Android 的线程分为主线程和子线程。
主线程
更新 UI子线程
执行耗时操作AsyncTask
封装了线程池和 Handler,主要为了方便在子线程中更新 UI。IntentService
一个服务,系统对其进行了封装,IntentService 内部采用 HandlerThread 来执行任务,执行完会自动退出。HandlerThread
一种具有消息循环的线程,它的内部可以使用 Handler。
在操作系统中,线程是操作系统调度的最小单元,线程的创建和销毁都会有相应的开销。线程池可以缓存一定数量的线程,通过线程池可以避免频繁创建和销毁线程造成的开销。
11.1 主线程和子线程
默认一个进程中只有一个主线程,其他都是子线程。
11.2 Android 中的线程形态
11.2.1 AsyncTask
public abstract class AsyncTask
onPreExecute:在主线程执行,在异步任务执行之前被调用
doInBackground:在线程池中执行,用于执行异步任务,params 表示异步任务输入的参数,可以通过 publishProgress 方法调用 onProgressUpdate 方法来更新进度条。
onProgressUpdate:在主线程执行,当后台任务的执行进度发生改变时调用;
onPreExecute:在主线程执行,异步任务执行后调用,result 是doInBackground 的返回值。
AsyncTask 在具体的使用过程中也是有一些条件限制的,主要有如下几点:
(1)AysncTask 的类必须在主线程中加载,这就意味着第一次访问 AsyncTask 必须在主线程,这个过程在 Android 4.0以上已经被系统自动完成了。
(2)AsyncTask 的对象必须在主线程中创建。
(3)execute 方法必须在 UI 线程调用。
(4)不要在程序中直接调用 onPreExecute、onPreExecute、doInBackground、onProgressUpdate 方法。
(5)一个 AsyncTask 对象只能执行一次,即只能调用一次 execute 方法,否则会报运行时异常。
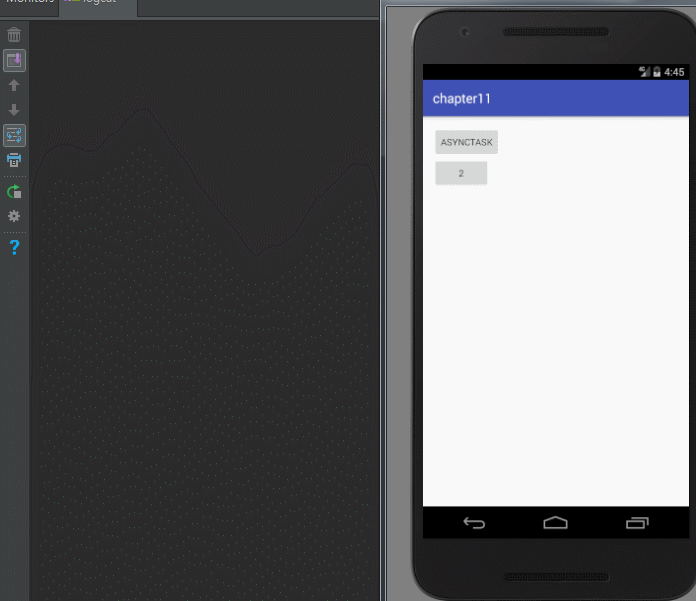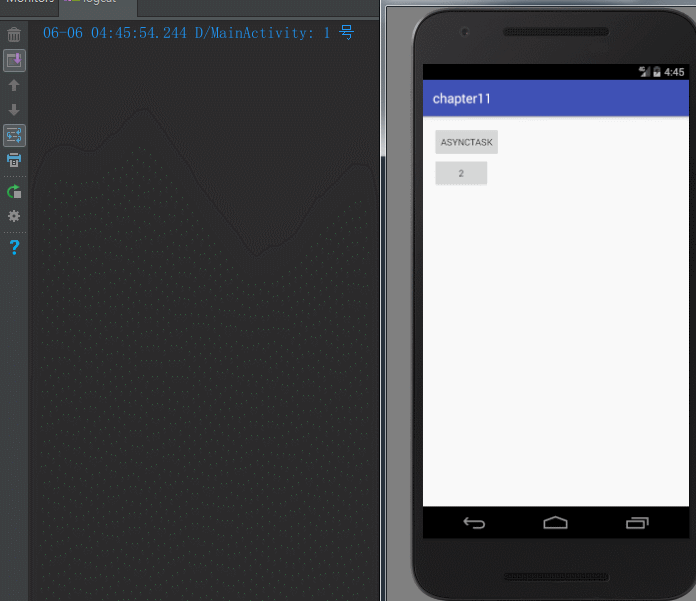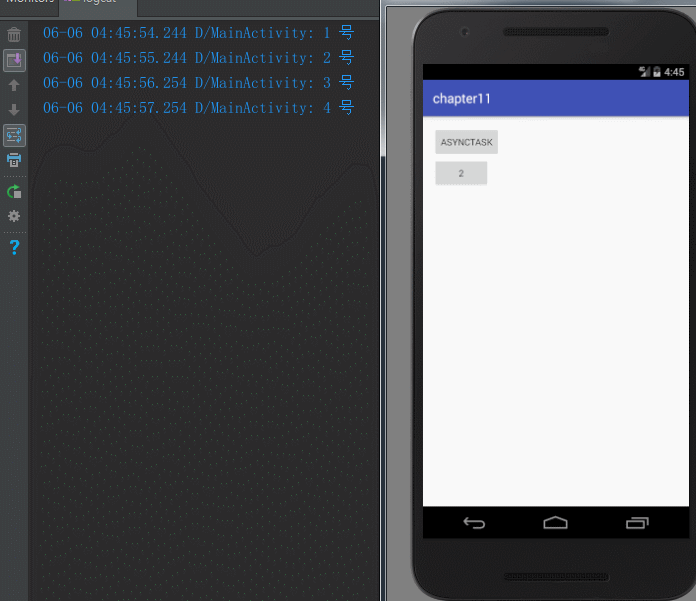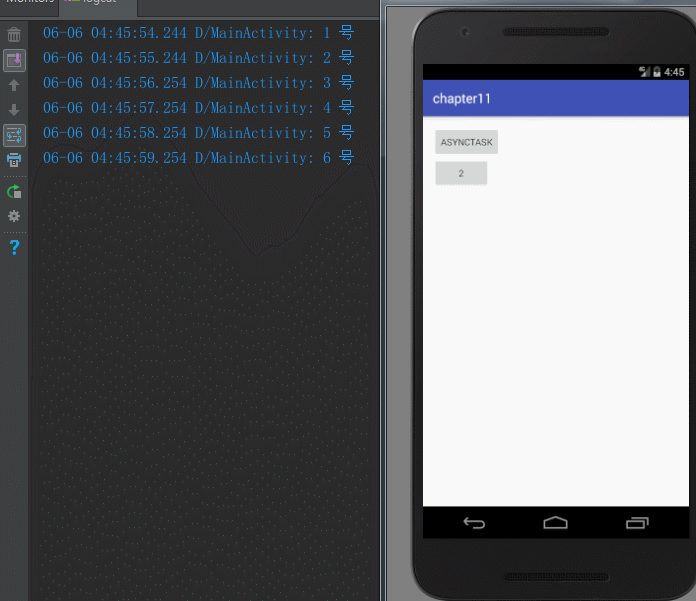
(6)Android 3.0 开始,AsyncTask 采用一个线程来执行串行任务。
public void click(View view) {
new MyAsyncTask("1 号").execute();
new MyAsyncTask("2 号").execute();
new MyAsyncTask("3 号").execute();
new MyAsyncTask("4 号").execute();
new MyAsyncTask("5 号").execute();
