前言
在平常的开发工作中,由于各种特殊业务的需求,以及UI的各种脑洞设计,在这种场景下,Android中的基本控件就有些力不从心了。由此,掌握自定义View已慢慢变成大家必备的技能之一了。今天,就带大家进入自定义View的基础篇。
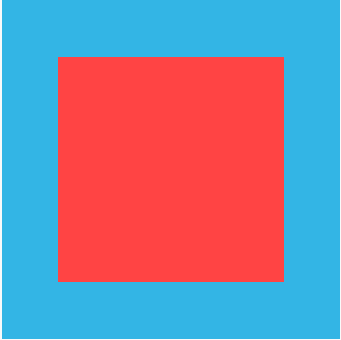
下边就是我们今天要实现的简单自定义View的效果图:
其中,蓝色的为CustomView背景色,中间红色区域为CustomView的内容显示区域,我们暂称为ContentView。
概括
自定义View的基本步骤如下:
1、 继承View类或View的子类
2、 实现自定义View属性
3、 重写onMeasure()方法
4、 重写onDraw()方法
小注:以上步骤2、3、4可以根据自己的需求定制,非必需实现步骤。
具体实现
1. 继承View类或View的子类
这一步比较简单,只需要实现一个继承自View或View子类的类,并实现构造方法即可。
若我们要完全自己定义View控件,可如下操作:
public class CustomView extends View {
public CustomView(Context context) {
this(context, null);
}
public CustomView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
//...其它初始化操作
}
}
此外,如果我们是在View子类的基础上进行自定义控件,类似操作如下:
public class CustomImageView extends ImageView {
public CustomImageView(Context context) {
this(context, null);
}
public CustomImageView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
//...其它初始化操作
}
}
2. 实现自定义View属性
①. 在项目res/values/下新建attrs.xml(当然其它名称也是可以的),在其中声明相关属性如下:
其中,attar的格式即单位有:dimension(尺寸)、boolean(布尔)、color(颜色)、enum(枚举)、flag(位或)、float(浮点)、fraction(百分比)、integer(整型)、reference(资源引用)、string(字符串)。
②. 在布局文件res/layout/activity_mian.xml的用法如下:
注意:引用自定义属性,需要声明命名空间:
xmlns:shorr="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
③. 然后,在CustomView的构造方法中初始化相关自定义属性:
/**
* 初始化View相关自定义属性
*
* @param context
* @param attrs
*/
private void initFromAttributes(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
//获取相关View属性
TypedArray a = context.getTheme().obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, R.styleable.CustomView, 0, 0);
try {
mContentWidth = a.getDimensionPixelSize(R.styleable.CustomView_contentWidth, 0);
mContentHeight = a.getDimensionPixelSize(R.styleable.CustomView_contentHeight, 0);
mContentColor = a.getColor(R.styleable.CustomView_contentColor, Color.TRANSPARENT);
mGravity = a.getInteger(R.styleable.CustomView_gravity, -1);
} finally {
//回收TypedArray
a.recycle();
}
}
注意:TypedArray对象是一个共享资源,使用后必须调用
recycle()回收。目的是为了缓存资源,这样每次调用TypedArray的时候都不再需要重新分配内存,方便了其它地方的复用。
3. 重写onMeasure()方法
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
//获取宽高的尺寸
int width = getMeasureSize(MeasureOrientation.WIDTH, mContentWidth, widthMeasureSpec);
int height = getMeasureSize(MeasureOrientation.HEIGHT, mContentHeight, heightMeasureSpec);
//设置测量尺寸
setMeasuredDimension(width, height);
}
/**
* 得到宽度测量的尺寸大小
*
* @param orientation 测量的方向(宽高)
* @param defalutSize 默认尺寸大小
* @param measureSpec 测量的规则
* @return 返回测量的尺寸
*/
private int getMeasureSize(MeasureOrientation orientation, int defalutSize, int measureSpec) {
