3 slf4j
3.1 简介
与commons-logging相同,slf4j也是一个通用的日志接口,在程序中与其他日志框架结合使用,并对外提供服务。
Simple Logging Facade for Java简称 slf4j,Java简单日志门面系统。在我们的代码中,不需要显式指定具体日志框架(例如:java.util.logging、logback、log4j),而是使用slf4j的API来记录日志便可,最终日志的格式、记录级别、输出方式等通过具体日志框架的配置来实现,因此可以在应用中灵活切换日志系统。
如果你对上面所说的,仍然不太理解。那么,简单的说slf4j可以理解为JDBC,都是提供接口服务,只不过比JDBC更为直观、简单些。在程序中,JDBC需要单独指定具体的数据库实现(例如:mysql),而slf4j并不需要。
接下来,我们讲解下关于slf4j具体的使用。
3.2 slf4j结构
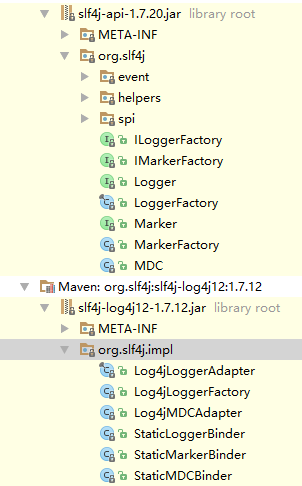
上面的截图,展示的是slf4j搭配log4j使用。
Logger:slf4j日志接口类,提供了trace < debug < info < warn < error这5个级别对应的方法,主要提供了占位符{}的日志打印方式;
Log4jLoggerAdapter:Logger适配器,主要对org.apache.log4j.Logger对象的封装,占位符{}日志打印的方式在此类中实现;
LoggerFactory:日志工厂类,获取实际的日志工厂类,获取相应的日志实现对象;
lLoggerFactory:底层日志框架中日志工厂的中介,再其实现类中,通过底层日志框架中的日志工厂获取对应的日志对象;
StaticLoggerBinder:静态日志对象绑定,在编译期确定底层日志框架,获取实际的日志工厂,也就是lLoggerFactory的实现类;
3.2 使用
同为Java日志接口框架,相对于commons-logging来说,slf4j的使用有点特殊。
在第一篇的文章中,笔者介绍了commons-logging的使用,对于commons-logging来说,无需在pom.xml文件中单独引入日志实现框架,便可进行日志打印。但是,slf4j并不支持此功能,必须在pom.xml中单独引入底层日志实现。
搭配log4j使用:
首先,需要在pom.xml文件中添加依赖:
//slf4j:
org.slf4j
slf4j-api
1.7.20
//slf4j-log4j:
org.slf4j
slf4j-log4j12
1.7.12
//log4j:
log4j
log4j
1.2.17
声明测试代码:
public class slf4j_log4jDemo {
Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(slf4j_log4jDemo.class);
@Test
public void test() throws IOException {
logger.error("Error Message!");
logger.warn("Warn Message!");
logger.info("Info Message!{}","你好");
logger.debug("Debug Message!");
logger.trace("Trace Message!");
}
}
接下来,在classpath下定义配置文件:log4j.xml:
对于slf4j来说,它只提供了一个核心模块--slf4j-api,这个模块下只有日志接口,没有具体的实现,所以在实际开发总需要单独添加底层日志实现。但是,这些底层日志类实际上跟slf4j并没有任何关系,因此slf4j又通过增加一层日志中间层来转换相应的实现,例如上文中的slf4j-log4j12。
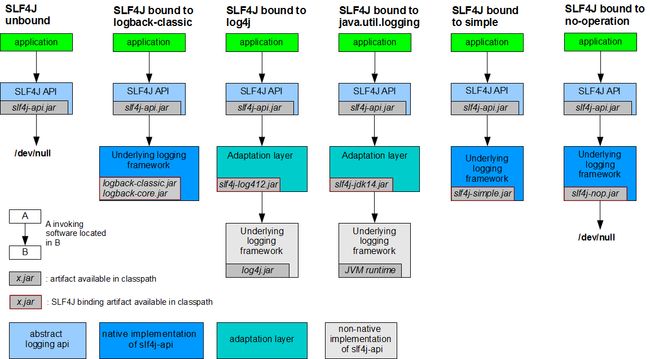
上图,是官方文档中slf4j与其他日志框架相结合的使用情况,具体总结如下:
logback:logback-classic 、logback-core
java.util.logging.Logging:slf4j-jdk14
commons-logging:jcl-over-slf4j
其中,commons-logging比较特殊。由于commons-logging诞生的比较早,一些年限久远的系统大体上都使用了commons-logging和log4j的日志框架组合,大名鼎鼎的spring框架也依然在使用commons-logging框架。那么,此时你的新系统如果想使用slf4j该如何处理?
