背景
在iOS开发中必不可少的要用到数据存储,数据的处理是iOS开发中的核心技术,适当的对数据进行持久化存储可以实现应用的离线功能,以此提高用户体验。所谓数据持久化,就是将数据保存到硬盘中,使得在应用程序或手机重启后可以继续访问之前保存的数据。在iOS开发中,有很多持久化得方案,接下来我将总结以下5种持久化方案:
1、plist(属性列表)
2、preference(偏好设置)
3、NSKeyedArchiver(归档)
4、SQList 3 (FMDB)
5、CoreData
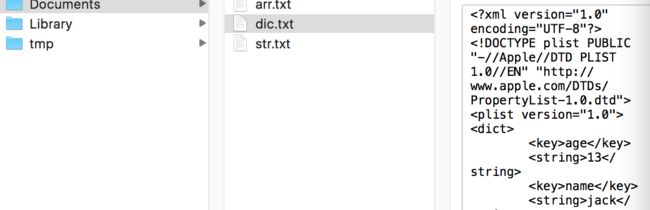
应用沙盒
在介绍各种存储方法之前,先说明下沙盒机制。每个iOS应用都有一个 应用沙盒「文件系统目录」,与其他文件系统隔离
应用必须在自己的沙盒里,其他应用不能访问他人的沙盒
Documents:保存应用运行时生成的需要持久化的数据,iTunes同步设备时会备份该目录。例如,游戏应用可将游戏存档保存在该目录
tmp:保存应用运行时所需的临时数据,使用完毕后再将相应的文件从该目录删除。应用没有运行时,系统也可能会清除该目录下的文件。iTunes同步设备时不会备份该目录
Library/Caches:保存应用运行时生成的需要持久化的数据,iTunes同步设备时不会备份该目录。一般存储体积大、不需要备份的非重要数据
Library/Preference:保存应用的所有偏好设置,iOS的Settings(设置)应用会在该目录中查找应用的设置信息。iTunes同步设备时会备份该目录
// 获取 Documents 文件路径
// 方法一、利用沙盒根目录拼接 ”Documents” 字符串
// 不建议采用,因为新版本的操作系统可能会修改目录名
NSString *home = NSHomeDirectory();
NSString *documents = [home stringByAppendingPathComponent:@"Documents"];
// 方法二、利用 NSSearchPathForDirectoriesInDomains 函数
/**
NSSearchPathForDirectoriesInDomains
@param NSDocumentDirectory 搜索目录是,Documents 目录
@param NSUserDomainMask 搜索范围是,用户文件夹
@param NO 不展开全路径:~/Library/Caches
@return NSArray*
*/
NSArray *documentArray = NSSearchPathForDirectoriesInDomains(NSDocumentDirectory, NSUserDomainMask, YES);
NSString *documentPath = [documentArray firstObject];
NSLog(@"documentPath = %@",documentPath);
NSString *libraryPath = [NSSearchPathForDirectoriesInDomains(NSLibraryDirectory, NSUserDomainMask, YES)firstObject];
NSLog(@"libraryPath = %@",libraryPath);
NSString *preferencePath =[libraryPath stringByAppendingString:@"/preferences"];
NSLog(@"%@",preferencePath);
NSString *cachesPath = [NSSearchPathForDirectoriesInDomains(NSCachesDirectory, NSUserDomainMask, YES)firstObject];
NSLog(@"cachesPath = %@",cachesPath);
// 获取 tmp 文件路径
NSString *tmpPath = NSTemporaryDirectory();
plist(属性列表)
iOS提供了一种plist格式的文件(属性列表)用于存储轻量级的数据,属性列表是一种XML格式的文件,拓展名为plist。如果对象是NSString、NSDictionary、NSArray、NSData类型,就可以使用writeToFile:atomically:⽅法 直接将对象写到属性列表文件中该格式保存的数据可以直接使用NSDictionary和NSArray读取 。plist文件在iOS开发中属于Write写入方式,可以以Property List列表形式显示,也可以以xml格式显示。对于数据管理是很方便的。掌握使用plist文件数据操作很有必要.
