我们在使用bindservice的整个调用过程为
MainActivity.bindService->ServerService.onCreate->ServerService.onBind->MainActivity.ServiceConnection.onServiceConnection-->IUmBrellaService.Stub.asInterface(service);
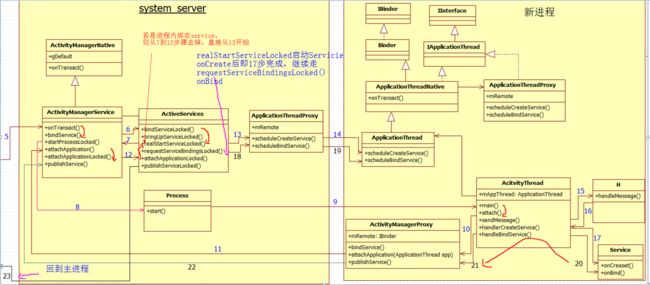
总体流程图:
主要顺序流程:
1、MainActivity.bindService 到ActivityManagerService 启动ServerService服务(如果是新进程,则启动新进程参考上一篇启动新进程servicestartService源码从应用主进程到AMS进程和startService源码从AMS进程到service新进程启动分析)并调用ServerService的onCreate函数
2、ActivityManagerService 继续调用ServerService的onBind函数,返回一个Binder对象给ActivityManagerService
3、ActivityManagerService拿到Binder对象后,作为参数传递到ServiceConnection对象的onServiceConnected函数
4、通过onServiceConnected函数返回的IBinder,改造下IUmBrellaService.Stub.asInterface(service),就可以调用IUmBrellaService提供的接口了。
Step1:ContextImpl.bindService:
@Override
public boolean bindService(Intent service, ServiceConnection conn,
int flags) {
warnIfCallingFromSystemProcess();
return bindServiceCommon(service, conn, flags, mMainThread.getHandler(),
Process.myUserHandle());
}
private boolean bindServiceCommon(Intent service, ServiceConnection conn, int flags, Handler
handler, UserHandle user) {
IServiceConnection sd;
...
if (mPackageInfo != null) {
sd = mPackageInfo.getServiceDispatcher(conn, getOuterContext(), handler, flags);
}
try {
IBinder token = getActivityToken();
...
int res = ActivityManagerNative.getDefault().bindService(
mMainThread.getApplicationThread(), getActivityToken(), service,
service.resolveTypeIfNeeded(getContentResolver()),
sd, flags, getOpPackageName(), user.getIdentifier());
...
return res != 0;
}
}
其中mMainThread是ActivityThread,getHandler是返回mH,即是Handler,后面会用到这个handler发送消息队列,把service onBinder返回的对象发到主线程,实行ServiceConnection对象的onServiceConnected函数去。
mPackageInfo 是LoadedApk,调用getServiceDispatcher()函数来获得一个IServiceConnection接口,看下getServiceDispatcher的实现:
Step2:
public final class LoadedApk {
.....
public final IServiceConnection getServiceDispatcher(ServiceConnection c,
Context context, Handler handler, int flags) {
synchronized (mServices) {
LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher sd = null;
...
sd = new ServiceDispatcher(c, context, handler, flags);
...
return sd.getIServiceConnection();
}
}
.....
static final class ServiceDispatcher {
private final ServiceDispatcher.InnerConnection mIServiceConnection;
private final ServiceConnection mConnection;
private final Context mContext;
private final Handler mActivityThread;
private final ServiceConnectionLeaked mLocation;
private final int mFlags;
.....
private static class InnerConnection extends IServiceConnection.Stub {
final WeakReference mDispatcher;
InnerConnection(LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher sd) {
mDispatcher = new WeakReference(sd);
}
public void connected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) throws RemoteException {
LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher sd = mDispatcher.get();
if (sd != null) {
sd.connected(name, service);
}
}
}
...
ServiceDispatcher(ServiceConnection conn,
Context context, Handler activityThread, int flags) {
mIServiceConnection = new InnerConnection(this);
mConnection = conn;
mContext = context;
mActivityThread = activityThread;
mLocation = new ServiceConnectionLeaked(null);
...
