前言
因为弃了很长一段时间的CoreData没用,最近想稍微捋一捋,就跟着网上的方法和朋友的提示去操作,结果踩了一万个坑(鬼知道我经历了什么- -!),最后跌跌撞撞,才勉强弄了个demo出来,所以本文主旨是介绍新版CoreData的基本创建使用,顺带分享一下自己由字典类型->对象模型的转换方法(很浅显,欢迎大神指导)。
第一步
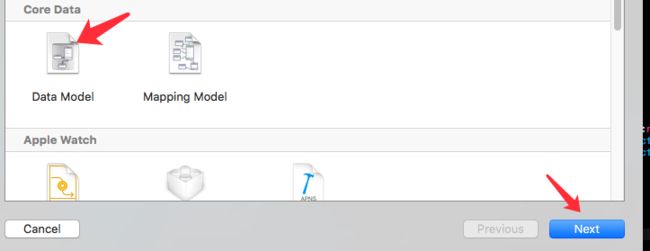
不说废话 直接看图
Next之后生成一个xcdatamodeld后缀的文件,然后继续看图
然后注意了,按照图示操作完后,以前是需要如下操作,创建另外4个文件
现在由xcode自动创建,并且是不可见的,但是可以导入。到此不用写代码的部分就over了,是不是相比之前那些简便许多,更简便的还是代码部分,请各位看官继续往下滑~
第二步
由于现在是使用NSPersistentContainer 代替以前NSManagedObjectModel, NSManagedObjectContext NSPersistentStoreCoordinator这三个对象,所以代码部分异常简洁。先看一下以前的,有对比才会有差距嘛。
@synthesize managedObjectContext = _managedObjectContext;
@synthesize managedObjectModel = _managedObjectModel;
@synthesize persistentStoreCoordinator = _persistentStoreCoordinator;
- (NSURL *)applicationDocumentsDirectory {
// The directory the application uses to store the Core Data store file. This code uses a directory named "BUPT.Daily" in the application's documents directory.
return [[[NSFileManager defaultManager] URLsForDirectory:NSDocumentDirectory inDomains:NSUserDomainMask] lastObject];
}
- (NSManagedObjectModel *)managedObjectModel {
// The managed object model for the application. It is a fatal error for the application not to be able to find and load its model.
if (_managedObjectModel != nil) {
return _managedObjectModel;
}
NSURL *modelURL = [[NSBundle mainBundle] URLForResource:@"School" withExtension:@"momd"];
_managedObjectModel = [[NSManagedObjectModel alloc] initWithContentsOfURL:modelURL];
return _managedObjectModel;
}
- (NSPersistentStoreCoordinator *)persistentStoreCoordinator {
// The persistent store coordinator for the application. This implementation creates and returns a coordinator, having added the store for the application to it.
if (_persistentStoreCoordinator != nil) {
return _persistentStoreCoordinator;
}
// Create the coordinator and store
_persistentStoreCoordinator = [[NSPersistentStoreCoordinator alloc] initWithManagedObjectModel:[self managedObjectModel]];
NSURL *storeURL = [[self applicationDocumentsDirectory] URLByAppendingPathComponent:@"School?.sqlite"];
NSError *error = nil;
NSString *failureReason = @"There was an error creating or loading the application's saved data.";
if (![_persistentStoreCoordinator addPersistentStoreWithType:NSSQLiteStoreType configuration:nil URL:storeURL options:nil error:&error]) {
// Report any error we got.
NSMutableDictionary *dict = [NSMutableDictionary dictionary];
dict[NSLocalizedDescriptionKey] = @"Failed to initialize the application's saved data";
dict[NSLocalizedFailureReasonErrorKey] = failureReason;
dict[NSUnderlyingErrorKey] = error;
error = [NSError errorWithDomain:@"YOUR_ERROR_DOMAIN" code:9999 userInfo:dict];
// Replace this with code to handle the error appropriately.
// abort() causes the application to generate a crash log and terminate. You should not use this function in a shipping application, although it may be useful during development.
