Kubernetes集群一经启动,就会有一个缺省的Service:kubernetes,这个服务对应的endpoints就是我们启动的API Server进程,这个服务是不需要手工创建,我们可以删除这个service,但是可以观察到它会立即重新生成,这个service的目的是什么?它又是怎么生成的呢?
在K8S集群中观察
首先,在CreateKubeAPIServerConfig函数中,会根据运行参数调用master.DefaultServiceIPRange函数拿出第一个ip作为API Server的Service IP地址,保存在master.Config的APIServerServiceIP成员中,同时指定APIServerServicePort:443。
下面我们观察一下线上的数据。
yuxianbing@ubuntu:~$ kubectl get service
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
kubernetes ClusterIP 10.254.0.1 443/TCP 38d
yuxianbing@ubuntu:~$ kubectl get endpoints
NAME ENDPOINTS AGE
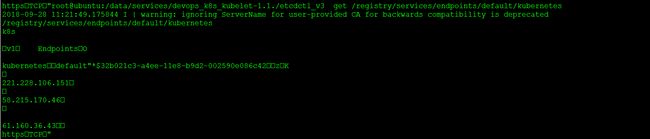
kubernetes 221.228.106.151:6443,58.215.170.46:6443,61.160.36.43:6443 38d
下面是从etcd中读取到的kubernetes服务的基本信息以及Endpoints信息:
从上面数据中可以看出,Kubernetes的ClusterIP为10.254.0.1,Endpoints就是我们启动的API Server所在IP地址。那这些IP是如何写到对应的ETCD目录中的呢?
GenericAPIServer的启动中的辅助功能
这里就要研究一下GenericAPIServer的启动过程中的另外一项工作,PostStartHook/PreShutdownHook:
master.Config {
ExtraConfig: master.ExtraConfig{
......
EnableCoreControllers: true,
......
}
}
func (m *Master) InstallLegacyAPI(c *completedConfig, restOptionsGetter generic.RESTOptionsGetter, legacyRESTStorageProvider corerest.LegacyRESTStorageProvider) {
......
if c.ExtraConfig.EnableCoreControllers {
controllerName := "bootstrap-controller"
coreClient := coreclient.NewForConfigOrDie(c.GenericConfig.LoopbackClientConfig)
bootstrapController := c.NewBootstrapController(legacyRESTStorage, coreClient, coreClient, coreClient)
m.GenericAPIServer.AddPostStartHookOrDie(controllerName, bootstrapController.PostStartHook)
m.GenericAPIServer.AddPreShutdownHookOrDie(controllerName, bootstrapController.PreShutdownHook)
}
......
}
在Master的GenericAPIServer中添加了PostStartHook和ShutdownHook操作。在操作中,会执行启动和停止BootstrapController。
Controller
本节专门分析上面的BootstrapController,它与集群中的kube-controller没有任何关系,属于API Server的一部分代码,具体的代码在:k8s.io/kubernetes/pkg/master/controller.go中,具体的结构名为Controller。
// Controller is the controller manager for the core bootstrap Kubernetes
// controller loops, which manage creating the "kubernetes" service, the
// "default", "kube-system" and "kube-public" namespaces, and provide the IP
// repair check on service IPs
type Controller struct {
ServiceClient coreclient.ServicesGetter
NamespaceClient coreclient.NamespacesGetter
EventClient coreclient.EventsGetter
ServiceClusterIPRegistry rangeallocation.RangeRegistry
ServiceClusterIPInterval time.Duration
ServiceClusterIPRange net.IPNet
ServiceNodePortRegistry rangeallocation.RangeRegistry
ServiceNodePortInterval time.Duration
ServiceNodePortRange utilnet.PortRange
EndpointReconciler reconcilers.EndpointReconciler
EndpointInterval time.Duration
SystemNamespaces []string
SystemNamespacesInterval time.Duration
PublicIP net.IP // API Server绑定的IP,这个IP会作为kubernetes service的Endpoint的IP
// ServiceIP indicates where the kubernetes service will live. It may not be nil.
