基本了解后可以写一个项目来讲SpringMVC和Thymeleaf来简单应用一下。
1.环境准备&需求
1.环境准备:
1.JQuery
2.Bootstrap
3.一些必要的静态资源(放在static文件夹中)
4.静态页面(放在templates中)
5.开发工具idea
6.SpringBoot
2.需求
1)、登录(实现拦截器),实现国际化;
2)、RestfulCRUD:CRUD满足Rest风格;
URI: /资源名称/资源标识 HTTP请求方式区分对资源CRUD操作
| 普通CRUD(uri来区分操作) | RestfulCRUD | |
|---|---|---|
| 查询 | getEmp | emp---GET |
| 添加 | addEmp?xxx | emp---POST |
| 修改 | updateEmp?id=xxx&xxx=xx | emp/{id}---PUT |
| 删除 | deleteEmp?id=1 | emp/{id}---DELETE |
3)、实验的请求架构;
| 实验功能 | 请求URI | 请求方式 |
|---|---|---|
| 查询所有员工 | emps | GET |
| 查询某个员工(来到修改页面) | emp/1 | GET |
| 来到添加页面 | emp | GET |
| 添加员工 | emp | POST |
| 来到修改页面(查出员工进行信息回显) | emp/1 | GET |
| 修改员工 | emp | PUT |
| 删除员工 | emp/1 | DELETE |
3.实现国际化
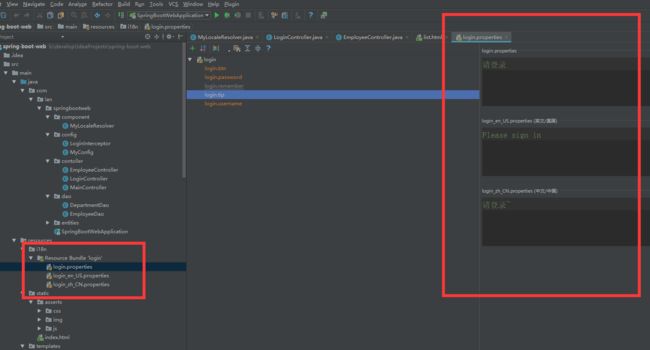
1)、编写国际化配置文件
2)、使用ResourceBundleMessageSource管理国际化资源文件(SpringBoot自动配置好了管理国际化资源文件的组件)
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.messages")
public class MessageSourceAutoConfiguration {
/**
* Comma-separated list of basenames (essentially a fully-qualified classpath
* location), each following the ResourceBundle convention with relaxed support for
* slash based locations. If it doesn't contain a package qualifier (such as
* "org.mypackage"), it will be resolved from the classpath root.
*/
private String basename = "messages";
//我们的配置文件可以直接放在类路径下叫messages.properties;
@Bean
public MessageSource messageSource() {
ResourceBundleMessageSource messageSource = new ResourceBundleMessageSource();
if (StringUtils.hasText(this.basename)) {
//设置国际化资源文件的基础名(去掉语言国家代码的)
messageSource.setBasenames(StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray(
StringUtils.trimAllWhitespace(this.basename)));
}
if (this.encoding != null) {
messageSource.setDefaultEncoding(this.encoding.name());
}
messageSource.setFallbackToSystemLocale(this.fallbackToSystemLocale);
messageSource.setCacheSeconds(this.cacheSeconds);
messageSource.setAlwaysUseMessageFormat(this.alwaysUseMessageFormat);
return messageSource;
}
3)、在页面使用fmt:message取出国际化内容
我们知道取国际化的Thymeleaf的标签是#{}
Signin Template for Bootstrap
-
测试
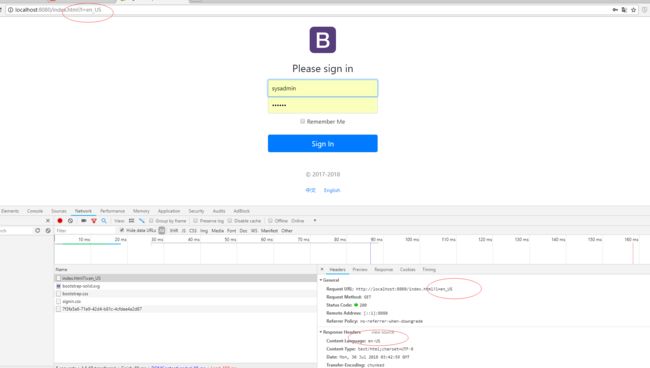
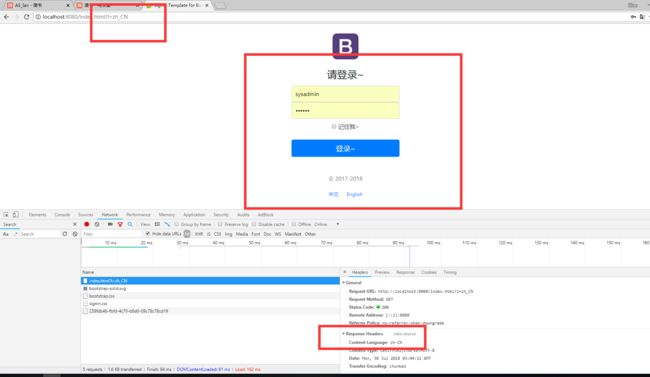
我们看看下面有两个按钮,中文,English;
我们怎样可以做到点击这两个按钮,分别切换到不同语言呢?
