一、思维导图
多姿多彩的控件
二、重述知识
这节就讲了几个常用的控件,
TextView、EditText、Button等等,
还有一些View的通用属性。
三、具体应用场景
随便一个App的登录页面都有这几个控件。
四、扩展理解
1.fill_parent已弃用
在官方文档对ViewGroup.LayoutParams这个静态类的概述中,有以下的描述:
The base LayoutParams class just describes how big the view wants to be for both width and height. For each dimension, it can specify one of:
- FILL_PARENT (renamed MATCH_PARENT in API Level 8 and higher), which means that the view wants to be as big as its parent (minus padding)
- WRAP_CONTENT, which means that the view wants to be just big enough to enclose its content (plus padding)
- an exact number
There are subclasses of LayoutParams for different subclasses of ViewGroup. For example, AbsoluteLayout has its own subclass of LayoutParams which adds an X and Y value.
可见,fill_parent这个属性在API 8以上的版本就被重命名为match_parent了。
某个子view控件相对于它的父布局(或者说容器)来说有多大,就是用下面两个属性描述:
- match_parent : 跟父容器一样大
- wrap_content :填充它显示的内容那么大就够了
2.排列方式
把控件放在布局上,默认都是从左上角开始。
而关于布局,还要特别注意android:gravity和android:layout_gravity两个属性的运用。
详见我另一篇博文:点击链接
其实记住下面这些就行了:
- 对于
horizontal的LinearLayout,把android:layout_gravity设为top、center、bottom、center_vertical才有意义; - 对于
vertical的LinearLayout,把android:layout_gravity设为left、center、right、center_horizontal才有意义; -
RelativeLayout对android:layout_gravity不起作用 -
center已经包含了center_vertical和center_horizontal两种意义了,用的时候不要忘了
3.尽量用引用
把按钮的内容的字符串,或者一些颜色,
写到res/values/strings.xml和res/values/colors.xml文件中,
然后去引用,不要直接android:text="Text"这样写死。
4.限制显示内容
可以用android:singleLine来限制TextView或者EditText是否在一行显示,值为true或者false;
还可以用android:maxLines="3"来限制文字显示的最大行数,具体值按需决定。
上面这样最会显示单行。
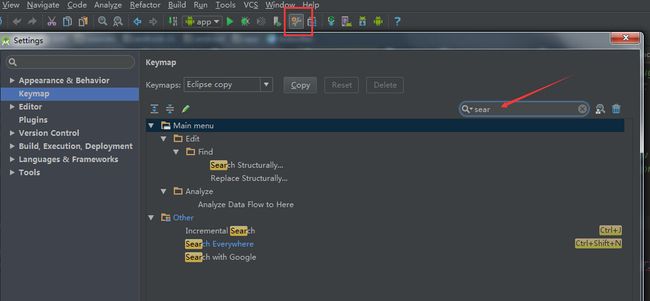
5.查找"类"的快捷键
如果按AndroidStudio的默认快捷键,就参考这篇《AndroidStudio快捷键汇总》吧。
如果你像我一样,习惯了Eclipse的快捷键,设了Eclipse的快捷键,
那么这个全局搜索某个类的快捷键是空缺的。
要自己去keymap设置:
我设了跟AndroidStudio Default一样,是【ctrl+shift+N】。
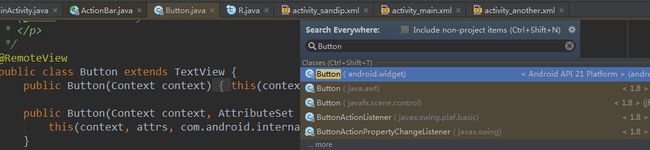
6.Button extends TextView
有了上面这个快捷键,输入“Button”就看到“Button extends TextView”。
7.各种EditText
根据EditText的输入内容,有各种EditText供选择。
具体到代码,其实就是android:inputType这个属性不一样,看这里。
五、核心代码或操作
发送微博时,140字的限制。该操作其中包含EditText的"点击"、"长按"、"文本改变"等操作。
@Override
public void afterTextChanged(Editable s) {
int textSum = s.toString().length();
if(textSum<130){
textView.setText("");
}
if(textSum>=130&&textSum<=140){
textView.setText(String.valueOf(140-textSum));
textView.setTextColor(getResources().getColor(R.color.gray));
}
if(textSum>140){
textView.setText(String.valueOf(140-textSum));
textView.setTextColor(getResources().getColor(R.color.red));
}
}
详见我另一篇博文:关于addTextChangedListener()方法的上机记录。
另外,我发现原来新浪微博数字只算半个字,
如果不是这个上机,根本不会留意到这个细节。
六、相关面试题
待补充。
七、脑内记忆
这一节比较重要的就是关于布局的排列问题,
LinearLayout的android:layout_gravity设置的限制,
我就把它想象为坐标轴的X、Y轴吧。
例如水平方向,那只能按Y轴方向上下移动,也就是Top - Bottom,
而垂直方向,则是按X轴指的方向移动,那就是Left - Right。
八、参考资料
1.android布局-RelativeLayout(相对布局)详解