《Modern Statistics for Modern Biology》Chapter 一: 离散数据模型的预测(1.1 - 1.3)
《Modern Statistics for Modern Biology》Chapter 一: 离散数据模型的预测(1.4 - 1.5)
《Modern Statistics for Modern Biology》Chapter 二: 统计建模(2.1-2.3)
《Modern Statistics for Modern Biology》Chapter 二: 统计建模(2.4-2.5)
《Modern Statistics for Modern Biology》Chapter 二 统计建模(2.6 - 2.7)
《Modern Statistics for Modern Biology》Chapter 二 统计建模(2.8 - 2.9)
《Modern Statistics for Modern Biology》Chapter 二 统计建模(2.10 完结)
《Modern Statistics for Modern Biology》Chapter 三:R语言中的高质量图形(3.1-3.4)
《Modern Statistics for Modern Biology》Chapter 三:R语言中的高质量图形(3.5-3.6)
从这章开始最开始记录一些markdown等小知识
$\hat{p}=\frac{1}{12}$:
掌握R语言中的apply函数族
卡方检验
Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium( 哈迪-温伯格平衡 )
带你理解beta分布
简单介绍一下R中的几种统计分布及常用模型
- 统计分布每一种分布有四个函数:
d――density(密度函数),p――分布函数,q――分位数函数,r――随机数函数。比如,正态分布的这四个函数为dnorm,pnorm,qnorm,rnorm。下面我们列出各分布后缀,前面加前缀d、p、q或r就构成函数名:norm:正态,t:t分布,f:F分布,chisq:卡方(包括非中心)unif:均匀,exp:指数,weibull:威布尔,gamma:伽玛,beta:贝塔lnorm:对数正态,logis:逻辑分布,cauchy:柯西,binom:二项分布,geom:几何分布,hyper:超几何,nbinom:负二项,pois:泊松signrank:符号秩,wilcox:秩和,tukey:学生化极差
如何预测一条序列是否含有CpG岛
图片输出尽量保存为矢量图
结合setNames函数与scale_fill_manual函数来指定ggplot2的填充颜色(Figure 3.13)