new MyAsyncTask("6 号").execute();
}
private static class MyAsyncTask extends AsyncTask {
public String mName = "AsyncTask";
public MyAsyncTask(String name) {
super();
mName = name;
}
@Override
protected String doInBackground(String... params) {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return mName;
}
@Override
protected void onPostExecute(String s) {
super.onPostExecute(s);
Log.d(TAG, s);
}
}
11.2.4 IntentService
IntentService 处理后台任务是排队执行的,执行顺序就是发起请求的顺序。
IntentService 继承 Service,所以它能够运行在后台。
public class LocalIntentService extends IntentService {
public static final String TAG = "LocalIntentService";
public LocalIntentService() {
super(TAG);
}
@Override
protected void onHandleIntent(Intent intent) {
String action = intent.getStringExtra("task_action");
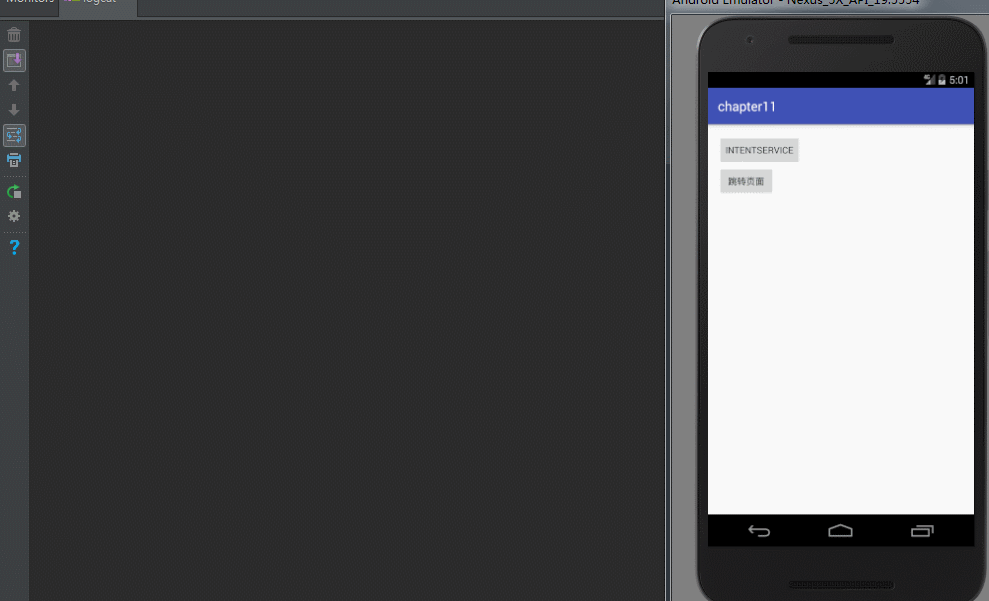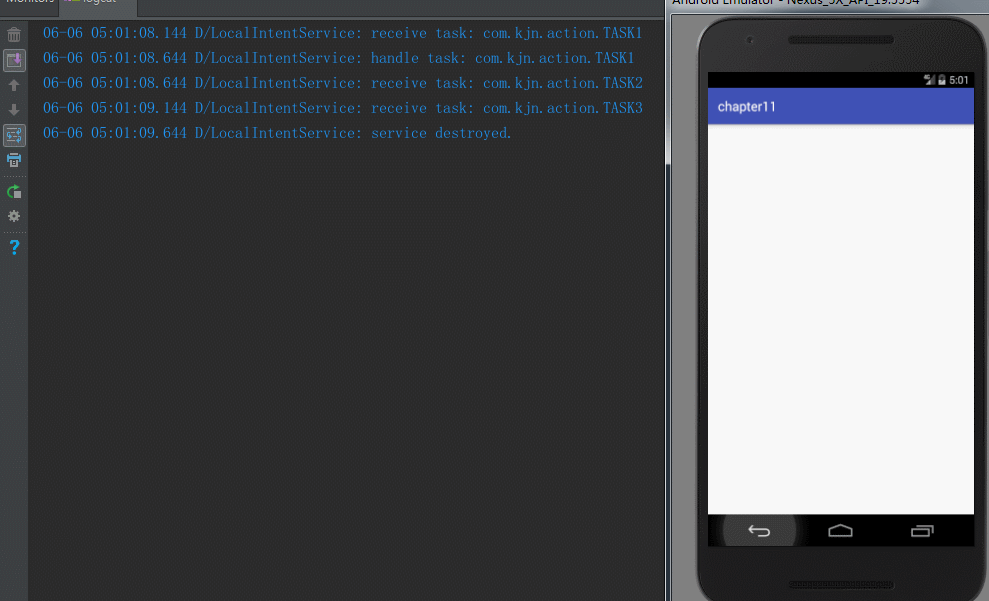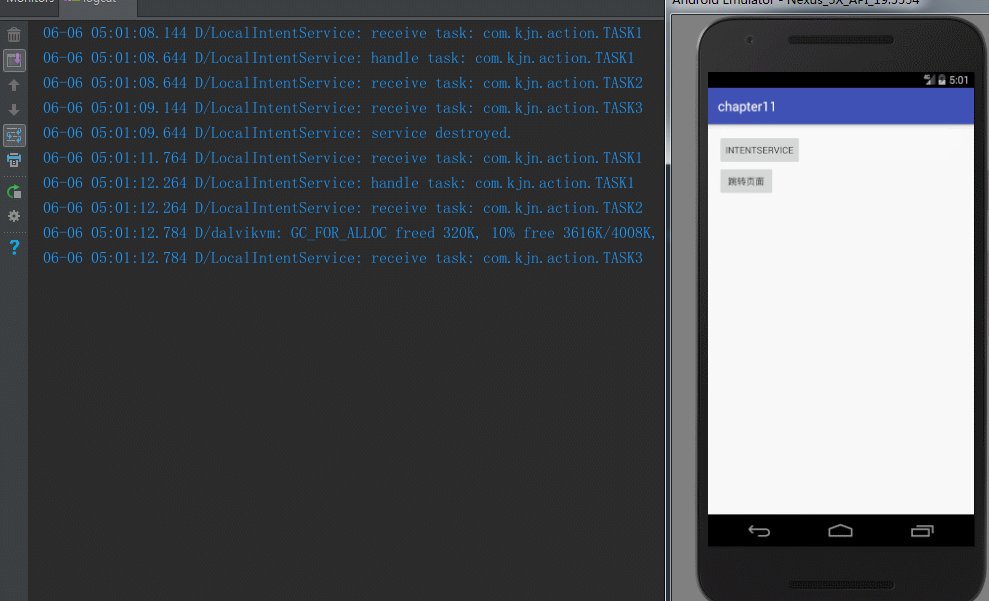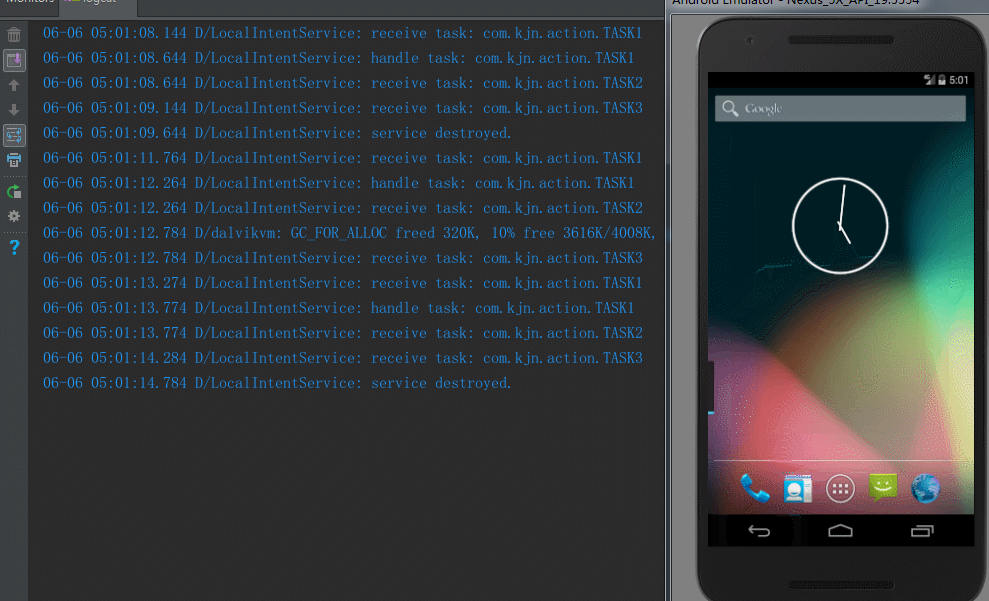
Log.d(TAG, "receive task: " + action);
SystemClock.sleep(500);
if ("com.kjn.action.TASK1".equals(action)) {
Log.d(TAG, "handle task: " + action);
}
}
@Override
public void onDestroy() {
Log.d(TAG, "service destroyed.");
super.onDestroy();
}
}
点击事件
public void click(View view) {
if (view.getId() == R.id.btn1) {
start(this,"com.kjn.action.TASK1");
start(this,"com.kjn.action.TASK2");
start(this,"com.kjn.action.TASK3");
