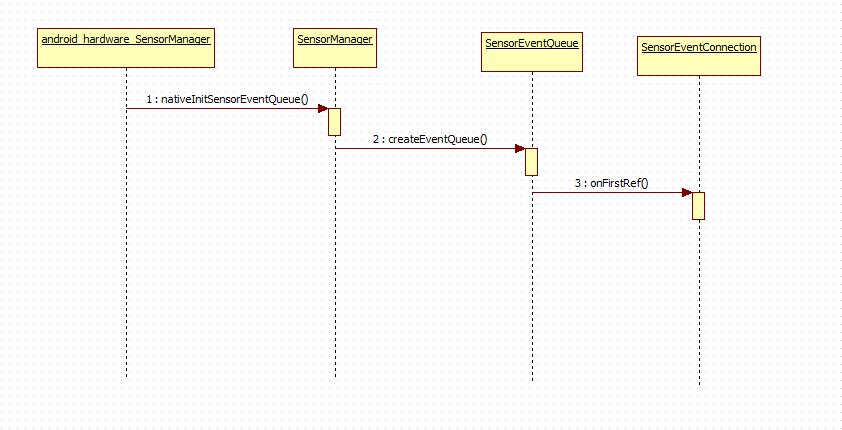
传感器服务,是通过binder进行业务控制,使用socket进行传感器感应数据传输。
客户端是/frameworks/native/libs/gui/SensorManager.cpp
服务端是/frameworks/native/services/sensorservice/SensorService.cpp
我们走一下使能sensor上电的过程吧!
/frameworks/base/core/java/android/hardware/SystemSensorManager.java
首先进入enableSensor,其中nSensorEventQueue是jni层创建SensorEventQueue的返回值,标识一个queue。
private int enableSensor(
Sensor sensor, int rateUs, int maxBatchReportLatencyUs) {
if (nSensorEventQueue == 0) throw new NullPointerException();
if (sensor == null) throw new NullPointerException();
return nativeEnableSensor(nSensorEventQueue, sensor.getHandle(), rateUs,
maxBatchReportLatencyUs);
}
调用到jni接口nativeEnableSensor
static jint nativeEnableSensor(JNIEnv *env, jclass clazz, jlong eventQ, jint handle, jint rate_us,
jint maxBatchReportLatency) {
sp receiver(reinterpret_cast(eventQ));
return receiver->getSensorEventQueue()->enableSensor(handle, rate_us, maxBatchReportLatency,
0);
}
进入receiver的getSensorEventQueue()->enableSensor,看看receiver的定义,他是在构建native层的SensorEventQueue是创建的,里面保存着队列SensorEventQueue
class Receiver : public LooperCallback {
sp mSensorQueue;
sp mMessageQueue;
jobject mReceiverWeakGlobal;
jfloatArray mScratch;
public:
Receiver(const sp& sensorQueue,
const sp& messageQueue,
jobject receiverWeak, jfloatArray scratch) {
JNIEnv* env = AndroidRuntime::getJNIEnv();
mSensorQueue = sensorQueue;
mMessageQueue = messageQueue;
mReceiverWeakGlobal = env->NewGlobalRef(receiverWeak);
mScratch = (jfloatArray)env->NewGlobalRef(scratch);
}
~Receiver() {
JNIEnv* env = AndroidRuntime::getJNIEnv();
env->DeleteGlobalRef(mReceiverWeakGlobal);
env->DeleteGlobalRef(mScratch);
}
sp getSensorEventQueue() const {
return mSensorQueue;
}
/frameworks/native/libs/gui/SensorEventQueue.cpp
进而进入SensorEventQueue的enableSensor方法,他是通过服务端与客户端的连接SensorEventConnection来发送数据给服务端SensorService。
status_t SensorEventQueue::enableSensor(Sensor const* sensor) const {
return mSensorEventConnection->enableDisable(sensor->getHandle(), true, 0, 0, false);
}
SensorEventConnection也是基于binder架构的,客户端的SensorEventConnection其实是个代理,不是真正的SensorEventConnection,真正的SensorEventConnection在服务器端呢。
/frameworks/native/services/sensorservice/SensorService.cpp
sp SensorService::createSensorEventConnection(const String8& packageName,
int requestedMode, const String16& opPackageName) {
uid_t uid = IPCThreadState::self()->getCallingUid();
sp result(new SensorEventConnection(this, uid, packageName,
requestedMode == DATA_INJECTION, opPackageName));
//创建一个SensorEventConnection
return result;
}
//SensorEventConnection的构造函数
SensorService::SensorEventConnection::SensorEventConnection(
const sp& service, uid_t uid, String8 packageName, bool isDataInjectionMode,
const String16& opPackageName)
: mService(service), mUid(uid), mWakeLockRefCount(0), mHasLooperCallbacks(false),
mDead(false), mDataInjectionMode(isDataInjectionMode), mEventCache(NULL),
mCacheSize(0), mMaxCacheSize(0), mPackageName(packageName), mOpPackageName(opPackageName) {
mChannel = new BitTube(mService->mSocketBufferSize);
#if DEBUG_CONNECTIONS
mEventsReceived = mEventsSentFromCache = mEventsSent = 0;
mTotalAcksNeeded = mTotalAcksReceived = 0;
#endif
}
接下来会利用这个代理的SensorEventConnection构造一个队列SensorEventQueue,直接传入代理SensorEventConnection来构造队列。
sp SensorManager::createEventQueue(String8 packageName, int mode) {
.......
sp queue;
queue = new SensorEventQueue(connection);
return queue;
}
真正的传感器测量数据传输不在SensorEventConnection,而是利用一个管道BitTube,他用socket实现,便于大量数据传输,每个SensorEventConnection都配套一个BitTube,BitTube在SensorEventConnection的构造函数中构建了。那这个东西在服务器端构建了,如何传给客户端呢?是在SensorEventQueue的onFirstRef()函数中产生的,利用代理的SensorEventConnection来远程调用getSensorChannel,最后生成本地的管道BitTube。
void SensorEventQueue::onFirstRef()
{
mSensorChannel = mSensorEventConnection->getSensorChannel();
}
/frameworks/native/libs/gui/ISensorEventConnection.cpp
在客户端调用transact,发送GET_SENSOR_CHANNEL
//客户端调用transact
virtual sp getSensorChannel() const
{
Parcel data, reply;
data.writeInterfaceToken(ISensorEventConnection::getInterfaceDescriptor());
remote()->transact(GET_SENSOR_CHANNEL, data, &reply);
return new BitTube(reply);
}
//服务器端处理消息
case GET_SENSOR_CHANNEL: {
CHECK_INTERFACE(ISensorEventConnection, data, reply);
sp channel(getSensorChannel());
channel->writeToParcel(reply);
return NO_ERROR;
}
最后,服务器和客户端就利用这个管道BitTube进行通信了。
但是,然并卵,使能上电并不需要传输传感器数据,最后会在服务器端SensorService上了下电而已!!
status_t SensorService::enable(const sp& connection,
int handle, nsecs_t samplingPeriodNs, nsecs_t maxBatchReportLatencyNs, int reservedFlags,
const String16& opPackageName)
{
......
BatteryService::enableSensor(connection->getUid(), handle);
return err;
.....
}
参考:
Service与Android系统设计(6)--- Native Service
Android BitTube进程间数据传递
Android6.0 Sensor架构和问题分析