要善于用stat_summary来自定义函数结合ggplot2进行绘图
本章颜值担当一定要放最前面
3.7 2D可视化数据:散点图
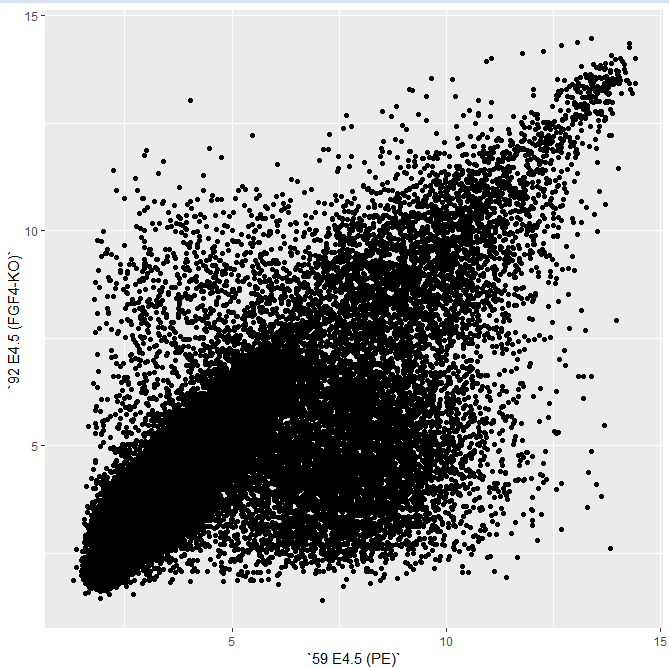
- 查看
WT和FGF3-KO样本中基因的差异表达。
dfx = as.data.frame(Biobase::exprs(x))
library(ggplot2)
> scp = ggplot(dfx, aes(x = `59 E4.5 (PE)` ,
+ y = `92 E4.5 (FGF4-KO)`))
> scp + geom_point()
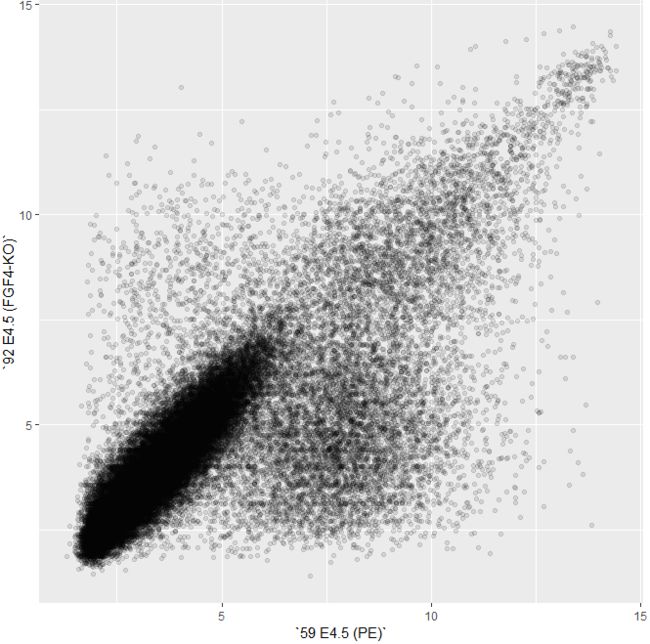
- 使用
alpha调整散点图的透明度
> scp + geom_point(alpha = 0.1)
- 另一种选择是
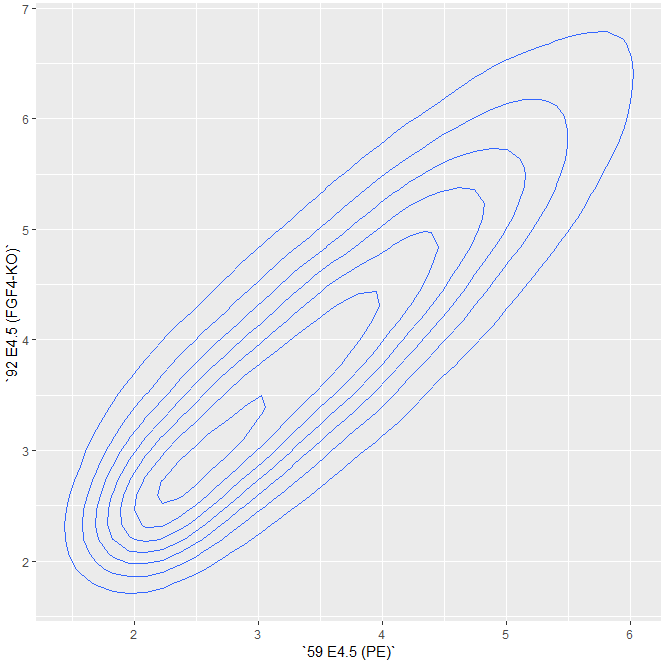
2D密度的等高线图,其具有不渲染图上所有点的附加益处。
> scp + geom_density2d()
- 但是,我们在
图 3.27中看到,右下角的点云(包含相对较少的点数)没有显示。我们可以通过调整geom_density2d的bandwidth和binning参数来克服这一点:
> scp + geom_density2d(h = 0.5, bins = 60)
> library("RColorBrewer")
> colorscale = scale_fill_gradientn(
+ colors = rev(brewer.pal(9, "YlGnBu")),
+ values = c(0, exp(seq(-5, 0, length.out = 100))))
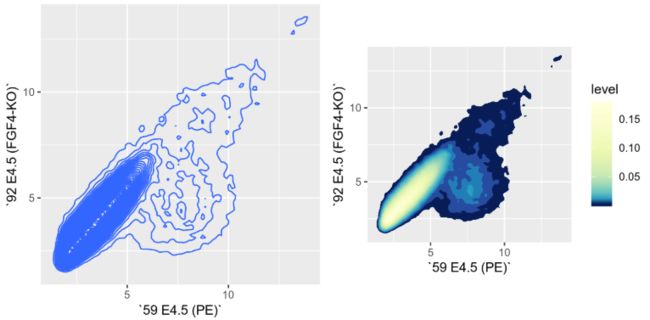
> scp + stat_density2d(h = 0.5, bins = 60,
+ aes( fill = ..level..), geom = "polygon") +
+ colorscale + coord_fixed()
我们可以用
点的相对密度来填充等高线之间的每个空间,方法是调用stat_density2d函数(对于这个函数,geom_density2d是一个wrapper),并使用几何对象多边形polygon。如 图3.28右边我们使用RColorBrewer的
brewer.pal函数来定义颜色,使用coord_fixed函数来调整画图的长宽比例。
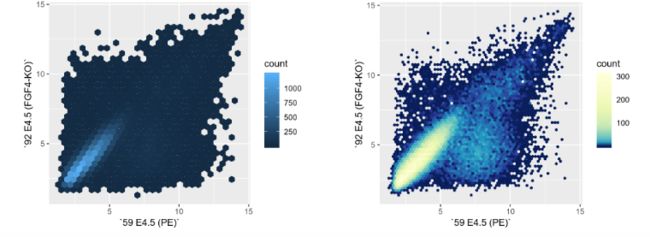
