这一节我们主要在2 排序基础 - 1选择排序法
基础上增添了模板:
C++代码:
Student.h:
#ifndef INC_02_SELECTION_SORT_USING_TEMPLATE_STUDENT_H
#define INC_02_SELECTION_SORT_USING_TEMPLATE_STUDENT_H
#include
#include
using namespace std;
struct Student {
string name;
int score;
// 重载小于运算法,定义Student之间的比较方式
// 如果分数相等,则按照名字的字母序排序
// 如果分数不等,则分数高的靠前
bool operator<(const Student& otherStudent) {
return score != otherStudent.score ?
score > otherStudent.score : name < otherStudent.name;
}
// 重载<<符号, 定义Student实例的打印输出方式
// * 很多同学看到这里的C++语法, 头就大了, 甚至还有同学表示要重新学习C++语言
// * 对于这个课程, 大可不必。C++语言并不是排序重点,
friend ostream& operator<<(ostream &os, const Student &student) {
os << "Student: " << student.name << " " << student.score << endl;
return os;
}
};
#endif //INC_02_SELECTION_SORT_USING_TEMPLATE_STUDENT_H
main.cpp:
#include
#include
#include
#include "Student.h"
using namespace std;
template
void selectionSort(T arr[], int n) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
// 寻找[i, n)区间里的最小值
int minIndex = i;
for (int j = i + 1; j < n; j++)
if (arr[j] < arr[minIndex])
minIndex = j;
swap(arr[i], arr[minIndex]);
}
}
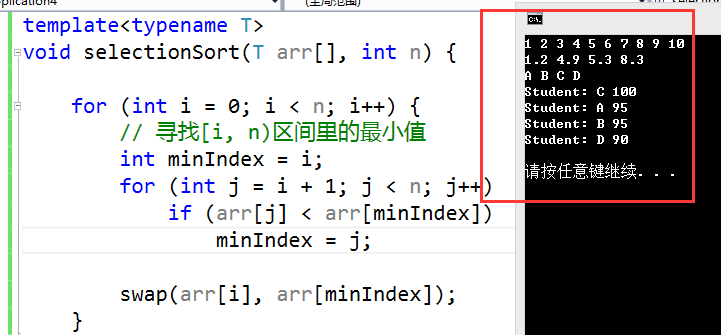
int main() {
int a[10] = { 10,9,8,7,6,5,4,3,2,1 };
selectionSort(a, 10);
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
cout << a[i] << " ";
cout << endl;
float b[4] = {1.2,5.3,4.9,8.3};
selectionSort(b, 4);
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
cout << b[i] << " ";
cout << endl;
string c[4] = {"D","C","B","A"};
selectionSort(c, 4);
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
cout << c[i] << " ";
cout << endl;
Student d[4] = { {"D",90},{"C",100},{"B",95},{"A",95} };
selectionSort(d, 4);
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i ++) {
cout << d[i];
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
C++结果:
java代码:
Student.java:
import java.util.*;
public class Student implements Comparable {
private String name;
private int score;
public Student(String name, int score){
this.name = name;
this.score = score;
}
// 定义Student的compareTo函数
// 如果分数相等,则按照名字的字母序排序
// 如果分数不等,则分数高的靠前
@Override
public int compareTo(Student that) {
if( this.score == that.score )
return this.name.compareTo(that.name);
if( this.score < that.score )
return 1;
else if( this.score > that.score )
return -1;
else // this.score == that.score
return 0;
}
// 定义Student实例的打印输出方式
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student: " + this.name + " " + Integer.toString( this.score );
}
}
SelectionSort.java:
import java.util.*;
public class SelectionSort {
// 我们的算法类不允许产生任何实例
private SelectionSort(){}
public static void sort(Comparable[] arr){
int n = arr.length;
for( int i = 0 ; i < n ; i ++ ){
// 寻找[i, n)区间里的最小值的索引
int minIndex = i;
for( int j = i + 1 ; j < n ; j ++ )
// 使用compareTo方法比较两个Comparable对象的大小
if( arr[j].compareTo( arr[minIndex] ) < 0 )
minIndex = j;
swap( arr , i , minIndex);
}
}
private static void swap(Object[] arr, int i, int j) {
Object t = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[j];
arr[j] = t;
}
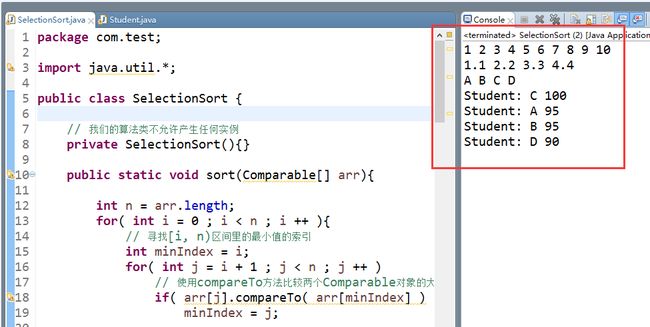
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 测试Integer
Integer[] a = {10,9,8,7,6,5,4,3,2,1};
SelectionSort.sort(a);
for( int i = 0 ; i < a.length ; i ++ ){
System.out.print(a[i]);
System.out.print(' ');
}
System.out.println();
// 测试Double
Double[] b = {4.4, 3.3, 2.2, 1.1};
SelectionSort.sort(b);
for( int i = 0 ; i < b.length ; i ++ ){
System.out.print(b[i]);
System.out.print(' ');
}
System.out.println();
// 测试String
String[] c = {"D", "C", "B", "A"};
SelectionSort.sort(c);
for( int i = 0 ; i < c.length ; i ++ ){
System.out.print(c[i]);
System.out.print(' ');
}
System.out.println();
// 测试自定义的类 Student
Student[] d = new Student[4];
d[0] = new Student("D",90);
d[1] = new Student("C",100);
d[2] = new Student("B",95);
d[3] = new Student("A",95);
SelectionSort.sort(d);
for( int i = 0 ; i < d.length ; i ++ )
System.out.println(d[i]);
}
}
java结果: