匈牙利算法的理论依据-最优解定理
费用矩阵的一行(或列)的各个元素减去该行(或列)的最小元素所得到的新费用矩阵,与原费用矩阵对应的指派问题具有相同的最优解!
匈牙利算法的基本思路
- 通过行/列变换让费用矩阵的每行和每列都出现0
- 找出不同行不同列的n个0
- 这些0对应的指派就是最优指派
匈牙利算法的主要步骤
- 步骤一:对费用矩阵先作行变换,再作列变换
行变换:费用矩阵的每一行的各个元素分别减去该行的最小元素
列变换:费用矩阵的每一列的各个元素分别减去该列的最小元素,有0的列则无需作列变换 - 步骤二:在经过行变换和列变换的费用矩阵中寻找n个不同行不同列的0元素
如找到,则这n个不同行不同列的0元素位置即对应最优指派
否则,进行步骤三
在步骤二中,一般使用标记法来寻找n个不同行不同列的0元素
(1)依次检查新费用矩阵的各行,找出只有一个没有加标记的0元素的行,并将这个0元素加上标记“”,而与这个0元素在同一列的0元素全划去。
(2)依次检查新费用矩阵的各列,找出只有一个没有加标记的0元素的列,并将这个0元素加上标记“”,而与这个0元素在同一行的0元素全划去。 - 步骤三:对新费用矩阵进行调整
(1)对每一个加了标记的0元素画一条横线或竖线,使得这些横线和竖线覆盖全部0元素
(2)在这些横线和竖线没有经过的元素中找出最小的元素
(3)未画横线的各行元素减去这个最小的数,画竖线的各列元素加上这个最小的数
(4)重新在费用矩阵中找出n个不同行不同列的0元素,从而找出最优指派
更详细的内容见离散老师的课件2333
function [Matching,Cost] = Hungarian()
%
% [MATCHING,COST] = Hungarian_New(WEIGHTS)
%
% A function for finding a minimum edge weight matching given a MxN Edge
% weight matrix WEIGHTS using the Hungarian Algorithm.
%
% An edge weight of Inf indicates that the pair of vertices given by its
% position have no adjacent edge.
%
% MATCHING return a MxN matrix with ones in the place of the matchings and
% zeros elsewhere.
%
% COST returns the cost of the minimum matching
% Written by: Alex Melin 30 June 2006
Perf = [0 2 4 6 ; Inf 0 2 5; Inf 0 inf 4; inf inf inf 0];
% Initialize Variables
Matching = zeros(size(Perf));
% Condense the Performance Matrix by removing any unconnected vertices to
% increase the speed of the algorithm
% Find the number in each column that are connected
num_y = sum(~isinf(Perf),1);
% Find the number in each row that are connected
num_x = sum(~isinf(Perf),2);
% Find the columns(vertices) and rows(vertices) that are isolated
x_con = find(num_x~=0);
y_con = find(num_y~=0);
% Assemble Condensed Performance Matrix
P_size = max(length(x_con),length(y_con));
P_cond = zeros(P_size);
P_cond(1:length(x_con),1:length(y_con)) = Perf(x_con,y_con);
if isempty(P_cond)
Cost = 0;
return
end
% Ensure that a perfect matching exists
% Calculate a form of the Edge Matrix
Edge = P_cond;
Edge(P_cond~=Inf) = 0;
% Find the deficiency(CNUM) in the Edge Matrix
cnum = min_line_cover(Edge);
% Project additional vertices and edges so that a perfect matching
% exists
Pmax = max(max(P_cond(P_cond~=Inf)));
P_size = length(P_cond)+cnum;
P_cond = ones(P_size)*Pmax;
P_cond(1:length(x_con),1:length(y_con)) = Perf(x_con,y_con);
%*************************************************
% MAIN PROGRAM: CONTROLS WHICH STEP IS EXECUTED
%*************************************************
exit_flag = 1;
stepnum = 1;
while exit_flag
switch stepnum
case 1
[P_cond,stepnum] = step1(P_cond);
case 2
[r_cov,c_cov,M,stepnum] = step2(P_cond);
case 3
[c_cov,stepnum] = step3(M,P_size);
case 4
[M,r_cov,c_cov,Z_r,Z_c,stepnum] = step4(P_cond,r_cov,c_cov,M);
case 5
[M,r_cov,c_cov,stepnum] = step5(M,Z_r,Z_c,r_cov,c_cov);
case 6
[P_cond,stepnum] = step6(P_cond,r_cov,c_cov);
case 7
exit_flag = 0;
end
end
% Remove all the virtual satellites and targets and uncondense the
% Matching to the size of the original performance matrix.