int result = defalutSize;
int specMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(measureSpec);
int specSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(measureSpec);
switch (specMode) {
case MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED: //无限制大小
result = defalutSize;
break;
case MeasureSpec.AT_MOST: //对应wrap_content
//如果设置了gravity属性,则忽略padding属性
if (mGravity != -1) {
result = defalutSize;
break;
}
if (orientation == MeasureOrientation.WIDTH) {
//测量的宽
result = getPaddingLeft() + defalutSize + getPaddingRight();
} else if (orientation == MeasureOrientation.HEIGHT) {
//测量的高
result = getPaddingTop() + defalutSize + getPaddingBottom();
}
break;
case MeasureSpec.EXACTLY: //对应match_parent or dp/px
result = specSize;
break;
}
return result;
}
在getMeasureSize()方法中,我们通过measureSpec得到当前测量的大小和模式。并通过不同的模式我们计算得到了最终的CustomeView的尺寸大小。
SpecMode有三种类型:
- UNSPECIFIED:父容器对View没有任何限制。多用于系统内部的测量中。
- AT_MOST:父容器给View的最大可用尺寸。它对应于View的
wrap_content属性。 - EXACTLY:父容器给View的具体可用尺寸。它对应于View的
match_parent或dp/px(具体的尺寸)。
注意:在AT_MOST模式,即
wrap_content属性下,要处理好View的padding属性。
此外,MeasureOrientation为自定义的枚举,为了区分记录View测量的方向(宽、高):
private enum MeasureOrientation { //View测量方向(宽、高)的枚举
WIDTH, HEIGHT
}
最后,得到测量后的值后,我们需要通过setMeasuredDimension(width, height);来为CustomeView设置测量值。
4. 重写onDraw()方法
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
//获取测量后的宽高
int width = getWidth();
int height = getHeight();
//获取View的Padding
int paddingLeft = getPaddingLeft();
int paddingRight = getPaddingRight();
int paddingTop = getPaddingTop();
int paddingBottom = getPaddingBottom();
//设置ContentView的Rect
Rect rect = null;
if (mGravity == -1) { //如果没有设置gravity属性,设置padding属性
rect = new Rect(paddingLeft, paddingTop, width - paddingRight, height - paddingBottom);
} else { //如果设置gravity属性,不设置padding属性
rect = getContentRect(width, height, mGravity);
}
//绘制ContentView
canvas.drawRect(rect, mPaint);
}
在onDraw()方法中,我们首先获取了CustomView的宽高、padding值,并根据有无设置gravity属性来分别处理了ContentView要显示矩形范围。最后,通过drawRect()方法绘制出了要显示的ContentView。
效果展示
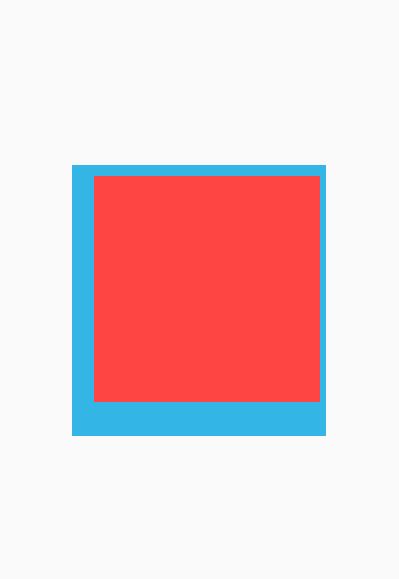
设置padding属性
效果图:
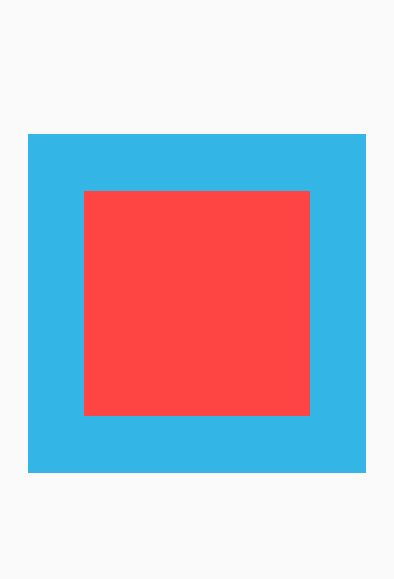
设置gravity属性
效果图:
CustomView完整代码
package cn.shorr.customview;
import android.content.Context;
import android.content.res.TypedArray;
import android.graphics.Canvas;
import android.graphics.Color;
import android.graphics.Paint;
import android.graphics.Rect;
import android.util.AttributeSet;
import android.view.View;
/**
* 自定义简易View
* Created by Shorr on 2016/11/20.