NSLog(@"Unresolved error %@, %@", error, [error userInfo]);
abort();
}
return _persistentStoreCoordinator;
}
- (NSManagedObjectContext *)managedObjectContext {
// Returns the managed object context for the application (which is already bound to the persistent store coordinator for the application.)
if (_managedObjectContext != nil) {
return _managedObjectContext;
}
NSPersistentStoreCoordinator *coordinator = [self persistentStoreCoordinator];
if (!coordinator) {
return nil;
}
_managedObjectContext = [[NSManagedObjectContext alloc] initWithConcurrencyType:NSMainQueueConcurrencyType];
[_managedObjectContext setPersistentStoreCoordinator:coordinator];
return _managedObjectContext;
}
#pragma mark - Core Data Saving support
- (void)saveContext {
NSManagedObjectContext *managedObjectContext = self.managedObjectContext;
if (managedObjectContext != nil) {
NSError *error = nil;
if ([managedObjectContext hasChanges] && ![managedObjectContext save:&error]) {
// Replace this implementation with code to handle the error appropriately.
// abort() causes the application to generate a crash log and terminate. You should not use this function in a shipping application, although it may be useful during development.
NSLog(@"Unresolved error %@, %@", error, [error userInfo]);
abort();
}
}
}
以上代码就是之前使用coredata需要写好的,封装也是需要写一遍的(代码复制网上的),而现在仅需要NSPersistentContainer即可,具体如下所示
- (NSPersistentContainer *)persistentContainer {
// The persistent container for the application. This implementation creates and returns a container, having loaded the store for the application to it.
@synchronized (self) {
if (_persistentContainer == nil) {
_persistentContainer = [[NSPersistentContainer alloc] initWithName:@"Model"];
[_persistentContainer loadPersistentStoresWithCompletionHandler:^(NSPersistentStoreDescription *storeDescription, NSError *error) {
if (error != nil) {
NSLog(@"Unresolved error %@, %@", error, error.userInfo);
abort();
}
}];
}
}
return _persistentContainer;
}
#pragma mark - Core Data Saving support
- (void)saveContext {
NSManagedObjectContext *context = self.persistentContainer.viewContext;
NSError *error = nil;
if ([context hasChanges] && ![context save:&error]) {
NSLog(@"Unresolved error %@, %@", error, error.userInfo);
abort();
}
}
没了。。。了。。。
是不是超简单?我们点进去看一下NSPersistentContainer的说明,会看到
API_AVAILABLE(macosx(10.12),ios(10.0),tvos(10.0),watchos(3.0))
@interface NSPersistentContainer : NSObject {
#if (!__OBJC2__)
@private
id _name;
NSManagedObjectContext *_viewContext;
id _storeCoordinator;
id _storeDescriptions;
#endif
}
+ (instancetype)persistentContainerWithName:(NSString *)name;
+ (instancetype)persistentContainerWithName:(NSString *)name managedObjectModel:(NSManagedObjectModel *)model;
+ (NSURL *)defaultDirectoryURL;
@property (copy, readonly) NSString *name;
@property (strong, readonly) NSManagedObjectContext *viewContext;
@property (strong, readonly) NSManagedObjectModel *managedObjectModel;
@property (strong, readonly) NSPersistentStoreCoordinator *persistentStoreCoordinator;
@property (copy) NSArray *persistentStoreDescriptions;
// Creates a container using the model named `name` in the main bundle
- (instancetype)initWithName:(NSString *)name;
- (instancetype)initWithName:(NSString *)name managedObjectModel:(NSManagedObjectModel *)model NS_DESIGNATED_INITIALIZER;
// Load stores from the storeDescriptions property that have not already been successfully added to the container. The completion handler is called once for each store that succeeds or fails.
