概念
顺序表(Sequential List) 就是按照顺序存储方式存储的线性表,该线性表的结点按照逻辑次序一次存放在计算机的一组连续的存储单元中.
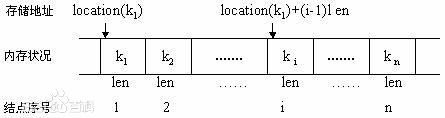
由于顺序表示一次存放的,只要知道了该顺序表的首地址及每个数据元素所占用的存储长度,那么就很容易计算出任何一个数据元素
所在的位置.
如下图:
准备数据
下面我们开始顺序表的程序设计,首先需要准备数据,也就是准备在顺序表中需要用到的变量及数据结构等.代码如下:
static final int MAXLEN = 100; //定义顺序表的最大长度
class DATA //存储在数据结点的数据,可以当做学生
{
String key;
String name;
int age;
}
class SLType //定义顺序表结构
{
DATA [] ListData = new DATA[MAXLEN]; //保存顺序表的结构数据
int ListLen; //顺据表已存结点的数量
}
上面的代码中,定义了顺序表的最大长度MAXLEN,顺序表的数据元素DATA及顺序表的类SLType,ListLen为顺序表已存结点的
数量,即当前顺序表的长度,ListData是一个对象数组,用来存放各个数据结点.
由于我们用java语言中数组都是从下表0开始的,在这里,为了讲述和理解的方便,从下标1开始记录数据结点,下标0的位置不用.
初始化顺序表
在使用顺序表之前,首先要创建一个空的顺序表,这里我们只需要设置顺序表的结点数量ListLen为0就可以了
public void SLInit(SLType SL){
SL.ListLen = 0;
}
计算顺序表的长度
由于ListLen就是代表顺序表已存结点的数量,所以直接返回它就可以了.
public int SLLength(SLType SL){
return SL.ListLen;
}
插入结点
插入结点就是在顺序表的第i个位置插入一个新的结点,使得其后的所有结点都向后移动一个位置,也就是编号依次加1,
线性表的长度变为n+1,插入结点的难点在于随后的每个位置都需要进行移动.
public int Insert(SLType SL,int n,DATA data){
int i;
if(SL.ListLen>=MAXLEN){ //判断顺序表是否已满
System.out.println("顺序表已满,不能插入结点!\n");
return 0;
}
if(n<1||n>SL.ListLen+1){ //判断插入符号是否正确
System.out.println("插入元素序号错误,不能插入元素!\n");
return 0;
}
for (int j = SL.ListLen; j>n; j--) { //将顺序表中的数据向后移动
SL.ListData[j+1]=SL.ListData[j];
}
SL.ListData[n]=data; //插入位置
SL.ListLen++;
return 1; //成功插入,返回1
}
在上述代码中,在程序中首先判断顺序表结点数量是否已经满了,以及插入结点后是否正确,所有条件都满足后,然后将顺序表中数据向后移动一个位置,同时插入结点,并更新结点的数量.
追加结点
追加结点因为不需要移动数据,所以事先起来比较简单:
public int SLAdd(SLType SL,DATA data){
if(SL.ListLen >= MAXLEN){ //判断是否已满
System.out.println("顺序表已满,不能再添加结点了");
return 0;
}
SL.ListData[++SL.ListLen] = data;
return 1;
}
删除结点
删除结点即删除线性表L中第i个结点,使得其后的所有结点便后依次减一,删除一个结点之后,线性表L的长度变为n-1,删除类似添加,删除后需要进行大量的数据移动.
public int SLDeleteType(SLType SL,int n){
int i;
if(n<1||n>SL.ListLen+1){ //判断插入符号是否正确
System.out.println("删除元素符号错误!\n");
return 0;
}
for (i = n; i <= SL.ListLen; i++) { //顺序表中的元素向前移动
SL.ListData[n+1] = SL.ListData[n];
}
SL.ListLen--; //顺序表的元素数量减一
return 1;
}
查找结点
查找结点就是根据线性表L中查找x的结点,并返回该结点在L中位置,如果没有找到该结点,则返回一个错误标识,根据x的不同,
有两种方式来查找,一种是x是结点位置,直接同x返回该结点的数据,如果x是关键字,则通过比对关键字,然后返回x的位置.
