z=0 处的场分布为
式中,为二维平面矢量;为 Gauss 部分的束腰宽度;为方位角;为缔合 Laguerre 多项式;为拓扑荷,ie. 光束中每个光子携带的轨道角动量;为径向指数, ie. 光束的(n+1)个径向节点, Gauss 光束以及 Gauss 涡旋光束都是其特殊情况。
利用广义 Huygens-Fresnel 原理,并调用谢尔相关项进行计算,最终可以得到LG光束在大气湍流中的交叉谱密度函数的解析表达式为
其中,为输出平面的两点,而为复杂积分带来的几何系数。
根据光谱相干度定义,可以得出相干涡旋位置所满足的方程组:
,
定义为相干度.
————Journal of Optoelectronics . Laser Vol.27 No.7 July 2016