如果仅仅想知道如何使用TestNG,请阅读官方文档。如果想知道TestNG背后代码是如何运行的,继续往下:
我们运行TestNG从开始执行用例到最终输出报告,是通过一条命令行实现的:
$java org.testng.TestNG testng.xml
这段命令行的背后代码是如何运行的?
1.首先从github/testng下载源码
TestNG使用gradle作为构建工具,可以学习下gradle如何进行java程序编译和打包就可以编译TestNG的源码了
2.查找TestNG源码入口main函数:
java org.testng.TestNG这条命令的意思是执行TestNG的main函数,所以我们首先找到TestNG这个类的main函数定义
执行$java org.testng.TestNG testng1.xml [testng2.xml testng3.xml ...]的背后代码如下:
/**
* The TestNG entry point for command line execution.
*
* @param argv the TestNG command line parameters.
* @throws FileNotFoundException
*/
public static void main(String[] argv) {
TestNG testng = privateMain(argv, null);
System.exit(testng.getStatus());
}
3.TestNG#privateMain核心逻辑如下
public static TestNG privateMain(String[] argv, ITestListener listener) {
TestNG result = new TestNG();
result.addListener((Object)listener);
// 1.解析参数并配置TestNG对象result
CommandLineArgs cla = new CommandLineArgs();
m_jCommander = new JCommander(cla, argv);
validateCommandLineParameters(cla);
result.configure(cla);
// 2.执行用例
result.run();
return result;
}
4.上一步中TestNG#run的代码如下:
/** Run TestNG. */
public void run() {
initializeEverything();
sanityCheck();
runExecutionListeners(true /* start */);
runSuiteAlterationListeners();
m_start = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 执行用例
List suiteRunners = runSuites();
m_end = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 生成用例报告
if (null != suiteRunners) {
generateReports(suiteRunners);
}
runExecutionListeners(false /* finish */);
......
}
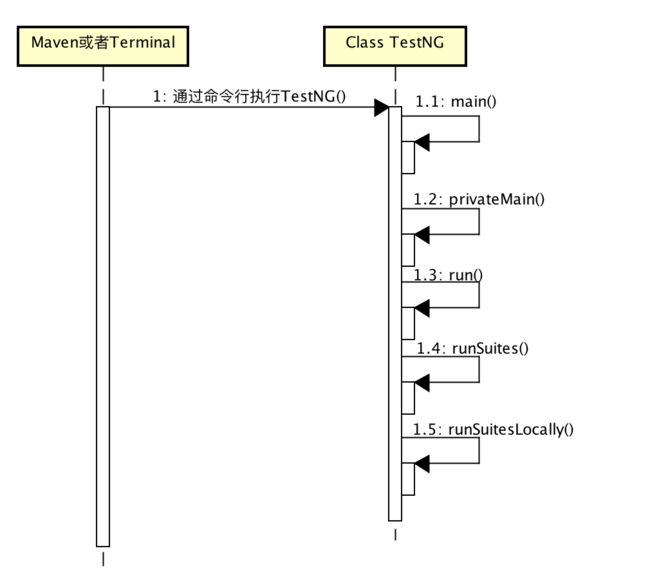
5.看看执行用例的时序图,TestNG#run()最终是调用了TestNG#runSuiteLocally()来实现核心逻辑:
TestNG#runSuiteLocally()的实现如下(去除非核心代码)
public List runSuitesLocally() {
SuiteRunnerMap suiteRunnerMap = new SuiteRunnerMap();
// 判断是否有测试用例,没有报错No test suite found. Nothing to run
if (m_suites.size() > 0) {
// 重要:创建测试套执行器
for (XmlSuite xmlSuite : m_suites) {
createSuiteRunners(suiteRunnerMap, xmlSuite);
}
// 重要:执行测试套
if (m_suiteThreadPoolSize == 1 && !m_randomizeSuites) {
// 串行执行测试套
for (XmlSuite xmlSuite : m_suites) {
// 核心逻辑1:递归执行测试套(先执行子测试套,然后再执行父测试套)
runSuitesSequentially(xmlSuite, suiteRunnerMap, getVerbose(xmlSuite),
getDefaultSuiteName());
}
} else {
// 多线程执行测试套
DynamicGraph suiteGraph = new DynamicGraph<>();
for (XmlSuite xmlSuite : m_suites) {
populateSuiteGraph(suiteGraph, suiteRunnerMap, xmlSuite);
}
IThreadWorkerFactory factory = new SuiteWorkerFactory(suiteRunnerMap,
0 /* verbose hasn't been set yet */, getDefaultSuiteName());
GraphThreadPoolExecutor pooledExecutor =
new GraphThreadPoolExecutor<>("suites", suiteGraph, factory, m_suiteThreadPoolSize,
m_suiteThreadPoolSize, Integer.MAX_VALUE, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue());
Utils.log("TestNG", 2, "Starting executor for all suites");
// 核心逻辑2:并发执行测试套
pooledExecutor.run();
// 等待测试套执行结束
try {
pooledExecutor.awaitTermination(Long.MAX_VALUE, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
pooledExecutor.shutdownNow();
}
catch (InterruptedException handled) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
error("Error waiting for concurrent executors to finish " + handled.getMessage());
}
}
}
else {
setStatus(HAS_NO_TEST);
error("No test suite found. Nothing to run");
usage();
}
return Lists.newArrayList(suiteRunnerMap.values());
}
runSuitesLocally有3个核心逻辑需要详细走读下代码(放在后续SuiteRunner代码走读里研究):
1.createSuiteRunners创建测试套执行器的实现。
2.runSuiteSequentially串行执行测试套的实现。
3.populateSuiteGraph/GraphThreadPoolExecutor等批量并行执行测试套的实现。
同时需要看下m_suites变量是如何初始化的,m_suites变量是读取自testng.xml中的suite节点
6.m_suites的初始化:
回到TestNG#privateMain()中调用的result.run()方法:
/**
* Run TestNG.
