参考Lambda、MethodHandle、CallSite调用简单性能测试与调优
1.基准版本
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
public class ReflectionPerTest1 {
public static void target(int i) {
// 空方法
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Class klass = Class.forName("com.enjoy.learn.core.oop.reflection.ReflectionPerTest1");
Method method = klass.getMethod("target", int.class);
long current = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 1; i <= 2_000_000_000; i++) {
if (i % 100_000_000 == 0) {
long temp = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(temp - current);
current = temp;
}
method.invoke(null, 128);
}
}
}
305
304
304
318
313
查看其字节码,可以看到有两项额外的操作:
1)128自动装箱为Integer类型
2)生成一个Object数组,并存储传入参数
这两个操作除了带来性能开销外,还可能占用堆内存,使得GC更加频繁。(-XX:+PrintGC)
public static void main(java.lang.String[]) throws java.lang.Exception;
descriptor: ([Ljava/lang/String;)V
flags: (0x0009) ACC_PUBLIC, ACC_STATIC
Code:
stack=6, locals=8, args_size=1
0: ldc #2 // String com.enjoy.learn.core.oop.reflection.ReflectionPerTest1
2: invokestatic #3 // Method java/lang/Class.forName:(Ljava/lang/String;)Ljava/lang/Class;
5: astore_1
6: aload_1
7: ldc #4 // String target
9: iconst_1
10: anewarray #5 // class java/lang/Class
13: dup
14: iconst_0
15: getstatic #6 // Field java/lang/Integer.TYPE:Ljava/lang/Class;
18: aastore
19: invokevirtual #7 // Method java/lang/Class.getMethod:(Ljava/lang/String;[Ljava/lang/Class;)Ljava/lang/reflect/Method;
22: astore_2
23: invokestatic #8 // Method java/lang/System.currentTimeMillis:()J
26: lstore_3
27: iconst_1
28: istore 5
30: iload 5
32: ldc #9 // int 2000000000
34: if_icmpgt 88
37: iload 5
39: ldc #10 // int 100000000
41: irem
42: ifne 63
45: invokestatic #8 // Method java/lang/System.currentTimeMillis:()J
48: lstore 6
50: getstatic #11 // Field java/lang/System.out:Ljava/io/PrintStream;
53: lload 6
55: lload_3
56: lsub
57: invokevirtual #12 // Method java/io/PrintStream.println:(J)V
60: lload 6
62: lstore_3
63: aload_2
64: aconst_null
65: iconst_1
66: anewarray #13 // class java/lang/Object
69: dup
70: iconst_0
71: sipush 128
74: invokestatic #14 // Method java/lang/Integer.valueOf:(I)Ljava/lang/Integer;
77: aastore
78: invokevirtual #15 // Method java/lang/reflect/Method.invoke:(Ljava/lang/Object;[Ljava/lang/Object;)Ljava/lang/Object;
81: pop
82: iinc 5, 1
85: goto 30
88: return
2.避免自动装箱
Integer I128 = Integer.valueOf(128);
for (int i = 1; i <= 2_000_000_000; i++) {
if (i % 100_000_000 == 0) {
long temp = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(temp - current);
current = temp;
}
method.invoke(null, I128);
}
78: iconst_0
79: aload 5
81: aastore
82: invokevirtual #15 // Method java/lang/reflect/Method.invoke:(Ljava/lang/Object;[Ljava/lang/Object;)Ljava/lang/Object;
LocalVariableTable:
Start Length Slot Name Signature
58 13 7 temp J
38 54 6 i I
0 93 0 args [Ljava/lang/String;
6 87 1 klass Ljava/lang/Class;
23 70 2 method Ljava/lang/reflect/Method;
27 66 3 current J
35 58 5 I128 Ljava/lang/Integer;
192
195
190
189
190
Java缓存[-128,127]所有整数所定义的Integer对象,可以将范围扩大至覆盖128.