Matching(x_con,y_con) = M(1:length(x_con),1:length(y_con));
Cost = sum(sum(Perf(Matching==1)));
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
% STEP 1: Find the smallest number of zeros in each row
% and subtract that minimum from its row
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
function [P_cond,stepnum] = step1(P_cond)
P_size = length(P_cond);
% Loop throught each row
for ii = 1:P_size
rmin = min(P_cond(ii,:));
P_cond(ii,:) = P_cond(ii,:)-rmin;
end
stepnum = 2;
%**************************************************************************
% STEP 2: Find a zero in P_cond. If there are no starred zeros in its
% column or row start the zero. Repeat for each zero
%**************************************************************************
function [r_cov,c_cov,M,stepnum] = step2(P_cond)
% Define variables
P_size = length(P_cond);
r_cov = zeros(P_size,1); % A vector that shows if a row is covered
c_cov = zeros(P_size,1); % A vector that shows if a column is covered
M = zeros(P_size); % A mask that shows if a position is starred or primed
for ii = 1:P_size
for jj = 1:P_size
if P_cond(ii,jj) == 0 && r_cov(ii) == 0 && c_cov(jj) == 0
M(ii,jj) = 1;
r_cov(ii) = 1;
c_cov(jj) = 1;
end
end
end
% Re-initialize the cover vectors
r_cov = zeros(P_size,1); % A vector that shows if a row is covered
c_cov = zeros(P_size,1); % A vector that shows if a column is covered
stepnum = 3;
%**************************************************************************
% STEP 3: Cover each column with a starred zero. If all the columns are
% covered then the matching is maximum
%**************************************************************************
function [c_cov,stepnum] = step3(M,P_size)
c_cov = sum(M,1);
if sum(c_cov) == P_size
stepnum = 7;
else
stepnum = 4;
end
%**************************************************************************
% STEP 4: Find a noncovered zero and prime it. If there is no starred
% zero in the row containing this primed zero, Go to Step 5.
% Otherwise, cover this row and uncover the column containing
% the starred zero. Continue in this manner until there are no
% uncovered zeros left. Save the smallest uncovered value and
% Go to Step 6.
%**************************************************************************
function [M,r_cov,c_cov,Z_r,Z_c,stepnum] = step4(P_cond,r_cov,c_cov,M)
P_size = length(P_cond);
zflag = 1;
while zflag
% Find the first uncovered zero
row = 0; col = 0; exit_flag = 1;
ii = 1; jj = 1;
while exit_flag
if P_cond(ii,jj) == 0 && r_cov(ii) == 0 && c_cov(jj) == 0
row = ii;
col = jj;
exit_flag = 0;
end
jj = jj + 1;
if jj > P_size; jj = 1; ii = ii+1; end
if ii > P_size; exit_flag = 0; end
end
% If there are no uncovered zeros go to step 6
if row == 0
stepnum = 6;
zflag = 0;
Z_r = 0;
Z_c = 0;
else
% Prime the uncovered zero
M(row,col) = 2;
% If there is a starred zero in that row
% Cover the row and uncover the column containing the zero
if sum(find(M(row,:)==1)) ~= 0
r_cov(row) = 1;
zcol = find(M(row,:)==1);
c_cov(zcol) = 0;
else
stepnum = 5;
zflag = 0;
Z_r = row;
Z_c = col;
end
end
end
%**************************************************************************
% STEP 5: Construct a series of alternating primed and starred zeros as
% follows. Let Z0 represent the uncovered primed zero found in Step 4.
