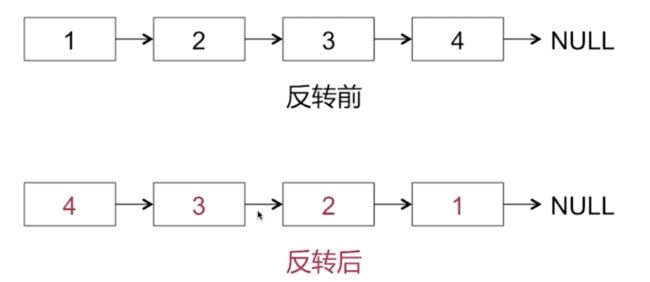
字符串反转
将字符串hello, world反向输出
void char_reverse(char*cha){
// 指向第一个字符
char * begin = cha;
// 指向最后一个字符
char * end = cha + strlen(cha) -1;
while (begin < end){
//交换两个字符的位置,并向中间移动一位
char temp = *begin;
*(begin ++) = *end;
*(end--) = temp;
}
}
char ch[] = "hello,world";
char_reverse(ch);
printf("reverse result is %s",ch);
链表反转
ReverseList.h
#import
NS_ASSUME_NONNULL_BEGIN
//定义一个链表
struct Node {
int data;
struct Node * next;
};
@interface ReverseList : NSObject
//链表反转
struct Node * reverseList(struct Node * head);
//构造一个链表
struct Node * constructList(void);
//打印链表中的数据
void printList(struct Node * head);
@end
ReverseList.m
#import "ReverseList.h"
@implementation ReverseList
struct Node * reverseList(struct Node * head){
//定义遍历指针,初始化为头节点
struct Node * p = head;
//反转后的b链表头部
struct Node * newH = NULL;
while (p != NULL) {
//记录下一个节点
struct Node * temp = p->next;
//当前节点的next指向新链表头部
p->next = newH;
//更改新链表头部为当前节点
newH = p;
//移动p指针
p = temp;
}
//返回反转后的链表头节点
return newH;
}
//构造一个链表
struct Node * constructList(void){
//头节点定义
struct Node * head = NULL;
//记录当前节点尾节点
struct Node * cur = NULL;
for (int i = 1; i < 5; i++) {
struct Node * node = malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
node->data = I;
if (head == NULL) {
head = node;
}
else{
//当前节点的next为新节点
cur->next = node;
}
cur = node;
}
return head;
}
//打印链表中的数据
void printList(struct Node * head){
struct Node * temp = head;
while (temp != NULL) {
printf("node is %d \n",temp->data);
temp = temp->next;
}
}
@end
调用
//单链表反转
struct Node * head = constructList();
printList(head);
printf("--------------------\n");
struct Node * newHead = reverseList(head);
printList(newHead);
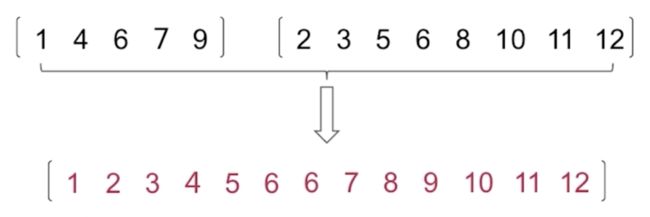
有序数组合并
思想
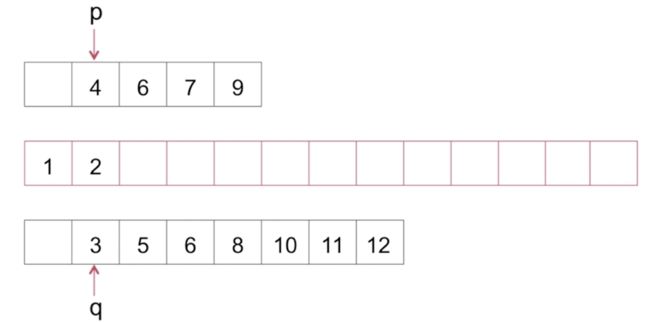
如上图,比较p、q两个指针分别指向的数据大小,小的填充带新数组中,兵移动相应指针,大的数据指针不动,然后继续这样比较,当一个数组的数据被完全填充后, 把另一个数组的数据依次填充到新数组中。
算法实现
MergeSortedList.h
#import
NS_ASSUME_NONNULL_BEGIN
@interface MergeSortedList : NSObject
//将有序数组a和有序数组b合并到一个数组result当中,且仍然保持有序
void mergeList(int a[], int aLen, int b[], int bLen, int result[]);
@end
NS_ASSUME_NONNULL_END
MergeSortedList.m
#import "MergeSortedList.h"
@implementation MergeSortedList
//将有序数组a和有序数组b合并到一个数组result当中,且仍然保持有序
void mergeList(int a[], int aLen, int b[], int bLen, int result[])
{
int p = 0;//遍历数组a的指针
int q = 0;//遍历数组b的指针
int i = 0;//记录当前储存位置
//任一数组没有达到边界遍历
while (p < aLen && q < bLen) {
//如果a数组对应位置小于b数组对应位置的值
if (a[p] < b[q]) {
//储存a数组的b值
result[i] = a[p];
//移动p指针的位置
p++;
}
else{
//储存b数组的b值
result[i] = b[q];
//移动q指针的位置
q++;
}
I++;
}
//如果a数组有剩余
while (p < aLen) {
result[i] = a[p++];
I++;
}
//如果b数组有剩余
while (q < bLen) {
result[i] = b[q++];
I++;
}
}
@end
算法调用
int a[5] = {1,4,6,7,9};
int b[8] = {2,3,5,6,8,10,11,12};
int result[13];
mergeList(a, 5, b, 8, result);
for (int i = 0; i < 13; i++) {
printf("%d ",result[I]);
}
Hash算法
在一个字符串中找出第一个只出现一次的字符;
如:输入abccdeff,则输出 b
算法思路
- 字符(char)是一个长度为8的数据类型,因此用功有2^8 =256种可能
