这里说的AMS进程,实际指的是System_server进程,System_server进程起来的时候启动AMS服务,AMS实际是ActivityManagerService的缩写。
ActivityManagerService
管理Activity的生命周期
ActivityManagerNative
ActivityManagerService在服务器端的实现,客户端的请求调用ActivityManagerProxy后,通过IBinder,最终会在ActivityManagerNative中实现。ActivityManagerNative再通过调用ActivityManagerService的相关功能,以完成客户端请求。
ActivityManagerProxy
ActivityManagerService的在客户端的代理。负责和服务器端的ActivityManagerNative通讯。
点击应用目录中应用icon的启动流程
(1)LauncherActivity通过Binder进程间通信的方式将应用的信息通过Intent的方式传递给AMS,由AMS进行调度。
(2)如果系统中不存在该进程时,AMS将会请求Zygote服务去fork一个子进程,成功后返回一个pid给AMS,并由AndroidRuntime机制调起ActivityThread中的main()方法。
(3)紧接着,应用程序的Main Looper被创建,ActivityThread被实例化成为对象并将Application的信息以进程间通信的方式再次回馈给AMS。此处指的是AMS会获得一个binder对象,即ApplicationThread。AMS就是通过这个binder对象来调用应用程序中的方法。同样的应用程序也通过AMS客户端的代理类,ApplicationProxy来调用AMS的方法。
(4)AMS接收到客户端发来的请求数据之后,首先将应用程序绑定,并启动应用程序的Activity,开始执行Activity的生命周期。
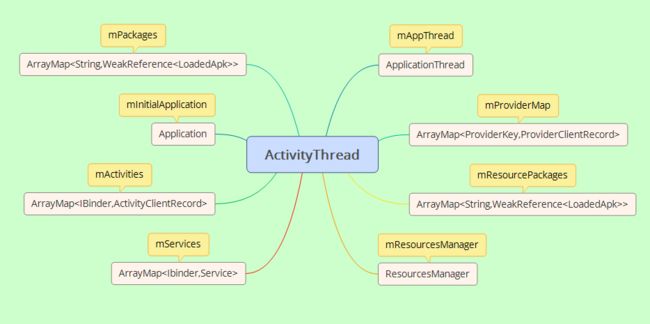
ActivityThread
从图中可以知道,mActivities、mServices和mProviderMap 这三个变量都被保存在ArrayMap之中,他们分别保存了应用中所有的Activity对象、Services对象、和ContentProvider对象。 咦?同为四大组件的BroadcastReceive去哪里了?注意,BroadcastReceiver对象没有必要用任何数据结构来保存,因为BroadcastReceiver对象的生命周期很短暂,属于我调用它时,再创建运行,因此不需要保存BroadcastReceiver的对象。
我们都知道应用中Applicaiton对象是唯一的,而mInitialApplication变量是恰恰是Application对象。当你的应用自定义一个派生Applicaiton类,则它就是mInitialApplication了。
ApplicationThread类型变量mAppThread是一个Binder实体对象,ActivityManagerService作为Client端调用ApplicationThread的接口,目的是用来调度管理Activity。
变量mResourcesManager管理着应用中的资源。
ActivityThread相当于一个CEO,管理调度着几乎所有的Android应用进程的资源和四大组件
ActivityThread的main函数
public static void More ...main(String[] args) {
5220 SamplingProfilerIntegration.start();
5221
5222 // CloseGuard defaults to true and can be quite spammy. We
5223 // disable it here, but selectively enable it later (via
5224 // StrictMode) on debug builds, but using DropBox, not logs.
5225 CloseGuard.setEnabled(false);
5226 // 初始化应用中需要使用的系统路径
5227 Environment.initForCurrentUser();
5228
5229 // Set the reporter for event logging in libcore
5230 EventLogger.setReporter(new EventLoggingReporter());
5231 //增加一个保存key的provider
5232 Security.addProvider(new AndroidKeyStoreProvider());
5233
5234 // Make sure TrustedCertificateStore looks in the right place for CA certificates //为应用设置当前用户的CA证书保存的位置
5235 final File configDir = Environment.getUserConfigDirectory(UserHandle.myUserId());
5236 TrustedCertificateStore.setDefaultUserDirectory(configDir);
5237 //设置进程的名称5238 Process.setArgV0("");
5239
5240 Looper.prepareMainLooper();
5241 //创建ActivityThread 对象
5242 ActivityThread thread = new ActivityThread();
5243 thread.attach(false);
5244
5245 if (sMainThreadHandler == null) {
5246 sMainThreadHandler = thread.getHandler();
5247 }
5248
5249 if (false) {
5250 Looper.myLooper().setMessageLogging(new
5251 LogPrinter(Log.DEBUG, "ActivityThread"));
5252 }
5253
5254 Looper.loop();
5255
5256 throw new RuntimeException("Main thread loop unexpectedly exited");
5257 }
下面的这段程序,首先Looper.prepareMainLooper();是为主线程创建了Looper,然后thread.getHandler();是保存了主线程的Handler,最后Looper.loop();进入消息循环。
Looper.prepareMainLooper(); //创建ActivityThread 对象
ActivityThread thread = new ActivityThread();
thread.attach(false);
if (sMainThreadHandler == null)
{
sMainThreadHandler =thread.getHandler();
}
if (false)
{
Looper.myLooper().setMessageLogging(new LogPrinter(Log.DEBUG,"ActivityThread"));
}
Looper.loop();
throw new RuntimeException("Main thread loop unexpectedly exited"); }
下面好好研究这段代码
ActivityThread thread = new ActivityThread();
thread.attach(false);
进入attach方法
private void attach(boolean system)
{
sCurrentActivityThread = this;
mSystemThread = system;
if (!system)
{ ...// 以上省略
RuntimeInit.setApplicationObject(mAppThread.asBinder());
final IActivityManager mgr = ActivityManagerNative.getDefault();
try
{
mgr.attachApplication(mAppThread);
}
catch (RemoteException ex)
{
throw ex.rethrowFromSystemServer();
} ...// 以下省略
}
}
mAppThread的初始化
final ApplicationThread mAppThread = new ApplicationThread();
mAppThread是ActivityThread的成员变量。调用ActivityManagerService的attachApplication()方法,将mAppThread 作为参数传入ActivityManagerService,这样ActivityManagerService就可以调用ApplicaitonThread的接口了。ActivityManagerService作为Client端调用ApplicaitonThread的接口管理Activity。
在应用中通过intent启动Activity的过程
首先调用startActivity,最后都会转到startActivityForResult。然后调用Instrumentation.execStartActivity,在execStartActivity里会调用ActivityManagerNative.getDefault().startActivity。ActivityManagerNative.getDefault()就是ActivityManagerProxy,这个是AMS在客户端进程使用的代理类,在ActivityManagerNative.getDefault()中会通过ServiceManager.getService("activity")获取ActivityManagerService 提供的 Binder 接口,并将这个binder传入ActivityManagerProxy。这样ActivityManagerProxy调用starActivity,里面就会调用了AMS的相应函数。这样就完成了从Activity到AMS的一次调用。那么如果AMS想要调用Activity的方法呢。这时候就用到刚才说的出入AMS的
参考资料:
Framework源码分析(一):ActivityManagerService
http://www.jianshu.com/p/194a37755fea
Framework源码分析(三):ActivityThread
http://www.jianshu.com/p/b6ac0c2fa240
ActivityThread的main方法究竟做了什么?
http://www.jianshu.com/p/0efc71f349c8
Android Activity生命周期是如何实现的
http://www.jianshu.com/p/27d06a6b7007
框架层理解Activity生命周期(APP启动过程)
http://www.cnblogs.com/feng9exe/p/5706890.html