}
IServiceConnection getIServiceConnection() {
return mIServiceConnection;
}
}
}
在getServiceDispatcher函数中,参数context是一个MainActivity实例,创建新的ServiceDispatcher,把ServiceConnection参数c和Hanlder参数保存,且创建一个InnerConnection mIServiceConnection Binder对象,继承IServiceConnection.Stub,用来和ActivityManagerService通讯,后面service 在onBInder返回的对象,会通过这个InnerConnection 到ServiceConnection再到Handler,回到ServiceConnection。
Step3:接着ActivityManagerNative.getDefault().bindService()即ActivityManagerProxy.bindService()通过Binder驱动程序会到AMS的bindService():
class ActivityManagerProxy implements IActivityManager{
public ActivityManagerProxy(IBinder remote){
mRemote = remote;
}
public int bindService(IApplicationThread caller, IBinder token,
Intent service, String resolvedType, IServiceConnection connection,
int flags, String callingPackage, int userId) throws RemoteException {
Parcel data = Parcel.obtain();
Parcel reply = Parcel.obtain();
data.writeInterfaceToken(IActivityManager.descriptor);
data.writeStrongBinder(caller != null ? caller.asBinder() : null);
data.writeStrongBinder(token);
service.writeToParcel(data, 0);
data.writeString(resolvedType);
data.writeStrongBinder(connection.asBinder());
data.writeInt(flags);
data.writeString(callingPackage);
data.writeInt(userId);
mRemote.transact(BIND_SERVICE_TRANSACTION, data, reply, 0);
reply.readException();
int res = reply.readInt();
data.recycle();
reply.recycle();
return res;
}
}
Step4:ActivityManagerService.bindService:
public final class ActivityManagerService extends ActivityManagerNative
implements Watchdog.Monitor, BatteryStatsImpl.BatteryCallback {
....
public int bindService(IApplicationThread caller, IBinder token, Intent service,
String resolvedType, IServiceConnection connection, int flags, String callingPackage,
int userId) throws TransactionTooLargeException {
enforceNotIsolatedCaller("bindService");
...
synchronized(this) {
return mServices.bindServiceLocked(caller, token, service,
resolvedType, connection, flags, callingPackage, userId);
}
}
}
其中mServices是ActiveServices,接着看ActiveServices.bindServiceLocked:
public final class ActiveServices {
int bindServiceLocked(IApplicationThread caller, IBinder token, Intent service,
String resolvedType, final IServiceConnection connection, int flags,
String callingPackage, final int userId) throws TransactionTooLargeException {
...
ServiceLookupResult res =
retrieveServiceLocked(service, resolvedType, callingPackage, Binder.getCallingPid(),
Binder.getCallingUid(), userId, true, callerFg, isBindExternal);
ServiceRecord s = res.record;
...
AppBindRecord b = s.retrieveAppBindingLocked(service, callerApp);
ConnectionRecord c = new ConnectionRecord(b, activity,
connection, flags, clientLabel, clientIntent);
IBinder binder = connection.asBinder();
ArrayList clist = s.connections.get(binder);
....
clist.add(c);
if ((flags&Context.BIND_AUTO_CREATE) != 0) {
s.lastActivity = SystemClock.uptimeMillis();
if (bringUpServiceLocked(s, service.getFlags(), callerFg, false,
permissionsReviewRequired) != null) {
return 0;
}
}
...
return 1;
}
}
参数token是MainActivity在ActivityManagerService里面的一个令牌,用来对应MainActivity的ActivityRecord取回来了,
其中ServiceReocrd描述的是一个Service对象,这里一开始绑定的ServerService,service是一开始绑定的Intent,且保存在ServiceRecord对象s中。ConnectionRecord 对象是参数connection(Binder对象,即LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher.InnerConnection)保存起来,后面会取出来ton通讯用。
Step5:ActiveServices.bringUpServiceLocked:
public final class ActiveServices {
private String bringUpServiceLocked(ServiceRecord r, int intentFlags, boolean execInFg,
boolean whileRestarting, boolean permissionsReviewRequired)
throws TransactionTooLargeException {
...
final String procName = r.processName;
ProcessRecord app;
if (!isolated) {
app = mAm.getProcessRecordLocked(procName, r.appInfo.uid, false);
if (app != null && app.thread != null) {
try {
app.addPackage(r.appInfo.packageName, r.appInfo.versionCode, mAm.mProcessStats);
realStartServiceLocked(r, app, execInFg);
return null;
}
....
}
}
...
// Not running -- get it started, and enqueue this service record
// to be executed when the app comes up.
if (app == null && !permissionsReviewRequired) {
if ((app=mAm.startProcessLocked(procName, r.appInfo, true, intentFlags,
"service", r.name, false, isolated, false)) == null) {
...
}
在AndroidManifest.xml中ServerService的配置没有设置process值,那就是应用程序的包名,在同一个进程内启动service的,
就执行realStartServiceLocked函数来执行下一步操作了。
如果这里得到的ProcessRecord变量app为null,说明这个service是新开的进程,则startProcessLocked函数来创建一个新的进程,新的进程中启动这个ServerService,参考startService源码从AMS进程到service的新进程的启动过程分析,(即进程创建后会实行到realStartServiceLocked函数,在这个函数中,会启动service的onCreate,onBind等操作)。
Step6:接下来看realStartServiceLocked,这个函数中会调用ServerService的onCreate和onBind
public final class ActiveServices {
private final void realStartServiceLocked(ServiceRecord r,
ProcessRecord app, boolean execInFg) throws RemoteException {
...
r.app = app;
...
app.thread.scheduleCreateService(r, r.serviceInfo,
mAm.compatibilityInfoForPackageLocked(r.serviceInfo.applicationInfo),
app.repProcState);
...
requestServiceBindingsLocked(r, execInFg);
...