> scp + geom_hex() + coord_fixed()
Warning message:
程辑包‘hexbin’是用R版本3.5.2 来建造的
> scp + geom_hex(binwidth = c(0.2, 0.2)) + colorscale +
+ coord_fixed()
3.7.1 Plot shapes
library(ggthemes)
library(tidyverse)
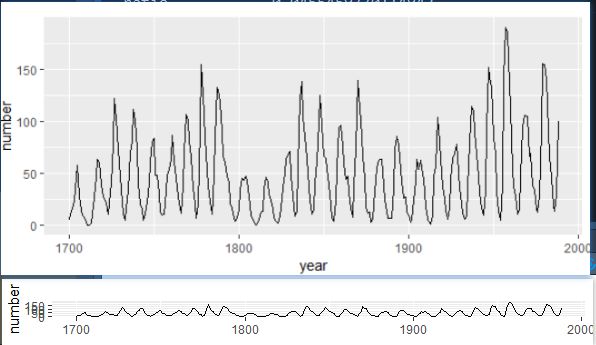
sunsp <- tibble(year = time(sunspot.year),
number = as.numeric(sunspot.year))
sp = ggplot(sunsp, aes(year, number)) +
geom_line()
sp
ratio = with(sunsp, bank_slopes(year, number))
sp + coord_fixed(ratio = ratio)
3.8 两个以上的维度的可视化
-
geom_point函数的相关参数- fill
- color
- shape
- size
- alpha
3.8.1 faceting 分面
library(magrittr)
library("Hiiragi2013")
data("x")
dftx = data.frame(t(Biobase::exprs(x)), pData(x))
dftx$lineage %<>% sub("^$", "no", .) #将空白的替换为’no'
dftx$lineage %<>% factor(levels = c("no", "EPI", "PE", "FGF4-KO")) # 变为factor
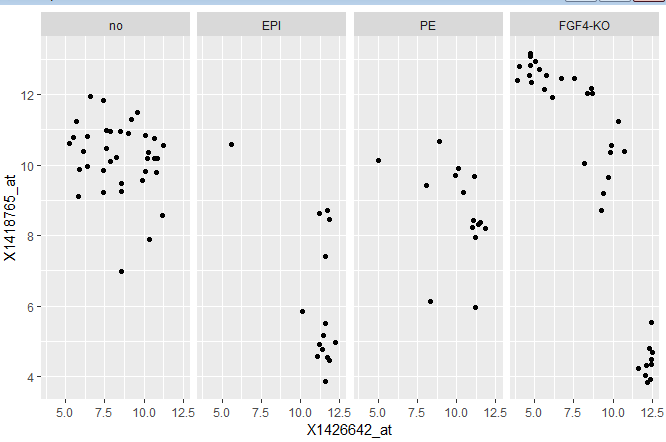
ggplot(dftx, aes(x = X1426642_at, y = X1418765_at)) +
geom_point() +
facet_grid(.~lineage)
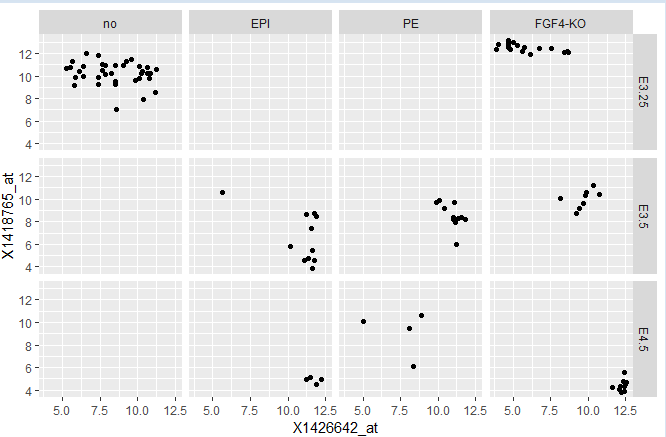
ggplot( dftx, aes( x = X1426642_at, y = X1418765_at)) +
geom_point() +
facet_grid( Embryonic.day ~ lineage )
- 另外一个分面函数
facet_wrap,结合mutate函数来进行清洗可视化数据。-
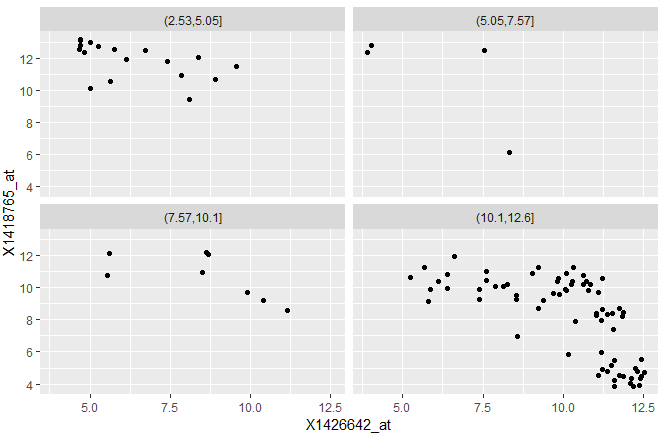