ServiceIP net.IP // 按照我们的启动参数,这里是:10.254.0.1
ServicePort int // 按照我们的启动参数,这里是:643
ExtraServicePorts []api.ServicePort // 为空
ExtraEndpointPorts []api.EndpointPort // 为空
PublicServicePort int // 按照我们的启动参数,这里是6443
KubernetesServiceNodePort int // 缺省是基于ClusterIP启动模式,那么这里为0
runner *async.Runner
}
Controller的主要功能:
- 创建kubernetes服务
- 创建default、kube-system和kube-public名字空间
- 并且基于Service的Cluster IP提供IP修复检查功能
Controller中的结构体中的几个重要的变量:
ServiceIP:是kubernetes对外服务的Cluster IP,按照启动样例,为:10.254.0.1
这个IP,是基于启动参数:service-cluster-ip-range而来,API Server启动过程中,会从中获取第一个Cluster IP网段中获取第一个IP,作为kubernetes这个服务的Cluster IP。
--service-cluster-ip-range ipNet A CIDR notation IP range from which to assign service cluster IPs. This must not overlap with any IP ranges assigned to nodes for pods.ServicePort:是kubernetes对外服务的Port,按照启动样例,为:443,目前是在创建master.Config时写死的,从master.ExtraConfig.APIServerServicePort中赋值过来
PublicServicePort:基于启动参数secure-port来指定,缺省为6443。
--secure-port int The port on which to serve HTTPS with authentication and authorization. If 0, don't serve HTTPS at all. (default 6443)PublicIP:apiserver在集群中的服务IP,参考下面的参数
--advertise-address ip The IP address on which to advertise the apiserver to members of the cluster. This address must be reachable by the rest of the cluster. If blank, the --bind-address will be used. If --bind-address is unspecified, the host's default interface will be used.
所以PublicIP的来源顺序:advertise-address > bind-address > default interface。
代码见:ServerRunOptions.DefaultAdvertiseAddress函数内容。一般是找到ipv4,ipv6第一个合格的IP。
- EndpointReconciler :负责Service的Endpoint的协调处理,还有一个成员EndpointInterval指定了对Endpoint进行协调处理的周期,所以,这个操作是周期性处理的。下面来看看这个成员是如何被赋值的?
func (c *completedConfig) NewBootstrapController(legacyRESTStorage corerest.LegacyRESTStorage, serviceClient coreclient.ServicesGetter, nsClient coreclient.NamespacesGetter, eventClient coreclient.EventsGetter) *Controller {
return &Controller{
......
EndpointReconciler: c.ExtraConfig.EndpointReconcilerConfig.Reconciler,
......
}
}
见k8s.io/kubernetes/pkg/master/master.go中
func (cfg *Config) Complete(informers informers.SharedInformerFactory) CompletedConfig {
......
if c.ExtraConfig.EndpointReconcilerConfig.Reconciler == nil {
c.ExtraConfig.EndpointReconcilerConfig.Reconciler = cfg.createEndpointReconciler()
}
......
}
func (c *Config) createEndpointReconciler() reconcilers.EndpointReconciler {
glog.Infof("Using reconciler: %v", c.ExtraConfig.EndpointReconcilerType)
switch c.ExtraConfig.EndpointReconcilerType {
// there are numerous test dependencies that depend on a default controller
case "", reconcilers.MasterCountReconcilerType:
return c.createMasterCountReconciler() // 缺省情况,见NewServerRunOptions函数
case reconcilers.LeaseEndpointReconcilerType:
return c.createLeaseReconciler()
case reconcilers.NoneEndpointReconcilerType:
return c.createNoneReconciler()
default:
glog.Fatalf("Reconciler not implemented: %v", c.ExtraConfig.EndpointReconcilerType)
}
return nil
}
可以通过endpoint-reconciler-type来指定endpoint的协调处理类型,缺省是MasterCountReconcilerType类型,这里我们就分析这种类型,如下所示,具体的类型为:masterCountEndpointReconciler:
func (c *Config) createMasterCountReconciler() reconcilers.EndpointReconciler {
endpointClient := coreclient.NewForConfigOrDie(c.GenericConfig.LoopbackClientConfig)
return reconcilers.NewMasterCountEndpointReconciler(c.ExtraConfig.MasterCount, endpointClient)
}
Controller的启动
Controller的启动代码如下:
func (c *Controller) Start() {
if c.runner != nil {
return
}
repairClusterIPs := servicecontroller.NewRepair(c.ServiceClusterIPInterval, c.ServiceClient, c.EventClient, &c.ServiceClusterIPRange, c.ServiceClusterIPRegistry)
repairNodePorts := portallocatorcontroller.NewRepair(c.ServiceNodePortInterval, c.ServiceClient, c.EventClient, c.ServiceNodePortRange, c.ServiceNodePortRegistry)
// run all of the controllers once prior to returning from Start.