}
}
这个函数执行了两个操作,一个是操作是调用app.thread.scheduleCreateService函数来在应用程序进程内部启动ServerService,这个操作会导致ServerService的onCreate函数被调用,具体流程参考startService源码从AMS进程到service新进程启动分析中第8步。
另一个操作是调用requestServiceBindingsLocked函数来向ServerService要一个Binder对象,这个操作会导致ServerService的onBind函数被调用。
Step7:ActiveServices.requestServiceBindingsLocked:
public final class ActiveServices{
private final void requestServiceBindingsLocked(ServiceRecord r, boolean execInFg)
throws TransactionTooLargeException {
for (int i=r.bindings.size()-1; i>=0; i--) {
IntentBindRecord ibr = r.bindings.valueAt(i);
if (!requestServiceBindingLocked(r, ibr, execInFg, false)) {
break;
}
}
}
private final boolean requestServiceBindingLocked(ServiceRecord r, IntentBindRecord i,
boolean execInFg, boolean rebind) throws TransactionTooLargeException {
....
r.app.thread.scheduleBindService(r, i.intent.getIntent(), rebind,
r.app.repProcState);
...
return true;
}
}
requestServiceBindingLocked调用了app.thread.scheduleBindService函数执行操作,app.thread是ApplicationThreadProxy,它是一个Binder对象的远程接口
Step8:ApplicationThreadProxy.scheduleBindService:
class ApplicationThreadProxy implements IApplicationThread {
public final void scheduleBindService(IBinder token, Intent intent, boolean rebind,
int processState) throws RemoteException {
Parcel data = Parcel.obtain();
data.writeInterfaceToken(IApplicationThread.descriptor);
data.writeStrongBinder(token);
intent.writeToParcel(data, 0);
data.writeInt(rebind ? 1 : 0);
data.writeInt(processState);
mRemote.transact(SCHEDULE_BIND_SERVICE_TRANSACTION, data, null,
IBinder.FLAG_ONEWAY);
data.recycle();
}
}
通过Binder驱动程序进入service(要绑定的service即ServerService)进程的ApplicationThread的scheduleBindService函数了;
Step9:进入要绑定service的进程,ApplicationThread在ActivityThread.java文件中:
private class ApplicationThread extends ApplicationThreadNative {
public final void scheduleBindService(IBinder token, Intent intent,
boolean rebind, int processState) {
updateProcessState(processState, false);
BindServiceData s = new BindServiceData();
s.token = token;
s.intent = intent;
s.rebind = rebind;
..
sendMessage(H.BIND_SERVICE, s);
}
}
Step 10. H.sendMessage函数中,要处理的消息类型是H.BIND_SERVICE:
public final class ActivityThread {
private class H extends Handler {
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
...
switch(msg.what)
case BIND_SERVICE:
handleBindService((BindServiceData)msg.obj);
break;
...
}
}
Step11:ActivityThread.handleBindService:
public final class ActivityThread {
private void handleBindService(BindServiceData data) {
Service s = mServices.get(data.token);
if (s != null) {
try {
...
try {
if (!data.rebind) {
IBinder binder = s.onBind(data.intent);
ActivityManagerNative.getDefault().publishService(
data.token, data.intent, binder);
} else {
...