cut:break = 4将数据分成四个级别
-
ggplot(mutate(dftx, Tdgf1 = cut(X1450989_at, breaks = 4)),
aes( x = X1426642_at, y = X1418765_at)) + geom_point() +
facet_wrap( ~ Tdgf1, ncol = 2 )
3.8.2 交互式可视化
-
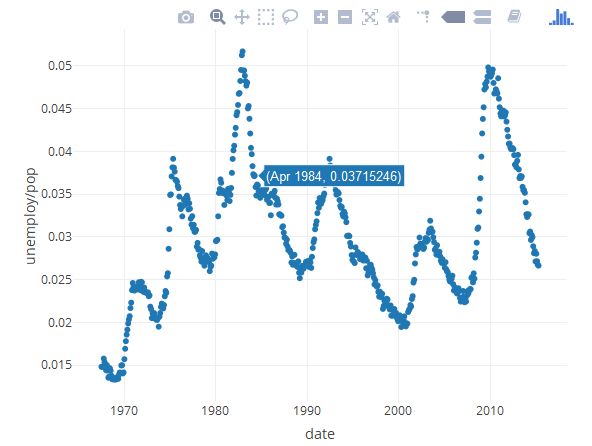
shiny、ggvis、plotly、
library("plotly")
plot_ly(economics, x = ~ date, y = ~ unemploy / pop)
rgl, webgl
data("volcano")
nrow(volcano)
[1] 87
volcanoData = list(
x = 10 * seq_len(nrow(volcano)),
y = 10 * seq_len(ncol(volcano)),
z = volcano,
col = terrain.colors(500)[cut(volcano, breaks = 500)]
)
# install.packages("rgl")
library("rgl")
with(volcanoData, persp3d(x, y, z, color = col))
3.9 Color 配色
pie(rep(1, 8), col=1:8)
- 然而默认的颜色搭配是很丑的。。所以这里要引入一个包
RColorBrewer。
library(RColorBrewer)
display.brewer.all() # 展示所以配色方案
head(brewer.pal.info)
maxcolors category colorblind
BrBG 11 div TRUE
PiYG 11 div TRUE
PRGn 11 div TRUE
PuOr 11 div TRUE
RdBu 11 div TRUE
RdGy 11 div FALSE
table(brewer.pal.info$category)
div qual seq
9 8 18
brewer.pal(4, "RdYlGn") # 查看具体的配色
[1] "#D7191C" "#FDAE61" "#A6D96A" "#1A9641"
- 如果我们需要更多的预设颜色(例如,我们可以用连续颜色绘制热图),我们可以使用
ColorRampPalette函数进行插值。
mypalette = colorRampPalette(c("darkorange3", "white","darkblue"))(100)