这会,就需要引入jcl-over-slf4j.jar包了,它会将commons-logging的“骗入”到slf4j中来,实现日志框架结合;
3.3 源码分析
以下源码基于slf4j-1.7.20、slf4j-log4j12-1.7.12和log4j-1.2.17(使用slf4j和log4j结合):
org.slf4j.LoggerFactory类:
public final class LoggerFactory {
static final int UNINITIALIZED = 0;
static final int ONGOING_INITIALIZATION = 1;
static final int FAILED_INITIALIZATION = 2;
static final int SUCCESSFUL_INITIALIZATION = 3;
static final int NOP_FALLBACK_INITIALIZATION = 4;
private static String STATIC_LOGGER_BINDER_PATH = "org/slf4j/impl/StaticLoggerBinder.class";
//初始化状态,默认为0;
static int INITIALIZATION_STATE = UNINITIALIZED;
//获取日志对象:
public static Logger getLogger(Class clazz) {
//获取日志对象:
Logger logger = getLogger(clazz.getName());
......
}
//获取日志对象,分为两个阶段:
public static Logger getLogger(String name) {
//获取日志工厂:实际为Log4jLoggerFactory:
ILoggerFactory iLoggerFactory = getILoggerFactory();
//通过Log4jLoggerFactory获取日志对象:
return iLoggerFactory.getLogger(name);
}
//获取日志工厂:
public static ILoggerFactory getILoggerFactory() {
//判断初始化状态:默认为0
if (INITIALIZATION_STATE == UNINITIALIZED) {
//将初始化状态至为1:
INITIALIZATION_STATE = ONGOING_INITIALIZATION;
//slf4j初始化操作:
performInitialization();
}
//完成初始化后,判断初始化结果:
switch (INITIALIZATION_STATE) {
case SUCCESSFUL_INITIALIZATION:
//通过StaticLoggerBinder单例对象,创建LoggerFactory实例:实际为Log4jLoggerFactory
return StaticLoggerBinder.getSingleton().getLoggerFactory();
case NOP_FALLBACK_INITIALIZATION:
return NOP_FALLBACK_FACTORY;
case FAILED_INITIALIZATION:
throw new IllegalStateException(UNSUCCESSFUL_INIT_MSG);
case ONGOING_INITIALIZATION:
return TEMP_FACTORY;
}
throw new IllegalStateException("Unreachable code");
}
//slf4j初始化流程:
private final static void performInitialization() {
//静态绑定,获取StaticLoggerBinder对象;
bind();
//判断初始化状态:如果初始化成功,则进行版本检查;
if (INITIALIZATION_STATE == SUCCESSFUL_INITIALIZATION) {
versionSanityCheck();
}
}
//静态绑定操作:找到与slf4j相结合的日志框架;
private final static void bind() {
try {
//在类路径下,查找org.slf4j.impl.StaticLoggerBinder类:
Set staticLoggerBinderPathSet = findPossibleStaticLoggerBinderPathSet();
//遍历Set集合,并将其中StaticLoggerBinder类的路径打印出来:
reportMultipleBindingAmbiguity(staticLoggerBinderPathSet);
//创建StaticLoggerBinder的对象:
StaticLoggerBinder.getSingleton();
//初始化完成,修改初始化状态:
INITIALIZATION_STATE = SUCCESSFUL_INITIALIZATION;
//如果在类路径下有多个StaticLoggerBinder类,此方法打印出具体实例化了哪个StaticLoggerBinder类:
reportActualBinding(staticLoggerBinderPathSet);
fixSubstitutedLoggers();
} catch (NoClassDefFoundError ncde) {
String msg = ncde.getMessage();