}
} catch (RemoteException ex) {
}
} catch (Exception e) {
}
}
}
}
在ActivityThread.handleCreateService函数中,已经将这个ServerService实例保存在mServices中,这里data.token值将它取回来,调用s.onBind,即ServerService.onBind获得一个Binder对象,再把这个Binder对象传递给ActivityManagerService进程。
public class ServerService extends Service {
private IBinder mBinder;
@Nullable
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
mBinder = new IUmBrellaImpl();
return mBinder;
}
public class IUmBrellaImpl extends IUmBrellaService.Stub{
@Override
public String umbrellaEevent(String client_str) throws RemoteException {
String serverString = "server string is from server";
return serverString;
}
@Override
public void umbreallaListener(IUmBrellaListener listener) throws RemoteException {
String serverString1 = "server string1 is from server";
String serverString2 = "server string2 is from server";
UmBrellaInfo umBrellaInfo = new UmBrellaInfo();
umBrellaInfo.setUmbrella1(serverString1);
umBrellaInfo.setUmbrella2(serverString2);
if(listener != null)
listener.onSuccess(umBrellaInfo);
}
}
}
Step12:ActivityManagerNative.getDefault().publishService即ActivityManagerProxy.publishService:
class ActivityManagerProxy implements IActivityManager {
public void publishService(IBinder token,
Intent intent, IBinder service) throws RemoteException {
Parcel data = Parcel.obtain();
Parcel reply = Parcel.obtain();
data.writeInterfaceToken(IActivityManager.descriptor);
data.writeStrongBinder(token);
intent.writeToParcel(data, 0);
data.writeStrongBinder(service);
mRemote.transact(PUBLISH_SERVICE_TRANSACTION, data, reply, 0);
reply.readException();
data.recycle();
reply.recycle();
}
}
mRemote.transact()通过Binder驱动程序就进入到ActivityManagerService的父类ActivityManagerNativie.onTransact,标示为PUBLISH_SERVICE_TRANSACTION,就进入了ActivityManagerService.publishService函数中去了
Step13:ActivityManagerService.publishService
public abstract class ActivityManagerNative extends Binder implements IActivityManager{
@Override
public boolean onTransact(int code, Parcel data, Parcel reply, int flags)
throws RemoteException {
switch (code) {
case PUBLISH_SERVICE_TRANSACTION: {
data.enforceInterface(IActivityManager.descriptor);
IBinder token = data.readStrongBinder();
Intent intent = Intent.CREATOR.createFromParcel(data);
IBinder service = data.readStrongBinder();
publishService(token, intent, service);
reply.writeNoException();
return true;
}
}
}
}
public final class ActivityManagerService extends ActivityManagerNative
implements Watchdog.Monitor, BatteryStatsImpl.BatteryCallback {
public void publishService(IBinder token, Intent intent, IBinder service) {
...
synchronized(this) {
...
mServices.publishServiceLocked((ServiceRecord)token, intent, service);
}
}
}
Step13:ActiveServices.publishServiceLocked:
public final class ActiveServices {
void publishServiceLocked(ServiceRecord r, Intent intent, IBinder service) {
...
if (r != null) {
Intent.FilterComparison filter
= new Intent.FilterComparison(intent);
IntentBindRecord b = r.bindings.get(filter);
if (b != null && !b.received) {
b.binder = service;
b.requested = true;
b.received = true;
for (int conni=r.connections.size()-1; conni>=0; conni--) {
ArrayList clist = r.connections.valueAt(conni);
...
ConnectionRecord c = clist.get(i);
...
c.conn.connected(r.name, service);
}
}
}
...
}
其中ConnectionRecord放在ServiceRecord.connections列表中的,ConnectionRecord.conn,它的类型是IServiceConnection,是一个Binder对象的远程接口,就是LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher.InnerConnection对象。所以,这里执行c.conn.connected函数通过binder驱动就进入到发起绑定的进程的LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher.InnerConnection.connected函数中去
Step14:LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher:
public final class LoadedApk {
...
static final class ServiceDispatcher {
...
private static class InnerConnection extends IServiceConnection.Stub {
final WeakReference mDispatcher;
InnerConnection(LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher sd) {
mDispatcher = new WeakReference(sd);
}
public void connected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) throws RemoteException {
LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher sd = mDispatcher.get();
if (sd != null) {
sd.connected(name, service);
}
}
}
...
public void connected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) {
if (mActivityThread != null) {
mActivityThread.post(new RunConnection(name, service, 0));
} else {
doConnected(name, service);
}
}
...
private final class RunConnection implements Runnable {
...
public void run() {
if (mCommand == 0) {
doConnected(mName, mService);
} else if (mCommand == 1) {
doDeath(mName, mService);
}
}
...
}
...
public void doConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) {
...
if (service != null) {
mConnection.onServiceConnected(name, service);
}
...
}
...
}
这里的mActivityThread是一个Handler实例,通过post切到主进程调用onServiceConnected,即绑定ServerService成功后回调到MainActivity.ServiceConnection.onServiceConnection即我们一开始定义的:
ServiceConnection mServiceConnection = new ServiceConnection() {
@Override
public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder binder) {
try {
mBinder = service;
mServerSerivce = IUmBrellaService.Stub.asInterface(binder);
mBinder.linkToDeath(mDeatRecipient,0);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Override
public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName name) {
}
};
1.MainActivity调用bindService函数通知ActivityManagerService进程,启动ServerService这个服务,如果是ServerService服务是新的进程,则ActivityManagerService先启动新进程参考startService源码从AMS进程到service的新进程的启动过程分析,启动ServerService,且调用onCreate函数。
2.ActivityManagerService把ServerService启动起来后,继续调用ServerService的onBind函数,ServerService返回一个Binder对象给它
3.ActivityManagerService从ServerService处得到这个Binder对象后,就把它传给MainActivity,即把这个Binder对象作为参数传递给MainActivity内部定义的ServiceConnection对象的onServiceConnected函数;
这样就完成了绑定全部过程。