head(mypalette)
[1] "#CD6600" "#CE6905" "#CF6C0A" "#D06F0F" "#D17214" "#D27519"
par(mai = rep(0.1, 4))
image(matrix(1:100, nrow = 100, ncol = 10),
col = mypalette,
xaxt = "n", yaxt = "n", useRaster = TRUE)
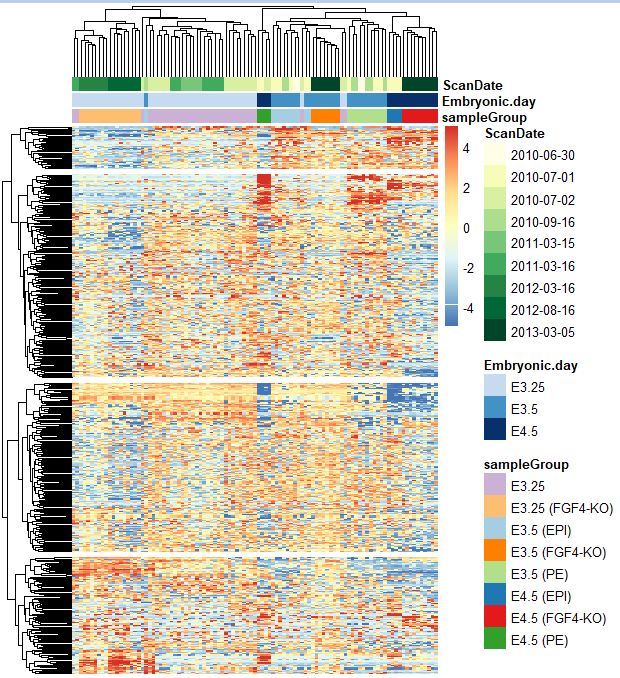
3.10 Heatmaps 热图
library("pheatmap")
topGenes = order(rowVars(Biobase::exprs(x)), decreasing = TRUE)[1:500]
head(topGenes)
[1] 33554 33434 18890 4404 2199 4405
rowCenter = function(x) { x - rowMeans(x) } ## 中心化均一化
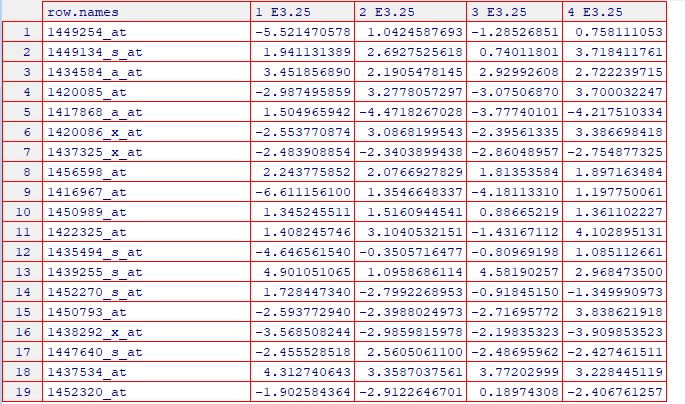
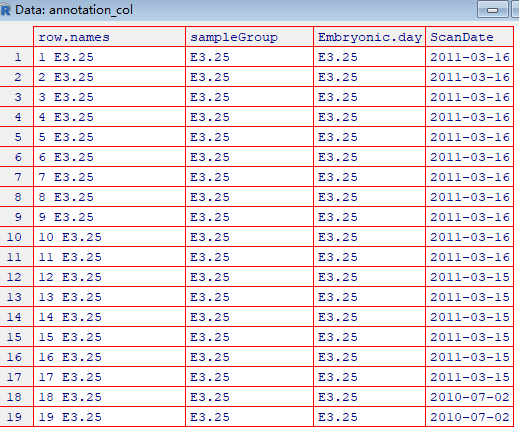
pheatmap( rowCenter(Biobase::exprs(x)[ topGenes, ] ),
show_rownames = FALSE, show_colnames = FALSE,
breaks = seq(-5, +5, length = 101),
annotation_col =
pData(x)[, c("sampleGroup", "Embryonic.day", "ScanDate") ],
annotation_colors = list(
sampleGroup = groupColor,
genotype = c(`FGF4-KO` = "chocolate1", `WT` = "azure2"),
Embryonic.day = setNames(brewer.pal(9, "Blues")[c(3, 6, 9)],
c("E3.25", "E3.5", "E4.5")),
ScanDate = setNames(brewer.pal(nlevels(x$ScanDate), "YlGn"),
levels(x$ScanDate))
),
cutree_rows = 4
)
> data <- rowCenter(Biobase::exprs(x)[ topGenes, ] )
