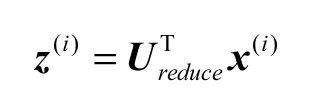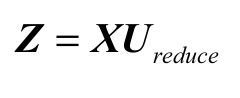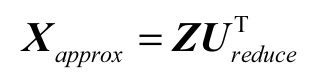PCA降维
一、算法原理
-
降维算法
-
还原算法
二、算法实现
import numpy as np
A = np.array([
[3, 2000],
[2, 3000],
[4, 5000],
[5, 8000],
[1, 2000]
])
# 对数据进行归一化操作
mean = np.mean(A, axis=0)
norm = A - mean
scope = np.max(norm, axis=0) - np.min(norm, axis=0)
norm = norm / scope
# 按协方差矩阵进行奇异值分解
U, S, V = np.linalg.svd(np.dot(norm.T, norm))
U_reduce = U[:, 0].reshape(len(U), 1)
# 降维运算
R = np.dot(norm, U_reduce)
# 还原运算
Z = np.dot(R, U_reduce.T)
np.multiply(Z, scope) + mean
三、scikit-learn PCA
from sklearn.decomposition import PCA
from sklearn.pipeline import Pipeline
from sklearn.preprocessing import MinMaxScaler
def std_PCA(**argv):
scalar = MinMaxScaler()
pca = PCA(**argv)
pipeline = Pipeline([('scalar', scalar), ('pca', pca)])
return pipeline
# 规定保留的轴的数量
pca = std_PCA(n_components=1)
R2 = pca.fit_transform(A)
# 还原数据
pca.inverse_transform(R2)
四、PCA降噪
1.加载数据集
from sklearn import datasets
digits = datasets.load_digits()
X = digits.data
y = digits.target
2.人工加入噪声
def plot_digits(data):
fig, axes = plt.subplots(10, 10, figsize=(10, 10),
subplot_kw={'xticks':[], 'yticks':[]},
gridspec_kw=dict(hspace=0.1, wspace=0.1))
for i, ax in enumerate(axes.flat):
ax.imshow(data[i].reshape(8, 8),cmap='binary', interpolation='nearest',clim=(0, 16))
plt.show()
# 人工加入噪声
noisy_digits = X + np.random.normal(0, 4, size=X.shape)
example_digits = noisy_digits[y==0,:][:10]
for num in range(1,10):
example_digits = np.vstack([example_digits, noisy_digits[y==num,:][:10]])
plot_digits(example_digits)
3.降噪
pca = PCA(0.5).fit(noisy_digits)
components = pca.transform(example_digits)
filtered_digits = pca.inverse_transform(components)
plot_digits(filtered_digits)