*/
public class CustomView extends View {
/*自定义属性*/
private int mContentWidth; //默认宽度,单位px
private int mContentHeight; //默认高度,单位px
private int mContentColor; //View的颜色
private int mGravity; //View的Gravity属性
private enum MeasureOrientation { //View测量方向(宽、高)的枚举
WIDTH, HEIGHT
}
private Paint mPaint; //定义一个画笔
public CustomView(Context context) {
this(context, null);
}
public CustomView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
//初始化相关自定义属性
initFromAttributes(context, attrs);
//初始化View
initView();
}
/**
* 初始化View相关自定义属性
*
* @param context
* @param attrs
*/
private void initFromAttributes(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
//获取相关View属性
TypedArray a = context.getTheme().obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, R.styleable.CustomView, 0, 0);
try {
mContentWidth = a.getDimensionPixelSize(R.styleable.CustomView_contentWidth, 0);
mContentHeight = a.getDimensionPixelSize(R.styleable.CustomView_contentHeight, 0);
mContentColor = a.getColor(R.styleable.CustomView_contentColor, Color.TRANSPARENT);
mGravity = a.getInteger(R.styleable.CustomView_gravity, -1);
} finally {
//回收TypedArray
a.recycle();
}
}
/**
* 初始化View操作
*/
private void initView() {
mPaint = new Paint(Paint.ANTI_ALIAS_FLAG);
//设置画笔颜色
mPaint.setColor(mContentColor);
}
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
//获取宽高的尺寸
int width = getMeasureSize(MeasureOrientation.WIDTH, mContentWidth, widthMeasureSpec);
int height = getMeasureSize(MeasureOrientation.HEIGHT, mContentHeight, heightMeasureSpec);
//设置测量尺寸
setMeasuredDimension(width, height);
}
/**
* 得到宽度测量的尺寸大小
*
* @param orientation 测量的方向(宽高)
* @param defalutSize 默认尺寸大小
* @param measureSpec 测量的规则
* @return 返回测量的尺寸
*/
private int getMeasureSize(MeasureOrientation orientation, int defalutSize, int measureSpec) {
int result = defalutSize;
int specMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(measureSpec);
int specSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(measureSpec);
switch (specMode) {
case MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED: //无限制大小
result = defalutSize;
break;
case MeasureSpec.AT_MOST: //对应wrap_content
//如果设置了gravity属性,则忽略padding属性
if (mGravity != -1) {
result = defalutSize;
break;
}
if (orientation == MeasureOrientation.WIDTH) {
//测量的宽
result = getPaddingLeft() + defalutSize + getPaddingRight();
} else if (orientation == MeasureOrientation.HEIGHT) {
//测量的高
result = getPaddingTop() + defalutSize + getPaddingBottom();
}
break;
case MeasureSpec.EXACTLY: //对应match_parent or dp/px
result = specSize;
break;
}
return result;
}
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
//获取测量后的宽高
int width = getWidth();
int height = getHeight();
//获取View的Padding
int paddingLeft = getPaddingLeft();
int paddingRight = getPaddingRight();
int paddingTop = getPaddingTop();
int paddingBottom = getPaddingBottom();
//设置ContentView的Rect
Rect rect = null;
if (mGravity == -1) { //如果没有设置gravity属性,设置padding属性
rect = new Rect(paddingLeft, paddingTop, width - paddingRight, height - paddingBottom);
} else { //如果设置gravity属性,不设置padding属性
rect = getContentRect(width, height, mGravity);
}
//绘制ContentView
canvas.drawRect(rect, mPaint);
}
/**
* 获取ContentView的Rect
*
* @param width View的Width
* @param height View的Height
* @param gravity View的Gravity
* @return
*/
private Rect getContentRect(int width, int height, int gravity) {
Rect rect = null;
switch (gravity) {
case 0: //left
rect = new Rect(0, 0,
width - (width - mContentWidth), height - (height - mContentHeight));
break;
case 1: //right
rect = new Rect(width - mContentWidth, 0,
height, height - (height - mContentHeight));
break;
case 2: //center
rect = new Rect((width - mContentWidth) / 2, (height - mContentHeight) / 2,
width - ((width - mContentWidth) / 2), height - ((height - mContentHeight) / 2));
break;
default:
break;
}
return rect;
}
}
结语
今天,主要介绍了要实现一个基础自定义View的步骤,本篇demo只是简单的实现了一个CustomView,具体的实现效果大家可以根据自己的需求进行具体的定制。下一篇,将结合项目具体需求,给大家带来一个自定义View的实例篇,敬请期待~
Demo源码 请点击此处下载(https://github.com/shorr/notes_demo/tree/master/CustomView)