} else if (view.getId() == R.id.btn2) {
Intent intent = new Intent(MainActivity.this, SecondActivity.class);
startActivity(intent);
}
}
public static void start(Context context,String action) {
Intent starter = new Intent(context, LocalIntentService.class);
starter.putExtra("task_action",action);
context.startService(starter);
}
11.3 Android 中的线程池
Android 中的线程池都是直接或者间接通过配置 ThreadPoolExecutor 来实现的。
线程池的优点:
(1)重用线程池中的线程,避免因为线程的创建和销毁所带来的性能开销。
(2)能有效控制线程池的最大并发数,避免大量的线程之间因互相抢占系统资源而导致的阻塞现象。
(3)能够对线程进行简单的管理,并提供定时执行以及指定间隔循环执行等功能。
11.3.1 ThreadPoolExecutor
public ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize,
int maximumPoolSize,
long keepAliveTime,
TimeUnit unit,
BlockingQueue workQueue,
ThreadFactory threadFactory)
- corePoolSize:
线程池的核心线程数,默认情况下,核心线程会在线程池中一直存活,如果将 ThreadPoolExecutor 的 allowCoreThreadTimeOut 属性设置为 true,那么闲置的核心线程在等待新任务到来时会有超时策略,这个时间间隔由 keepAliveTime 所指定,,当等待时间超过 keepAliveTime 所指定的时长后,核心线程就会被终止。
- maximumPoolSize:
线程池所能容纳的最大线程数,超出后,后续的新任务会被阻塞。
- keepAliveTime:
非核心线程闲置时的超时时长,超过这个时长,非核心线程就会被回收。当 ThreadPoolExecutor 的 allowCoreThreadTimeOut 属性设置为 true时,同样作用于核心线程。
unit:用于指定 keepAliveTime 参数的时间单位这是一个枚举,常用的有:
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS:毫秒
TimeUnit.SECONDS:秒
TimeUnit.MINUTES:分钟
workQueue:
线程池中的任务队列,通过 execute 方法提交的 Runnable 对象会存储在这个参数中。
- threadFactory:
线程工厂,为线程池提供创建新线程的功能,ThreadFactory 是一个接口,它只有一个方法: Thread newThread(Runnable r);
