前言
在学习Spring的过程中,自己算是好好体会了一把Spring配置文件的繁琐。
在学习Spring的时候,过多的标签我们不容易记住。而且Spring官方也积极的给我们提供了示例项目供我们参考,可见官方也不推荐我们去记住那么众多的配置文件,只是记住有这个东西存在就好,我们用到的时候只要去查阅引入配置标签即可。
今天在搞Spring项目的时候,由于自己最近都在开发SpringBoot相关的内容。所以长期不接触Spring最明显的问题就是配置文件不会写了。过去自己写的时候也一直都是能自己写出来的自己写,写不出来忘记了的的copy原来项目的配置文件。因为具体到业务代码的编写,很明显业务代码才是我们一个程序员应该关注的事情而不是去花大量的时间去搞配置文件,尤其是对于用过SpringBoot的我来说,真的再也受不了去死记硬背那些众多的配置文件了。
问题
开启Spring项目第一件事就是先配置不然你什么都做不了。首先我想要在项目中用我常用的注解@Autowired,我需要在配置文件中声明AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor这个bean。我又想要在项目中用到@Required这个注解,那我还需要再配置RequiredAnnotationBeanPostProcesso这个bean。一个功能一个bean搞得自己有点儿头大。后来查阅到要想支持这两个注解只需要在配置文件中声明
深入源码
这里我只是简单记录一下我好奇的地方,并记录自己解惑的过程。先上一段代码:
我们来看一下官方对该标签的说明:
As always, you can register them as individual bean definitions, but they can also be implicitly registered by including the following tag in an XML-based Spring configuration (notice the inclusion of the context namespace)
翻译过来:
与往常一样,您可以将它们注册为单独的bean定义,但也可以通过在基于XML的Spring配置中包含以下标记来隐式注册它们(注意包含上下文名称空间)
既然官网这么说,可是那么
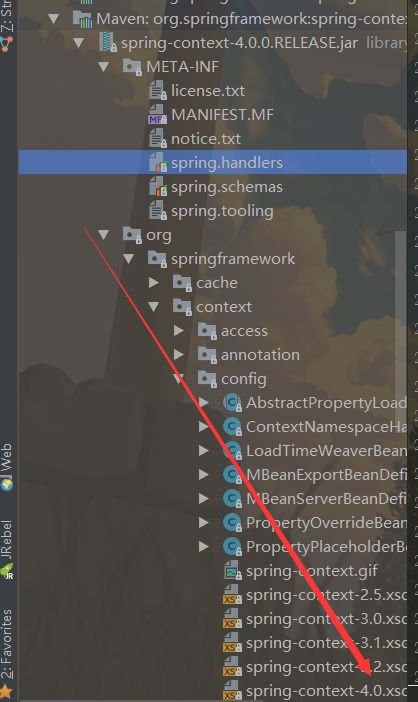
在Spring容器解析配置文件中时,会加载beans标签中配置的URL,如图:
我们按住Ctrl点击该标签进入到该目录下:
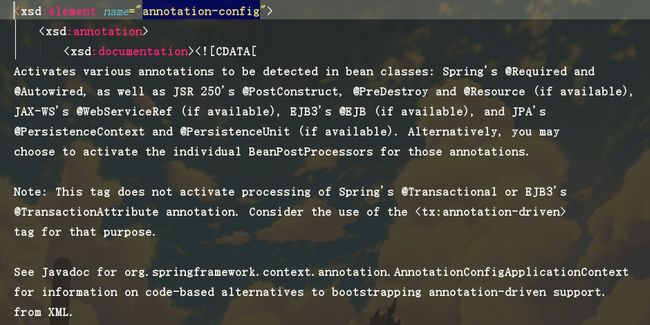
可以看到代码提供的注释这里写的很清楚,该标签提供了哪些注解的支持
然后我们再根据配置文件中beans标签中配置的xsi:schemaLocation的URL到spring.handlers文件中,找到对应的NamespaceHandler。
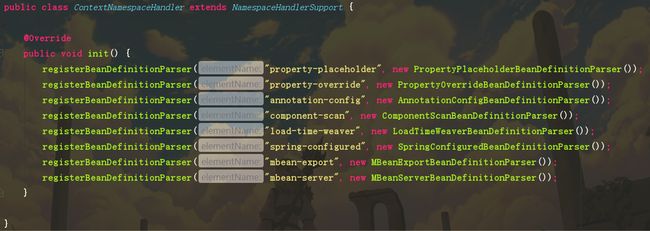
比如我上面的是spring.handlers文件中的ContextNamespaceHandler。然后Ctrl B进入
那么这个Handler是做什么的呢?就一个方法,在该方法中,可以看到它的作用就是创建这些标签所对应的解析类。什么是解析类呢?也就是所有的自定义命名空间(像mvc,context等)下的标签解析都是由BeanDefinitionParser接口的子类来完成的。可以看到annotation-config的解析类是AnnotationConfigBeanDefinitionParser。
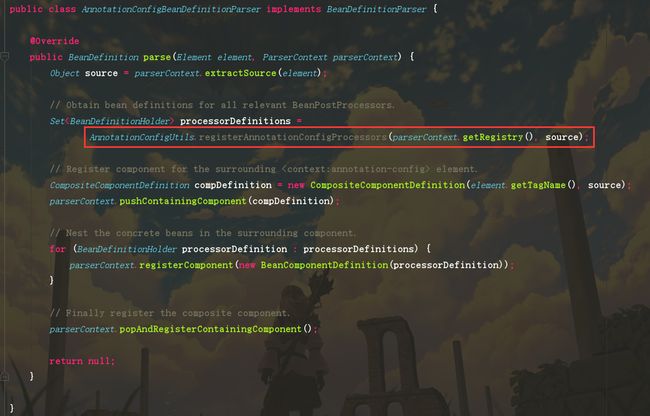
我们继续Ctrl B进入该类,看一下这个类如何解析这个标签的。
根据上面的代码可以看出真正的解析是在AnnotationConfigUtils.registerAnnotationConfigProcessors()方法中进行的
那就进去这个方法看看
这里代码篇幅太长,我们贴了代码:
public static Set registerAnnotationConfigProcessors(
BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, Object source) {
DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = unwrapDefaultListableBeanFactory(registry);
if (beanFactory != null) {
if (!(beanFactory.getDependencyComparator() instanceof AnnotationAwareOrderComparator)) {
beanFactory.setDependencyComparator(AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.INSTANCE);
}
if (!(beanFactory.getAutowireCandidateResolver() instanceof ContextAnnotationAutowireCandidateResolver)) {
beanFactory.setAutowireCandidateResolver(new ContextAnnotationAutowireCandidateResolver());
}
}
Set beanDefs = new LinkedHashSet(4);
// ConfigurationClassPostProcessor
if (!registry.containsBeanDefinition(CONFIGURATION_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)) {
RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition(ConfigurationClassPostProcessor.class);
def.setSource(source);
beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, CONFIGURATION_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME));
}
// AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor
if (!registry.containsBeanDefinition(AUTOWIRED_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)) {
RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition(AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.class);
def.setSource(source);
beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, AUTOWIRED_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME));
}
// RequiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor
if (!registry.containsBeanDefinition(REQUIRED_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)) {
RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition(RequiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.class);
def.setSource(source);
beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, REQUIRED_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME));
}
// CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor
// Check for JSR-250 support, and if present add the CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.
if (jsr250Present && !registry.containsBeanDefinition(COMMON_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)) {
RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition(CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.class);
def.setSource(source);
beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, COMMON_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME));
}
// PersistenceAnnotationBeanPostProcessor
// Check for JPA support, and if present add the PersistenceAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.
if (jpaPresent && !registry.containsBeanDefinition(PERSISTENCE_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)) {
RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition();
try {
ClassLoader cl = AnnotationConfigUtils.class.getClassLoader();
def.setBeanClass(cl.loadClass(PERSISTENCE_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_CLASS_NAME));
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Cannot load optional framework class: " + PERSISTENCE_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_CLASS_NAME, ex);
}
def.setSource(source);
beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, PERSISTENCE_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME));
}
return beanDefs;
}
到这里我们的问题就完美解决了。由代码可以看出,分别注册了AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor、RequiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor、CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor以及PersistenceAnnotationBeanPostProcessor、ConfigurationClassPostProcessor这5个BeanPostProcessor。