我们看看我们点击两个按钮的时候发送的请求;
我们用的原理就是根据请求头带来的区域信息获取Locale进行国际化
SpringBoot提供了国际化的自动配置
原理:
国际化Locale(区域信息对象);LocaleResolver(获取区域信息对象);
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
@ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "spring.mvc", name = "locale")
public LocaleResolver localeResolver() {
if (this.mvcProperties
.getLocaleResolver() == WebMvcProperties.LocaleResolver.FIXED) {
return new FixedLocaleResolver(this.mvcProperties.getLocale());
}
AcceptHeaderLocaleResolver localeResolver = new AcceptHeaderLocaleResolver();
localeResolver.setDefaultLocale(this.mvcProperties.getLocale());
return localeResolver;
}
默认的就是根据请求头带来的区域信息获取Locale进行国际化
4)、点击链接切换国际化
步骤:
1.实现LocaleResovler接口
/**
* 可以在连接上携带区域信息
*/
public class MyLocaleResolver implements LocaleResolver {
@Override
public Locale resolveLocale(HttpServletRequest request) {
String l = request.getParameter("l");
Locale locale = Locale.getDefault();
if(!StringUtils.isEmpty(l)){
String[] split = l.split("_");
locale = new Locale(split[0],split[1]);
}
return locale;
}
@Override
public void setLocale(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Locale locale) {
}
}
@Bean
public LocaleResolver localeResolver(){
return new MyLocaleResolver();
}
}
我们在resolveLocale方法在重写我们的方法,从请求头里面判断使用哪种标准化,然年将locale直接返回
2.改造login.html
加上以上两句话(全文的代码如上)
-
测试
4.实现登录功能
请求方式:post;
url:/user/login
返回:
- 成功:重定向到主页面
-
失败:返回登录界面
实现代码
@Controller
public class LoginController {
@PostMapping(value = "/user/login")
public String login(@RequestParam(name = "username") String username, @RequestParam(name = "password") String password
, HttpServletRequest request, Map map) {
//登录成功
if(!StringUtils.isEmpty(username) && password.equals("12345")) {
HttpSession session = (HttpSession) request.getSession();
session.setAttribute("loginUser",username);
return "redirect:/main.html";
}
//登录失败
map.put("msg","用户密码错误");
return "login";
}
}
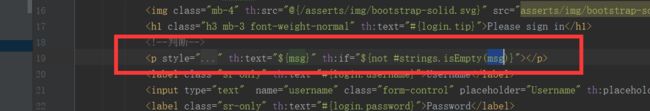
从上面的代码我们可以看到了有一个传递到页面的值msg,这个值如果是错误的话会返回到Login.html页面
那么我们怎么使用呢?如下图:
我们在页面中加上这句话,就可以进行判断
测试的时候我们稍后再测试~
我们再想想,我们学SpringMVC还有Servlet的时候在做登录的时候一般都要写个拦截器?不然直接使用功能,都不要用户登录啦,用户量还怎么来!
下面是实现登录拦截器
SpringBoot实现拦截器也很简单,基本步骤和SpringMVC差不多,都是:
1.实现HandlerInterceptor接口
2.注册,并设置要拦截的路径
public class LoginInterceptor implements HandlerInterceptor {
//在目标方法执行之前
@Override
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception {
HttpSession session = request.getSession();
if(session.getAttribute("loginUser") == null) {
request.setAttribute("msg","请先登录");
//请求转发,跳到登录界面
request.getRequestDispatcher("/index.html").forward(request,response);
//不放行
return false;
}
//已经登录
//放行,看看账号密码对不对
return true;
}
@Override
public void postHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, ModelAndView modelAndView) throws Exception {
}
@Override
public void afterCompletion(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, Exception ex) throws Exception {
}
}
在配置类中把拦截器加进去
@Configuration
public class MyConfig extends WebMvcConfigurerAdapter {
//设置映射的路径
//设置默认首页
@Override
public void addViewControllers(ViewControllerRegistry registry) {
registry.addViewController("/").setViewName("login");
registry.addViewController("/index.html").setViewName("login");
//如果登录成功的话就跳到这里
registry.addViewController("/main.html").setViewName("dashboard");
}
@Override
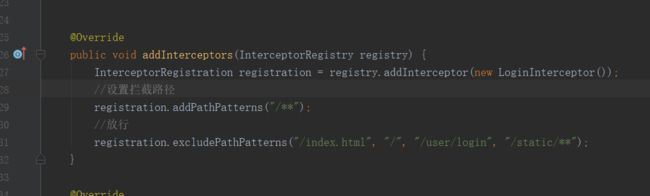
public void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) {
InterceptorRegistration registration = registry.addInterceptor(new LoginInterceptor());
//设置拦截路径
registration.addPathPatterns("/**");
//放行
registration.excludePathPatterns("/index.html", "/", "/user/login", "/static/**");
}
@Override
public void addResourceHandlers(ResourceHandlerRegistry registry) {
registry.addResourceHandler("/static/**").addResourceLocations("classpath:/static/");
}
@Bean
public MyLocaleResolver localeResolver() {
return new MyLocaleResolver();
}
}
-
测试
我们想直接访问main.html结果直接被拦截下来了
账号密码正确