*/
public void run() {
initializeEverything();
......
List suiteRunners = runSuites();
......
}
initializeEverything()的实现如下,整体逻辑是:从命令行参数->jar包路径->jar包中找到配置文件并解析出测试套。
public void initializeEverything() {
// The Eclipse plug-in (RemoteTestNG) might have invoked this method already
// so don't initialize suites twice.
if (m_isInitialized) {
return;
}
initializeSuitesAndJarFile();
initializeConfiguration();
initializeDefaultListeners();
initializeCommandLineSuites();
initializeCommandLineSuitesParams();
initializeCommandLineSuitesGroups();
m_isInitialized = true;
}
这里调用了initializeSuitesAndJarFile()实现了m_suites的初始化,去除和m_suites初始化无关的代码后:
public void initializeSuitesAndJarFile() {
if (m_suites.size() > 0) {
//to parse the suite files (), if any
for (XmlSuite s: m_suites) {
for (String suiteFile : s.getSuiteFiles()) {
try {
Collection childSuites;
if (s.getFileName() != null) {
Path rootPath = Paths.get(s.getFileName()).getParent();
try (InputStream is = Files.newInputStream(rootPath.resolve(suiteFile))) {
childSuites = getParser(is).parse();
}
} else {
childSuites = getParser(suiteFile).parse();
}
for (XmlSuite cSuite : childSuites){
cSuite.setParentSuite(s);
s.getChildSuites().add(cSuite);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace(System.out);
}
}
}
return;
}
// m_stringSuites是在TestNG#privateMain()中调用result.configure()里进行初始化,是通过命令行传入的测试套配置xml文件路径
for (String suitePath : m_stringSuites) {
if(LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOGGER.debug("suiteXmlPath: \"" + suitePath + "\"");
}
try {
// 从xml文件中解析测试套
Collection allSuites = getParser(suitePath).parse();
for (XmlSuite s : allSuites) {
// 如果参数中指定了测试用例名称,只执行指定用例
if (m_testNames != null) {
m_suites.add(extractTestNames(s, m_testNames));
}
else {
m_suites.add(s);
}
}
}
catch(IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace(System.out);
} catch(Exception ex) {
// Probably a Yaml exception, unnest it
Throwable t = ex;
while (t.getCause() != null) t = t.getCause();
if (t instanceof TestNGException) throw (TestNGException) t;
else throw new TestNGException(t);
}
}
// 如果测试套是通过命令行传入,优先级要高于在jar包路径下的测试套
if (m_jarPath != null && m_stringSuites.size() > 0) {
StringBuilder suites = new StringBuilder();
for (String s : m_stringSuites) {
suites.append(s);
}
Utils.log("TestNG", 2, "Ignoring the XML file inside " + m_jarPath + " and using "
+ suites + " instead");
return;
}
if (isStringEmpty(m_jarPath)) {
return;
}
// 没有指定xml文件,但是传入了一个jar包,试图从jar包中找到xml配置文件
File jarFile = new File(m_jarPath);
try {
Utils.log("TestNG", 2, "Trying to open jar file:" + jarFile);
boolean foundTestngXml = false;
List classes = Lists.newArrayList();
try (JarFile jf = new JarFile(jarFile)) {
Enumeration entries = jf.entries();
while (entries.hasMoreElements()) {
JarEntry je = entries.nextElement();
if (je.getName().equals(m_xmlPathInJar)) {
Parser parser = getParser(jf.getInputStream(je));
Collection suites = parser.parse();
for (XmlSuite suite : suites) {
// If test names were specified, only run these test names
if (m_testNames != null) {
m_suites.add(extractTestNames(suite, m_testNames));
} else {
m_suites.add(suite);
}
}
foundTestngXml = true;
break;
} else if (je.getName().endsWith(".class")) {
int n = je.getName().length() - ".class".length();
classes.add(je.getName().replace("/", ".").substring(0, n));
}
}
}
if (! foundTestngXml) {
Utils.log("TestNG", 1,
"Couldn't find the " + m_xmlPathInJar + " in the jar file, running all the classes");
XmlSuite xmlSuite = new XmlSuite();
xmlSuite.setVerbose(0);
xmlSuite.setName("Jar suite");
XmlTest xmlTest = new XmlTest(xmlSuite);
List xmlClasses = Lists.newArrayList();
for (String cls : classes) {
XmlClass xmlClass = new XmlClass(cls);
xmlClasses.add(xmlClass);
}
xmlTest.setXmlClasses(xmlClasses);
m_suites.add(xmlSuite);
}
}
catch(IOException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
}
代码中用到的2个变量m_stringSuites和m_jarPath都是通过可选命令行参数传入,它们都是在TestNG#privateMain()中调用result.configure()里进行初始化,具体实现可以看下result.configure()的源码。
命令行参数格式如下:
$java org.testng.TestNG m_stringSuites -testjar m_jarPath
例如:
$java org.testng.TestNG testng.xml
对于TestNG的入口代码的走读就到此结束,接下来会走读TestNG的核心类SuiteRunner,研究下它如何实现执行测试套/测试用例。