> View(data)
3.12 Mathematical symbols and other fonts
- 数学公式展示:支持
LaTeX语法
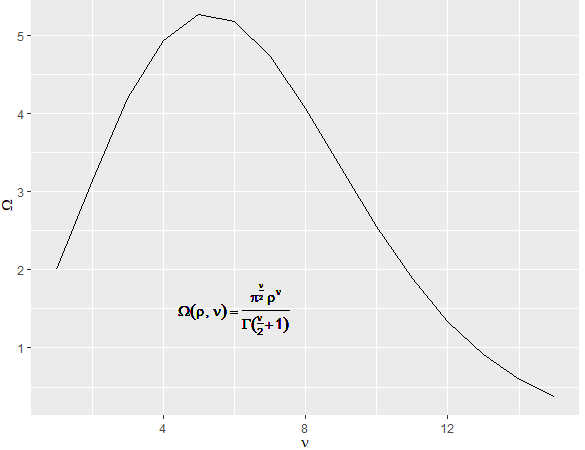
volume = function(rho, nu) pi^(nu/2) * rho^nu / gamma(nu/2+1)
ggplot(tibble(nu = 1:15,
Omega = volume(1, nu)), aes(x = nu, y = Omega)) +
geom_line() +
xlab(expression(nu)) + ylab(expression(Omega)) +
geom_text(label =
"Omega(rho,nu)==frac(pi^frac(nu,2)~rho^nu, Gamma(frac(nu,2)+1))",
parse = TRUE, x = 6, y = 1.5)
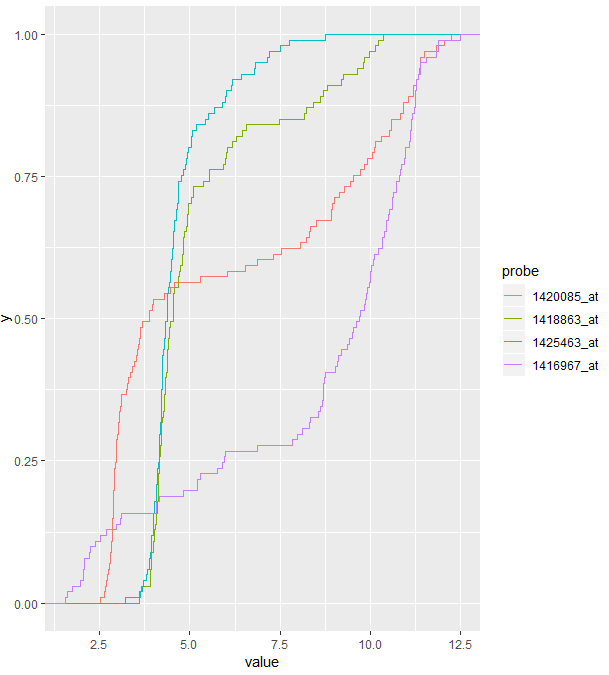
library(reshape2)
genes = melt(Biobase::exprs(x)[selectedProbes, ],
varnames = c("probe", "sample"))
ggplot(genes, aes( x = value, color = probe)) + stat_ecdf() +
theme(text = element_text(family = "Times"))
3.13 Genomic data
library("ggbio")
data("hg19IdeogramCyto", package = "biovizBase")
plotIdeogram(hg19IdeogramCyto, subchr = "chr1")
> hg19IdeogramCyto
GRanges object with 862 ranges and 2 metadata columns:
seqnames ranges strand | name gieStain
|
[1] chr1 0-2300000 * | p36.33 gneg
[2] chr1 2300000-5400000 * | p36.32 gpos25
[3] chr1 5400000-7200000 * | p36.31 gneg
[4] chr1 7200000-9200000 * | p36.23 gpos25
[5] chr1 9200000-12700000 * | p36.22 gneg
... ... ... ... . ... ...