ThreadPoolExecutor 执行任务时大致遵循如下规则:
(1)如果线程池中的线程数量未达到核心线程的数量,那么会直接启动一个核心线程来执行任务。
(2)如果线程池中的线程数量已经达到了或者超过了核心线程的数量,那么任务会被插入到任务队列中排队等待执行。
(3)如果在步骤(2)中无法将任务插入到任务队列中,这往往是由于任务队列已满,这个时候如果线程数量未达到线程池规定的最大值,那么会立刻启动一个非核心线程来执行任务。
(4)如果步骤(3)中线程数量已经达到线程池规定的最大值,那么就拒绝执行任务,ThreadPoolExecutor 会调用 RejectedExecutionHandler 的 rejectedExecution 方法来通知调用者。
配置参看 AsyncTask :
public abstract class AsyncTask {
private static final String LOG_TAG = "AsyncTask";
// CPU 数量
private static final int CPU_COUNT = Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors();
// 最大线程数 CPU 数量 +1
private static final int CORE_POOL_SIZE = CPU_COUNT + 1;
// 线程池的最大线程数为核心数的 2 倍 +1;
private static final int MAXIMUM_POOL_SIZE = CPU_COUNT * 2 + 1;
// 超时时间为 1 秒
private static final int KEEP_ALIVE = 1;
private static final ThreadFactory sThreadFactory = new ThreadFactory() {
private final AtomicInteger mCount = new AtomicInteger(1);
public Thread newThread(Runnable r) {
return new Thread(r, "AsyncTask #" + mCount.getAndIncrement());
}
};
// 任务队列的容量为 128。
private static final BlockingQueue sPoolWorkQueue =
new LinkedBlockingQueue(128);
public static final Executor THREAD_POOL_EXECUTOR
= new ThreadPoolExecutor(CORE_POOL_SIZE, MAXIMUM_POOL_SIZE, KEEP_ALIVE,
TimeUnit.SECONDS, sPoolWorkQueue, sThreadFactory);
核心线程数等于 CPU 核心数 +1;
线程池的最大线程数为核心数的 2 倍 +1;
核心线程无超时机制,非核心线程在闲置时的超时时间为 1 秒;