- 每个字母根据其ASCII码值作为数组的下标对应数组的一个数字
- 数组中存储的是每个字符出现的次数
哈希表概念
例:给定值是字母a,对应的ASCII值是97,数组索引下标为97
char ----f(key)---->index
f(key) = key
·存储和查找都通过该函数,有效提高查找效率·
算法实现
///查找第一个只出现一次的字符
char findFirstChar(char * cha){
char result = '\0';
//定义一个数组用来存储哥哥字母出现的次数
int array[256];
//对数组进行初始化操作
for (int i = 0; i<256; i++) {
array[i] = 0;
}
//定义一个指针 指向当前字符串的头部
char * p = cha;
//遍历每个字符
while (*p != '\0') {
//在字母对应存储位置 进行出现洗漱+1操作
array[*(p++)]++;
}
// 将P值装重新指向字符串头部
p = cha;
// 遍历每个字母出现的次数
while (*p != '\0') {
//遇到第一个出现次数为1的字符打印结果
if (array[*p] == 1) {
result = *p;
break;
}
//反之继续查找
p++;
}
return result;
}
char cha[] = "abaccdeff";
char fc = findFirstChar(cha);
printf("this char is %c \n",fc);
查找两个子视图的共同父视图
思路:
算法实现
///查找两个视图的共同父视图
- (NSArray *)findCommonSuperView:(UIView *)viewOne other:(UIView *)viewOther{
NSMutableArray * result = [NSMutableArray array];
//查找第一个视图的所有父视图
NSArray * arrayOne = [self findSuperViews:viewOne];
//查找第二个视图的所有父视图
NSArray * arrayOther = [self findSuperViews:viewOther];
int i = 0;
while (i < MIN((int)arrayOne.count, (int)arrayOther.count)) {
//倒序获取各个视图的父视图
UIView * superOne = [arrayOne objectAtIndex:arrayOne.count - i - 1];
UIView * superOther = [arrayOne objectAtIndex:arrayOther.count - i - 1];
if (superOne == superOther) {
[result addObject:superOne];
I++;
}
//如果不相同,结束遍历
else{
break;
}
}
return result;
}
-(NSArray *)findSuperViews:(UIView *)view{
//初始化为第一父视图
UIView * temp = view.superview;
//保存结果的数组
NSMutableArray * result = [NSMutableArray array];
while (temp) {
[result addObject:temp];
temp = temp.superview;
}
return result;
}
无序数组求中位数
首先理解一下中位数,比如[1,3,5,7,8],那么中位数就为“5”,若是[1,3,5,7,8,10],那么中位数便为中间两位的平局值,即(5+7)/2 = 6;
那么无序数组求中位数,有哪些方法?
- 排序算法+中位数
- 利用快排思想(分治思想)
排序算法+中位数
冒泡排序、快速排序、堆排序……
中位数
当n为奇数,为(n+1)/2;
当n为偶数,为((n/2)+(n/2)+1)/2;
快排思想
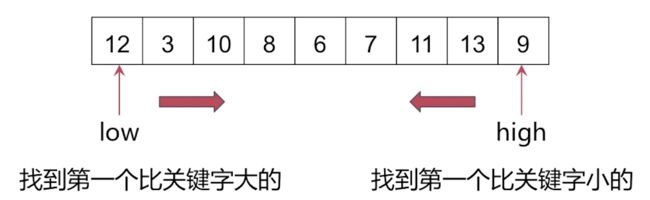
选取关键字,高低交替扫描
- 任意挑选一个元素,以该元素为支点,划分集合为两部分。
- 如果左侧集合长度恰好为(n-1)/2,那么支点恰为中位数。
- 如果左侧长度小于(n-1)/2,那么中位点在右侧;反之,中位数在右侧。
- 进入相应一侧继续寻找中位点。
算法实现
///无序数组中查找中位数
float findMideian(int a[], int aLen){
int low = 0;
int high = aLen - 1;
int mid = (aLen - 1)/2;
int div = PartSort(a , low, high);
while (div != mid) {
if (mid < div) {
//左半区找
div = PartSort(a, low, div - 1) ;
}
else{
//右半区找
div = PartSort(a, div + 1, high) ;
}
}
if (aLen % 2 == 1) {
//若为奇数
return a[mid];
}
else{
//若为偶数
int mid1 = (aLen + 1)/2;
while (div != mid1) {
if (mid1 < div) {
//左半区找
div = PartSort(a, low, div - 1) ;
}
else{
//右半区找
div = PartSort(a, div + 1, high) ;
}
}
return (a[mid] + a[mid1])/2.0;
}
}
///快排
int PartSort(int a[], int start, int end){
int low = start;
int high = end;
//选取关键字
int key = a[end];
while (low < high) {
//左边找比key大的值
while (low < high && a[low] <= key) {
++low;
}
//右边找比key小的值
while (low < high && a[high] >= key) {
--high;
}
if (low < high) {
//找到之后交换左右的值
int temp = a[low];
a[low] = a[high];
a[high] = temp;
}
}
int temp = a[high];
a[high] = a[end];
a[end] = temp;
return low;
}
具体源码可在这里查看。