[858] chrY 15100000-19800000 * | q11.221 gpos50
[859] chrY 19800000-22100000 * | q11.222 gneg
[860] chrY 22100000-26200000 * | q11.223 gpos50
[861] chrY 26200000-28800000 * | q11.23 gneg
[862] chrY 28800000-59373566 * | q12 gvar
-------
seqinfo: 24 sequences from an unspecified genome; no seqlengths
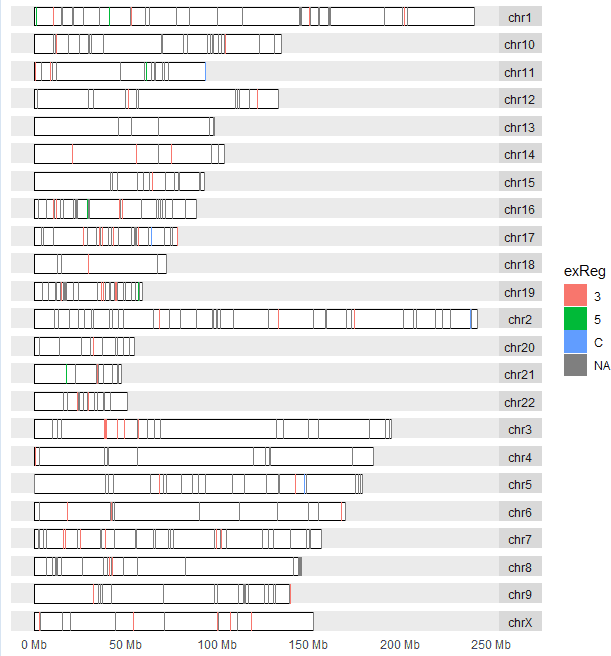
- The
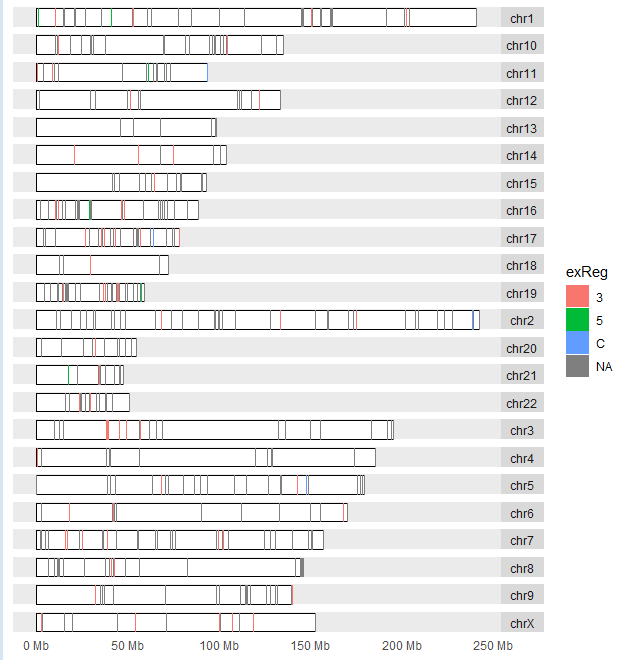
darned_hg19_subset500lists a selection of 500 RNA editing sites in the human genome. It was obtained from the Database of RNA editing in Flies, Mice and Humans(DARNED, http://darned.ucc.ie). The result is shown in Figure 3.46.
library("GenomicRanges")
data("darned_hg19_subset500", package = "biovizBase")
autoplot(darned_hg19_subset500, layout = "karyogram",
aes(color = exReg, fill = exReg))
> darned_hg19_subset500
GRanges object with 500 ranges and 10 metadata columns:
seqnames ranges strand | inchr inrna snp gene seqReg exReg source
|
[1] chr5 86618225 - | A I O amygdala
[2] chr7 99792382 - | A I O
[3] chr12 110929076 - | A I O salivary gland
[4] chr20 25818128 - | A I O brain, hippocampus
[5] chr3 132397992 + | A I O small intestine
... ... ... ... . ... ... ... ... ... ... ...
[496] chr9 115193271 + | A I HSDL2 I cerebellum
[497] chr8 145628605 - | A I CPSF1 I blood, adult leukocytes
[498] chr11 12501615 + | A I PARVA I mammary gland
[499] chr19 14845136 - | A I EMR2 E 3
[500] chr1 84980542 - | A I O liver
ests esta author
[1] 0 0 15342557
[2] 0 0 15342557
[3] 0 0 15342557
[4] 0 0 15342557
[5] 0 0 15342557
... ... ... ...
[496] 0 0 15342557
[497] 0 0 15258596:15342557
[498] 0 0 15258596:15342557
[499] 0 0 15258596
[500] 0 0 15342557
-------
seqinfo: 23 sequences from an unspecified genome; no seqlengths