任务队列的容量为 128。
11.3.2 线程池的分类
常见的有四类线程池:
(1)FixedThreadPool:
它是一种只有核心线程并且线程数量固定的线程池,他们不会被回收,除非线程池被关闭了。因为是核心线程,它能更加快速地响应外界的请求,没有超时机制,任务队列也没有大小限制。
Runnable command = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
SystemClock.sleep(2000);
}
};
// 通过 Executors 的 newFixedThreadPool 方法来创建。
ExecutorService fixedThreadPool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(4);
fixedThreadPool.execute(command);
public class Executors {
public static ExecutorService newFixedThreadPool(int nThreads) {
return new ThreadPoolExecutor(nThreads, nThreads,
0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue());
}
...
(2)CachedThreadPool
核心线程为 0 ,最大线程数为 Integer.MAX_VALUE,所以它只有非核心线程,超时时长为 60 秒,超过 60 秒闲置就会被回收。CachedThreadPool 的任务队列相当于一个空集合,这将导致任何任务都会立即被执行。CachedThreadPool 比较适合执行大量的耗时较少的任务,当闲置时,线程池中的线程都会因为超时而被停止,这时它几乎不占用任何系统资源。
ExecutorService cachedThreadPool = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
cachedThreadPool.execute(command);
public static ExecutorService newCachedThreadPool() {
return new ThreadPoolExecutor(0, Integer.MAX_VALUE,
60L, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new SynchronousQueue());
}
(3)ScheduledThreadPool
它的核心线程数是固定的,非核心线程数 Integer.MAX_VALUE,超时时间 0 ,闲置就会直接回收非核心线程,这类线程主要用于执行定时任务和具有固定周期的重复任务。
ScheduledExecutorService scheduledThreadPool = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(4);