-Djava.lang.Integer.IntegerCache.high=128
78: iconst_0
79: sipush 128
82: invokestatic #9 // Method java/lang/Integer.valueOf:(I)Ljava/lang/Integer;
85: aastore
86: invokevirtual #15 // Method java/lang/reflect/Method.invoke:(Ljava/lang/Object;[Ljava/lang/Object;)Ljava/lang/Object;
216
217
217
218
217
3.在循环外新建一个Object数组,避免频繁GC
但也有可能发生性能变坏,因为当对象不逃逸时,JIT可以选择栈分配甚至虚拟分配,不占用堆空间。
在堆外建立数组时,无法优化掉访问数组的操作。
Object[] argArray = new Object[1];
argArray[0] = 128;
for (int i = 1; i <= 2_000_000_000; i++) {
if (i % 100_000_000 == 0) {
long temp = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(temp - current);
current = temp;
}
method.invoke(null, argArray);
}
245
241
243
244
243
4.关闭反射调用的Inflation机制和权限检查
从而取消委派实现,直接使用动态实现。
此外,每次反射调用都会检查目标方法的权限,关闭掉。
-Dsun.reflect.noInflation=true
method.setAccessible(true); // 关闭权限检查
Integer I128 = Integer.valueOf(128);
for (int i = 1; i <= 2_000_000_000; i++) {
if (i % 100_000_000 == 0) {
long temp = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(temp - current);
current = temp;
}
method.invoke(null, I128);
}
123
124
123
125
122
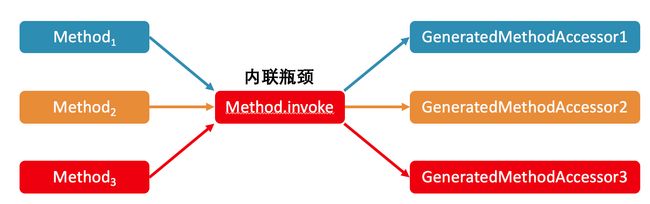
5.内联瓶颈——Method.invoke
变快的原因是JIT中的方法内联。在关闭Inflation的情况下,内联的瓶颈在于Method.invoke方法中对MethodAccessor.invoke方法的调用。
JVM无法同时记录多个类的关于调用点的类型profile,因此可能造成所测试的反射调用没有被内联。
类型profile:对于invokevirtula或者invokeinterface,JVM会记录下调用者的具体类型。
public class ReflectionPerTest1 {
public static void target(int i) {
// 空方法
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Class klass = Class.forName("com.enjoy.learn.core.oop.reflection.ReflectionPerTest1");
Method method = klass.getMethod("target", int.class);
method.setAccessible(true); // 关闭权限检查
polluteProfile();
long current = System.currentTimeMillis();
Integer I128 = Integer.valueOf(128);
for (int i = 1; i <= 2_000_000_000; i++) {
if (i % 100_000_000 == 0) {
long temp = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(temp - current);
current = temp;
}
method.invoke(null, 128);
}
}
public static void polluteProfile() throws Exception {
Method method1 = ReflectionPerTest1.class.getMethod("target1", int.class);
Method method2 = ReflectionPerTest1.class.getMethod("target2", int.class);
for (int i = 0; i < 2000; i++) {
method1.invoke(null, 0);
method2.invoke(null, 0);
}
}
public static void target1(int i) { }
public static void target2(int i) { }
}
1047
1024
1021
1030
1042
只要干扰了Method.invoke方法的类型profile,性能开销会急剧上升。
提高JVM关于每个调用能够记录的类型数目(-xx:TypeProfileWidth=3默认值为2)。测试结果无变化。
6.多次获取的Method是同一个对象
public static void polluteProfile() throws Exception {
Method method1 = ReflectionPerTest1.class.getMethod("target", int.class);
Method method2 = ReflectionPerTest1.class.getMethod("target", int.class);
System.out.println(method1.equals(method2));
for (int i = 0; i < 2000; i++) {
method1.invoke(null, 0);
method2.invoke(null, 0);
}
}
true
...
300
302
309
307
305