if err := repairClusterIPs.RunOnce(); err != nil {
// If we fail to repair cluster IPs apiserver is useless. We should restart and retry.
glog.Fatalf("Unable to perform initial IP allocation check: %v", err)
}
if err := repairNodePorts.RunOnce(); err != nil {
// If we fail to repair node ports apiserver is useless. We should restart and retry.
glog.Fatalf("Unable to perform initial service nodePort check: %v", err)
}
// Service definition is reconciled during first run to correct port and type per expectations.
if err := c.UpdateKubernetesService(true); err != nil {
glog.Errorf("Unable to perform initial Kubernetes service initialization: %v", err)
}
c.runner = async.NewRunner(c.RunKubernetesNamespaces, c.RunKubernetesService, repairClusterIPs.RunUntil, repairNodePorts.RunUntil)
c.runner.Start()
}
整个逻辑比较清晰,它主要四个内容:修复ClusterIP、修复NodePort、更新Kubernetes服务、创建几个default/kube-system/kube-public名字空间。启动过程中,首先在第一次启动的时候完成一次ClusterIP、NodePort和Kubernets服务的处理,然后异步循环运行上面的4个工作。
- 创建缺省名字空间的最终代码如下所示:
func createNamespaceIfNeeded(c coreclient.NamespacesGetter, ns string) error {
if _, err := c.Namespaces().Get(ns, metav1.GetOptions{}); err == nil {
// the namespace already exists
return nil
}
newNs := &api.Namespace{
ObjectMeta: metav1.ObjectMeta{
Name: ns,
Namespace: "",
},
}
_, err := c.Namespaces().Create(newNs)
if err != nil && errors.IsAlreadyExists(err) {
err = nil
}
return err
}
- 更新kubernetes服务的代码
func (c *Controller) UpdateKubernetesService(reconcile bool) error {
// Update service & endpoint records.
// TODO: when it becomes possible to change this stuff,
// stop polling and start watching.
// TODO: add endpoints of all replicas, not just the elected master.
if err := createNamespaceIfNeeded(c.NamespaceClient, metav1.NamespaceDefault); err != nil {
return err
}
servicePorts, serviceType := createPortAndServiceSpec(c.ServicePort, c.PublicServicePort, c.KubernetesServiceNodePort, "https", c.ExtraServicePorts)
if err := c.CreateOrUpdateMasterServiceIfNeeded(kubernetesServiceName, c.ServiceIP, servicePorts, serviceType, reconcile); err != nil {
return err
}
endpointPorts := createEndpointPortSpec(c.PublicServicePort, "https", c.ExtraEndpointPorts)
if err := c.EndpointReconciler.ReconcileEndpoints(kubernetesServiceName, c.PublicIP, endpointPorts, reconcile); err != nil {
return err
}
return nil
}
这里我们继续分析一下基于MasterCount类型的EndpointReconcier的ReconcileEndpoints方法。ReconcileEndpoints为指定service设置endpoints,它期望这些endpoints只被自己管理。
需求:
- 所有apiserver必须为他们的服务使用相同的端口;
- 所有apiserver必须使用且只使用ReconcoleEndpoints来管理服务的endpoints
- 所有apiserver必须知道,并且在apiservers期望运行数量(c.masterCount)达成一致
- 所有apiserver都周期性的运行ReconcileEndpoints
// ReconcileEndpoints sets the endpoints for the given apiserver service (ro or rw).
// ReconcileEndpoints expects that the endpoints objects it manages will all be
// managed only by ReconcileEndpoints; therefore, to understand this, you need only
// understand the requirements and the body of this function.
//
// Requirements:
// * All apiservers MUST use the same ports for their {rw, ro} services.
// * All apiservers MUST use ReconcileEndpoints and only ReconcileEndpoints to manage the
// endpoints for their {rw, ro} services.