1.按照序号查找结点
public DATA SLFindByNum(SLType SL,int n){ //根据序号返回数据元素
if(n<1||n>SL.ListLen+1){
System.out.println("查找符号错误!\n");
return null;
}
return SL.ListData[n];
}
2.按照关键字查找结点
public int SLFindByCout(SLType SL,String key){ //按照关键字查找元素
int j;
for (j = 1; j < SL.ListLen; j++) {
if(SL.ListData[j].key.compareTo(key)==0){
return j;
}
}
return 0;
}
下面是所有代码:
package SequentialList;
public class SLType {
static final int MAXLEN = 100;
//定义顺序表结构
DATA [] ListData = new DATA[MAXLEN+1];//保存顺序表的结构数组
int ListLen; //顺序表已存节点的数量
/**
* 初始化顺序表
* @param SL
*/
public void SLInit(SLType SL){
SL.ListLen=0;//初始化空表
}
/**
* 返回顺序表的元素数量
*/
public int SLLength(SLType SL){
return SL.ListLen;
}
/**
* 插入结点
* 插入结点就是在线性表的第i个位置插入一个新的结点,使得其后的结点编号依次加1,这时,插入一个结点后,线性表的长度L将变为
* n+1,插入结点的难点在于随后的每个结点的数据都要向后移动
* @return
*/
public int Insert(SLType SL,int n,DATA data){
int i;
if(SL.ListLen>=MAXLEN){ //判断顺序表是否已满
System.out.println("顺序表已满,不能插入结点!\n");
return 0;
}
if(n<1||n>SL.ListLen+1){ //判断插入符号是否正确
System.out.println("插入元素序号错误,不能插入元素!\n");
return 0;
}
for (int j = SL.ListLen; j>n; j--) { //将顺序表中的数据向后移动
SL.ListData[j+1]=SL.ListData[j];
}
SL.ListData[n]=data; //插入位置
SL.ListLen++;
return 1; //成功插入,返回1
}
/**
* 增加元素到顺序表尾部
* @param SL
* @param data
* @return
*/
public int SLAdd(SLType SL,DATA data){
if(SL.ListLen >= MAXLEN){ //判断是否已满
System.out.println("顺序表已满,不能再添加结点了");
return 0;
}
SL.ListData[++SL.ListLen] = data;
return 1;
}
/**
* 删除顺序表中的数据元素
* 顺序表删掉第i个结点,那么之后的所有结点的位置都需要向前移动一个位置
* @return
*/
public int SLDeleteType(SLType SL,int n){
int i;
if(n<1||n>SL.ListLen+1){ //判断插入符号是否正确
System.out.println("删除元素符号错误!\n");
return 0;
}
for (i = n; i < =SL.ListLen; i++) { //顺序表中的元素向前移动
SL.ListData[n+1] = SL.ListData[n];
}
SL.ListLen--; //顺序表的元素数量减一
return 1;
}
/**
* 按照序号查找结点
* @return
*/
public DATA SLFindByNum(SLType SL,int n){ //根据序号返回数据元素
if(n<1||n>SL.ListLen+1){
System.out.println("查找符号错误!\n");
return null;
}
return SL.ListData[n];
}
/**
* 按照关键字查找结点 返回结点序号
* @return
*/
public int SLFindByCout(SLType SL,String key){ //按照关键字查找元素
int j;
for (j = 1; j <= SL.ListLen; j++) {
if(SL.ListData[j].key.compareTo(key)==0){
return j;
}
}
return 0;
}
/**
* 返回所有结点
* @return
*/
public int SLAll(SLType SL){
int i;
for(i =1;i<=SL.ListLen;i++){
System.out.printf("(%s,%s,%d)\n",SL.ListData[i].key,SL.ListData[i].name,SL.ListData[i].age);
}
return i;
}
}
上面就是顺序表的java代码实现.
原来你是这样的数据结构之链表结构