- NSString 写入文件 读取
NSArray *documentArray = NSSearchPathForDirectoriesInDomains(NSDocumentDirectory, NSUserDomainMask, YES);
NSString *documentPath = [documentArray firstObject];
NSLog(@"documentPath = %@",documentPath);
NSString *filePath = [documentPath stringByAppendingPathComponent:@"str.txt"];
NSString *str = @"这是一个字符串";
//atomically是否进行线性操作(YES保证发生意外时有中转文件来保存信息 直至写入完成 但是损耗大. NO的时候写入速度快 但是没有安全保障)
[str writeToFile:filePath atomically:YES encoding:NSUTF8StringEncoding error:nil];
NSString *str1 = [NSString stringWithContentsOfFile:filePath encoding:NSUTF8StringEncoding error:nil];
//2017-03-19 15:28:09.740 信号量[3255:166796] 这是一个字符串
NSLog(@"%@",str1);
- NSArray 写入文件 读取
NSArray *documentArray = NSSearchPathForDirectoriesInDomains(NSDocumentDirectory, NSUserDomainMask, YES);
NSString *documentPath = [documentArray firstObject];
NSLog(@"documentPath = %@",documentPath);
NSString *filePath = [documentPath stringByAppendingPathComponent:@"arr.txt"];
NSArray *array = @[@"abc",@"def",@"ghi"];
[array writeToFile:filePath atomically:YES];
NSArray *getArray = [NSArray arrayWithContentsOfFile:filePath];
// 2017-03-19 15:34:52.261 信号量[3423:172597] (
// abc,
// def,
// ghi
// )
NSLog(@"%@",getArray);
- NSDictionary 写入文件 读取
NSArray *documentArray = NSSearchPathForDirectoriesInDomains(NSDocumentDirectory, NSUserDomainMask, YES);
NSString *documentPath = [documentArray firstObject];
NSLog(@"documentPath = %@",documentPath);
NSString *filePath = [documentPath stringByAppendingPathComponent:@"arr.txt"];
NSDictionary *dic = @{@"name":@"jack",@"age":@"13"};
[dic writeToFile:filePath atomically:YES];
NSDictionary *mydic = [NSDictionary dictionaryWithContentsOfFile:filePath];
// 2017-03-19 15:39:03.598 信号量[3479:176290] {
// age = 13;
// name = jack;
// }
NSLog(@"%@",mydic);
- NSData对象写入 读取
NSArray *documentArray = NSSearchPathForDirectoriesInDomains(NSDocumentDirectory, NSUserDomainMask, YES);
NSString *documentPath = [documentArray firstObject];
NSLog(@"documentPath = %@",documentPath);
NSString *filePath = [documentPath stringByAppendingPathComponent:@"22.png"];
UIImage *image = [UIImage imageNamed:@"22.png"];
NSData *data = UIImagePNGRepresentation(image);
[data writeToFile:filePath atomically:YES];
NSData *myData = [NSData dataWithContentsOfFile:filePath];
//2017-03-19 15:45:55.005 信号量[3666:183586] 3157
NSLog(@"%lu",(unsigned long)myData.length);
preference(偏好设置)
使用NSUserDefault 实现持久化
下面来看下 NSUserDefault 本地保存的位置,Library/Preferences 这个目录下的 plist 文件就是其保存的目录。
//1.获得NSUserDefaults文件
NSUserDefaults *userDefaults = [NSUserDefaults standardUserDefaults];
//2.向文件中写入内容
[userDefaults setObject:@"AAA" forKey:@"a"];
[userDefaults setBool:YES forKey:@"sex"];
[userDefaults setInteger:21 forKey:@"age"];
//2.1立即同步
[userDefaults synchronize];
//3.读取文件
NSString *name = [userDefaults objectForKey:@"a"];
BOOL sex = [userDefaults boolForKey:@"sex"];
NSInteger age = [userDefaults integerForKey:@"age"];
偏好设置是专门用来保存应用程序的配置信息的,一般不要在偏好设置中保存其他数据。
如果没有调用synchronize方法,系统会根据I/O情况不定时刻地保存到文件中。所以如果需要立即写入文件的就必须调用synchronize方法。
偏好设置会将所有数据保存到同一个文件中。即preference目录下的一个以此应用包名来命名的plist文件。
NSKeyedArchiver(归档)
#import
@interface Person : NSObject
@property (nonatomic, copy) NSString *name;
@property (nonatomic, assign) int age;
@end
#import "Person.h"
//遵守NSCoding协议
@interface Person()
@end
@implementation Person
#pragma mark 编码,对象属性进行编码
- (void)encodeWithCoder:(NSCoder *)aCoder
{
//前者(_age,_name)是属性,后者是关键字Key(age,name)
[aCoder encodeInt:_age forKey:@"age"];
[aCoder encodeObject:_name forKey:@"name"];
}
#pragma mark 解码,解码归档数据初始化对象
- (id)initWithCoder:(NSCoder *)aDecoder
{
if (self = [super init]) {
_age = [aDecoder decodeIntForKey:@"age"];
_name = [aDecoder decodeObjectForKey:@"name"];
}
return self;
}
@end
测试
NSArray *documentArray = NSSearchPathForDirectoriesInDomains(NSDocumentDirectory, NSUserDomainMask, YES);
NSString *documentPath = [documentArray firstObject];
NSLog(@"documentPath = %@",documentPath);
NSString *filePath = [documentPath stringByAppendingPathComponent:@"person"];
Person *p = [Person new];
p.name =@"wang";
p.age = 12;
//Encoding保存Person
[NSKeyedArchiver archiveRootObject:p toFile:filePath];
Person *pp = [NSKeyedUnarchiver unarchiveObjectWithFile:filePath];
// 2017-03-19 16:32:16.750 信号量[4359:217706] wang
// 2017-03-19 16:32:16.751 信号量[4359:217706] 12
NSLog(@"%@",pp.name);
NSLog(@"%d",pp.age);
SQList 3和CoreData下篇再写
SQList 3封装 http://www.jianshu.com/p/5471d001572c