// * All apiservers MUST know and agree on the number of apiservers expected
// to be running (c.masterCount).
// * ReconcileEndpoints is called periodically from all apiservers.
func (r *masterCountEndpointReconciler) ReconcileEndpoints(serviceName string, ip net.IP, endpointPorts []api.EndpointPort, reconcilePorts bool) error {
r.reconcilingLock.Lock()
defer r.reconcilingLock.Unlock()
if r.stopReconcilingCalled {
return nil
}
// 查询出服务中的 Endpoints,放到变量e
e, err := r.endpointClient.Endpoints(metav1.NamespaceDefault).Get(serviceName, metav1.GetOptions{})
if err != nil {
e = &api.Endpoints{
ObjectMeta: metav1.ObjectMeta{
Name: serviceName,
Namespace: metav1.NamespaceDefault,
},
}
}
if errors.IsNotFound(err) {
// Simply create non-existing endpoints for the service.
e.Subsets = []api.EndpointSubset{{
Addresses: []api.EndpointAddress{{IP: ip.String()}},
Ports: endpointPorts,
}}
_, err = r.endpointClient.Endpoints(metav1.NamespaceDefault).Create(e)
return err
}
// First, determine if the endpoint is in the format we expect (one
// subset, ports matching endpointPorts, N IP addresses).
// 检查服务中的 Endpoints信息,是否包含现有ip,端口是否符合,格式是否正确(只有一个subnet)等
formatCorrect, ipCorrect, portsCorrect := checkEndpointSubsetFormat(e, ip.String(), endpointPorts, r.masterCount, reconcilePorts)
if !formatCorrect { // 如果超过一个subnet,或者没有
// Something is egregiously wrong, just re-make the endpoints record.
e.Subsets = []api.EndpointSubset{{
Addresses: []api.EndpointAddress{{IP: ip.String()}},
Ports: endpointPorts,
}}
glog.Warningf("Resetting endpoints for master service %q to %#v", serviceName, e)
_, err = r.endpointClient.Endpoints(metav1.NamespaceDefault).Update(e) // 重新初始化,把自己写到Endpoints中
return err
}
if ipCorrect && portsCorrect {
return nil
}
if !ipCorrect { // 没有找到自己,把自己加进去
// We *always* add our own IP address.
e.Subsets[0].Addresses = append(e.Subsets[0].Addresses, api.EndpointAddress{IP: ip.String()})
// Lexicographic order is retained by this step.
e.Subsets = endpoints.RepackSubsets(e.Subsets)
// If too many IP addresses, remove the ones lexicographically after our
// own IP address. Given the requirements stated at the top of
// this function, this should cause the list of IP addresses to
// become eventually correct.
if addrs := &e.Subsets[0].Addresses; len(*addrs) > r.masterCount {
// addrs is a pointer because we're going to mutate it.
for i, addr := range *addrs {
if addr.IP == ip.String() {
for len(*addrs) > r.masterCount {
// wrap around if necessary.
remove := (i + 1) % len(*addrs)
*addrs = append((*addrs)[:remove], (*addrs)[remove+1:]...)
}
break
}
}
}
}
if !portsCorrect {
// Reset ports.
e.Subsets[0].Ports = endpointPorts
}
glog.Warningf("Resetting endpoints for master service %q to %v", serviceName, e)
_, err = r.endpointClient.Endpoints(metav1.NamespaceDefault).Update(e) // 把自己加进来,并更新完成
return err
}
- 纠正ClusterIP信息
ClusterIP Repaire是一个控制循环,周期性的检查所有服务分配的ClusterIP,记录错误信息,然后为所有分配的IP,并纠正。
处理的内容:
- 因为操作过程失误或者没有检测到的竞态条件下造成的重复ClusterIP
- 没有在正确配置范围的ClusterIP
- 已经分配给服务,但是因为Crash或者掉电造成没有正确创建的ClusterIP
- 自动迁移旧版本的Kubernetes服务到原子的ipallocator模型
它可以不太频繁的调用,最好是在master启动之初运行一次。它是水平驱动和幂等的,在没有竞争碰到的情况下,所有的ClusterIP都会被更新到ipallocator map中。
- 纠正NodePort信息
保证所有的ports都基于cluster创建,当没有与cluster同步时创建一个告警信息。