% Let Z1 denote the starred zero in the column of Z0 (if any).
% Let Z2 denote the primed zero in the row of Z1 (there will always
% be one). Continue until the series terminates at a primed zero
% that has no starred zero in its column. Unstar each starred
% zero of the series, star each primed zero of the series, erase
% all primes and uncover every line in the matrix. Return to Step 3.
%**************************************************************************
function [M,r_cov,c_cov,stepnum] = step5(M,Z_r,Z_c,r_cov,c_cov)
zflag = 1;
ii = 1;
while zflag
% Find the index number of the starred zero in the column
rindex = find(M(:,Z_c(ii))==1);
if rindex > 0
% Save the starred zero
ii = ii+1;
% Save the row of the starred zero
Z_r(ii,1) = rindex;
% The column of the starred zero is the same as the column of the
% primed zero
Z_c(ii,1) = Z_c(ii-1);
else
zflag = 0;
end
% Continue if there is a starred zero in the column of the primed zero
if zflag == 1;
% Find the column of the primed zero in the last starred zeros row
cindex = find(M(Z_r(ii),:)==2);
ii = ii+1;
Z_r(ii,1) = Z_r(ii-1);
Z_c(ii,1) = cindex;
end
end
% UNSTAR all the starred zeros in the path and STAR all primed zeros
for ii = 1:length(Z_r)
if M(Z_r(ii),Z_c(ii)) == 1
M(Z_r(ii),Z_c(ii)) = 0;
else
M(Z_r(ii),Z_c(ii)) = 1;
end
end
% Clear the covers
r_cov = r_cov.*0;
c_cov = c_cov.*0;
% Remove all the primes
M(M==2) = 0;
stepnum = 3;
% *************************************************************************
% STEP 6: Add the minimum uncovered value to every element of each covered
% row, and subtract it from every element of each uncovered column.
% Return to Step 4 without altering any stars, primes, or covered lines.
%**************************************************************************
function [P_cond,stepnum] = step6(P_cond,r_cov,c_cov)
a = find(r_cov == 0);
b = find(c_cov == 0);
minval = min(min(P_cond(a,b)));
P_cond(find(r_cov == 1),:) = P_cond(find(r_cov == 1),:) + minval;
P_cond(:,find(c_cov == 0)) = P_cond(:,find(c_cov == 0)) - minval;
stepnum = 4;
function cnum = min_line_cover(Edge)
% Step 2
[r_cov,c_cov,M,stepnum] = step2(Edge);
% Step 3
[c_cov,stepnum] = step3(M,length(Edge));
% Step 4
[M,r_cov,c_cov,Z_r,Z_c,stepnum] = step4(Edge,r_cov,c_cov,M);
% Calculate the deficiency
cnum = length(Edge)-sum(r_cov)-sum(c_cov);
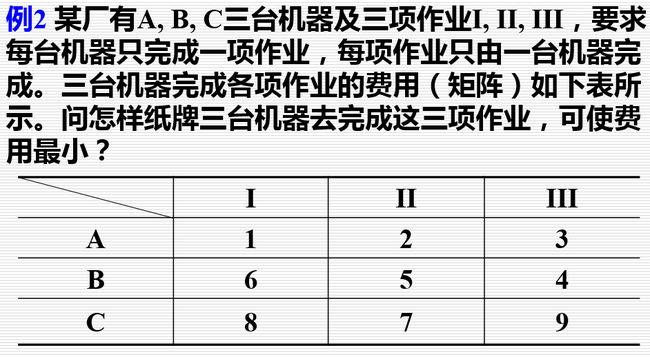
使用该算法时,把Perf的矩阵改为
Perf = [1 2 3;6 5 4;8 7 9];
求得指派矩阵为: