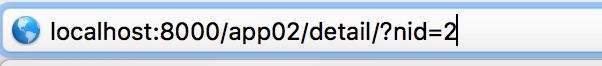
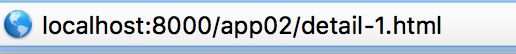
Django项目中的URL声明;Django站点的目录。称之为URL转发器。
基于正则表达式的url。
url(r'^detail-(\d+).html/', views.detail),
匹配:detail-1.html, detail-21.html, detail-3.html, 等等这样的。
通过include对路由分发
1)在设置目录的urls.py中:
需要导入include,和使用include(app名.urls)。
from django.conf.urls import url, include
urlpatterns = [
url(r'^app01/', include("app01.urls")),
]
2)在app包下建立urls.py模块。
urls.py里面需要和设置目录下的urls类似。
默认值:
命名空间:
分页页面:
浏览器中显示:
1)形式1
urls.py中:
class Index(View):
def dispatch(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
result = super(Index, self).dispatch(request, *args, **kwargs)
return result
def get(self, request):
return render(request, 'app02/index.html', {'user_list':USER_LIST})
def post(self, request):
return render(request, 'app02/index.html', {'user_list':USER_LIST})
class Detail(View):
def dispatch(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
result = super(Detail, self).dispatch(request, *args, **kwargs)
return result
def get(self, request):
print (request.GET.get('nid'))
return render(request, 'app02/detail.html')
def post(self, request):
return render(request, 'app02/detail.html')
模板中:
app02 index
{% for dict in user_list %}
{% for key,value in dict.items %}
{{value}}
{% endfor %}
{% endfor %}
如果GET和POST都需要的数据,我们使用全局变量关键字global:
class Detail(View):
def dispatch(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
nid = request.GET.get('nid')
# 全局变量
global DETAIL_INFO
DETAIL_INFO = {"name":"liao"+str(nid), "email":"email"+str(nid)}
result = super(Detail, self).dispatch(request, *args, **kwargs)
return result
def get(self, request):
return render(request, 'app02/detail.html', {'detail_info':DETAIL_INFO})
def post(self, request):
return render(request, 'app02/detail.html', {'detail_info':DETAIL_INFO})
2)形式2
动态路由(1对多)
请求时候:
{{value}}
urls.py中的匹配:
urlpatterns = [
url(r'^detail-(\d+).html', views.Detail.as_view()),
]
views.py中:
class Detail(View):
def dispatch(self, request, nid, *args, **kwargs):
#return HttpResponse(nid)
# 全局变量
global DETAIL_INFO
DETAIL_INFO = {"name":"liao"+str(nid), "email":"email"+str(nid)}
result = super(Detail, self).dispatch(request, *args, **kwargs)
return result
def get(self, request):
return render(request, 'app02/detail.html', {'detail_info':DETAIL_INFO})
def post(self, request):
return render(request, 'app02/detail.html', {'detail_info':DETAIL_INFO})
3)在url中传递多个参数
urls.py:
urlpatterns = [
url(r'^detail-(\d+)-(\d+).html', views.Detail.as_view()),
]
在views.py中:
class Detail(View):
# 就需要加 nid,uid 两个参数了。参数名可以自取
def dispatch(self, request, nid, uid, *args, **kwargs):
或者不需要加
4)url分组
urls.py:
urlpatterns = [
url(r'^detail-(?P\d+)-(?P\d+).html', views.Detail.as_view()),
]
那么在views.py中就不需要管理参数顺序了:
class Detail(View):
def dispatch(self, request, nid, uid, *args, **kwargs):
5)url的name
在urls.py中,url函数可接收第三个参数name
url(r'^login123/', app01_v.login, name='login'),
在form表单中可以:
在url中设置参数名:
urls.py:
url(r'^user_detail-(?P\d+)') # 这里的\d+匹配任意数字
在views.py中就可以取出参数:
def user_detail(request, nid):
pass
移除url的硬编码,urls的name
urls.py:
url(r'^music/(?P\d+)/', music_view.detail, name="detail"),
templtes中:
album.title
经验
1.url传递参数
在urls.py中:
url(r'^user_detail-(?P\d+)-(?P\d+).html', views.user_detail)
在views.py中:
def user_detail(request, *args, **kwargs):
print (kwargs) # 得到: {'nid':x, 'mid':x}
2.正则表达式,匹配a-z 、0-9 、\这三种类型的正则:
r'^delete_server_snapshot_(?P[a-z0-9\-]+)/',
注意[a-z0-9\-]与\d+的区别。
3.[ ] 和 slug:
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/47047843/whats-the-difference-when-add-to-regular-expressions