- (void)loadPersistentStoresWithCompletionHandler:(void (^)(NSPersistentStoreDescription *, NSError * _Nullable))block;
- (NSManagedObjectContext *)newBackgroundContext NS_RETURNS_RETAINED;
- (void)performBackgroundTask:(void (^)(NSManagedObjectContext *))block;
里面的内容一目了然,就不多赘述了,有兴趣的自己点进去研究研究。下面贴一些本人以用户对象作为测试用的代码,包括基本的增删改查。.h文件导入"User+CoreDataClass.h",后者就是xcode自动创建的不可见文件(应该是和Model.xcdatamodeld在同一个目录下面)
查询数据
- (User *)executeResult{
User *user1 = nil;
NSFetchRequest *fetchRequest = [[NSFetchRequest alloc] init];
NSEntityDescription *entity = [NSEntityDescription entityForName:kTableName inManagedObjectContext:self.persistentContainer.viewContext];
fetchRequest.entity = entity;
NSError *error = nil;
NSArray *fetchedObjects = [self.persistentContainer.viewContext executeFetchRequest:fetchRequest error:&error];
if (fetchedObjects == nil) {
NSLog(@"数据查询错误%@",error);
}else if(fetchedObjects.count == 0){
}else{
user1 = fetchedObjects.lastObject;
}
return user1;
}
更新数据
- (void)updateDataWithProperty:(NSString *)property updateContent:(NSString *)content{
User *user = [self executeResult];
unsigned int count = 0;
objc_property_t *properties = class_copyPropertyList([User class], &count);
for (int i = 0; i < count; i ++) {
const char *propertyName = property_getName(properties[i]);
NSString *name = [NSString stringWithUTF8String:propertyName];
if ([name isEqualToString:property]) {
if (content) {
[user setValue:content forKey:name];
}
}
}
[self saveContext];
}
删除数据
- (void)deleteAllData{
NSFetchRequest *fetchRequest = [[NSFetchRequest alloc] init];
NSEntityDescription *entity = [NSEntityDescription entityForName:kTableName inManagedObjectContext:self.persistentContainer.viewContext];
fetchRequest.entity = entity;
NSError *error = nil;
NSArray *fetchedObjects = [self.persistentContainer.viewContext executeFetchRequest:fetchRequest error:&error];
for (User *user in fetchedObjects) {
[self.persistentContainer.viewContext deleteObject:user];
}
[self saveContext];
}
增加数据
[self deleteAllData];//目前暂时只考虑数据库仅存储一个对象 多个对象取lastObject即为最近登录的用户
User *user = [NSEntityDescription insertNewObjectForEntityForName:kTableName inManagedObjectContext:self.persistentContainer.viewContext];
NSMutableArray *array = @[].mutableCopy;
unsigned int count = 0;
objc_property_t *properties = class_copyPropertyList([User class], &count);
for (int i = 0; i < count; i ++) {
const char *propertyName = property_getName(properties[i]);
NSString *name = [NSString stringWithUTF8String:propertyName];
NSLog(@"--%@",name);
[array addObject:name];//对象属性数组
//去掉字典中不包含以对象数组里面元素为key的键值对
if ([[dict valueForKey:name] isKindOfClass:[NSNull class]] || [dict valueForKey:name] == nil) {//其他类型数据同理判断
[user setValue:@" " forKey:name];
}else{
[user setValue:[dict valueForKey:name] forKey:name];
}
NSLog(@"--%@",[[dict valueForKey:name] class]);
}
//去掉与系统有冲突的键 上面未添加的 继续添加
for (NSString *idStr in dict.allKeys) {
if ([idStr isEqualToString:@"id"]) {
[user setValue:[dict valueForKey:@"id"] forKey:@"userId"];
}
}
[self saveContext];
之所以增加数据最后贴是想顺带提一下自己将字典转换成模型的处理方式,是因为这个demo主要是介绍下最新的CoreData创建及使用(属于现学现用吧,没完全理解透彻),所以这个数据转换用的类型都是很简易的,字典暂时仅考虑单级结构(表达可能有所欠缺,就是字典中不嵌套字典,数组等等),具体做法就是利用runtime的objc_property_t,获取到对象的所有属性名,然后去对比字典中的键,相同即赋值,不同的则代表对象用不到的属性,另外考虑到因为oc的一些关键字是不可作为属性名的,比如id,必须另行处理(见代码注释部分)。另外值得一说的是[self saveContext]操作,每次更新都需要在最后加上这句,这个跟使用FMDB一样,操作前打开,操作完关闭,不能少了哈。
结语
这个小demo很浅显,考虑不周的地方有很多,比如
1.实体属性名必须和后台一致 (这个很烦,得跟着后台走,很不爽)
2.目前仅存储一个对象 每次增加数据之前会删除之前的数据(酌情处理)
3.类似手机号码和邮箱登录方式的情况,实体添加两种属性即可 后台返回其中一种就代表这种有值 另外一个就是空(@“ ”)
4.不同的对象添加不同的实体即可 动态传入EntityName 不必使用kTableName宏定义
5.确保传入的数据为单级结构字典 多级结构需要继续优化完善
6.基本数据类型待优化
有时间会继续优化一下,不奢望达到大神级别的框架,最起码让自己也学点先进的封装思想
欢迎各路大神批评指正,有误导之处请及时提醒,感谢阅读