// 2000ms后执行command
scheduledThreadPool.schedule(command, 2000, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
// 延迟10ms后,每隔1000ms执行一次command
scheduledThreadPool.scheduleAtFixedRate(command, 10, 1000, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
public static ScheduledExecutorService newScheduledThreadPool(int corePoolSize) {
return new ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(corePoolSize);
}
public ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize) {
super(corePoolSize, Integer.MAX_VALUE, 0, NANOSECONDS,
new DelayedWorkQueue());
}
// super 调用构造方法
public ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize,
int maximumPoolSize,
long keepAliveTime,
TimeUnit unit,
BlockingQueue workQueue) {
this(corePoolSize, maximumPoolSize, keepAliveTime, unit, workQueue,
Executors.defaultThreadFactory(), defaultHandler);
}
(4)SingleThreadExecutor
这类线程池内部只有一个核心线程,它确保所有的任务都在同一个线程中按顺序执行,这使得这些任务之间不需要处理线程同步的问题。
ExecutorService singleThreadExecutor = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
singleThreadExecutor.execute(command);
public static ExecutorService newSingleThreadExecutor() {
return new FinalizableDelegatedExecutorService
(new ThreadPoolExecutor(1, 1,
0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue()));
}
本章源码:https://github.com/singwhatiwanna/android-art-res/tree/master/Chapter_11