if (messageContainsOrgSlf4jImplStaticLoggerBinder(msg)) {
INITIALIZATION_STATE = NOP_FALLBACK_INITIALIZATION;
} else {
failedBinding(ncde);
throw ncde;
}
} catch (java.lang.NoSuchMethodError nsme) {
String msg = nsme.getMessage();
if (msg != null && msg.indexOf("org.slf4j.impl.StaticLoggerBinder.getSingleton()") != -1) {
INITIALIZATION_STATE = FAILED_INITIALIZATION;
}
throw nsme;
} catch (Exception e) {
failedBinding(e);
throw new IllegalStateException("Unexpected initialization failure", e);
}
}
//在类路径下,查找org.slf4j.impl.StaticLoggerBinder类:
private static Set findPossibleStaticLoggerBinderPathSet() {
Set staticLoggerBinderPathSet = new LinkedHashSet();
try {
//获取LoggerFactory的类加载器:
ClassLoader loggerFactoryClassLoader = LoggerFactory.class.getClassLoader();
Enumeration paths;
//判断类加载器是否为null:
if (loggerFactoryClassLoader == null) {
//查找org.slf4j.impl.StaticLoggerBinder类:
paths = ClassLoader.getSystemResources(STATIC_LOGGER_BINDER_PATH);
} else {
//查找org.slf4j.impl.StaticLoggerBinder类:
paths = loggerFactoryClassLoader.getResources(STATIC_LOGGER_BINDER_PATH);
}
//遍历Enumeration对象:
while (paths.hasMoreElements()) {
//将StaticLoggerBinder类存在的路径添加到Set集合中:
URL path = (URL) paths.nextElement();
staticLoggerBinderPathSet.add(path);
}
} catch (IOException ioe) {}
return staticLoggerBinderPathSet;
}
//如果存在多个StaticLoggerBinder类,就打印每个StaticLoggerBinder类的路径:
private static void reportMultipleBindingAmbiguity(Set staticLoggerBinderPathSet) {
//判断Set集合长度:
if (isAmbiguousStaticLoggerBinderPathSet(staticLoggerBinderPathSet)) {
Util.report("Class path contains multiple SLF4J bindings.");
Iterator iterator = staticLoggerBinderPathSet.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
URL path = (URL) iterator.next();
Util.report("Found binding in [" + path + "]");
}
Util.report("See " + MULTIPLE_BINDINGS_URL + " for an explanation.");
}
}
//如果类路径下的StaticLoggerBinder类不止一个的话,就打印出具体实例化的对象是哪个:
private static void reportActualBinding(Set staticLoggerBinderPathSet) {
//判断Set集合长度:
if (isAmbiguousStaticLoggerBinderPathSet(staticLoggerBinderPathSet)) {
Util.report("Actual binding is of type [" + StaticLoggerBinder.getSingleton().getLoggerFactoryClassStr() + "]");
}
}
//检查slf4j-api和slf4j-log4j12的版本是否兼容;
private final static void versionSanityCheck() {
try {
//获取StaticLoggerBinder的api版本,也就是slf4j-log4j12所属版本
String requested = StaticLoggerBinder.REQUESTED_API_VERSION;
boolean match = false;
//判断StaticLoggerBinder的api版本是否属于slf4j-api所支持的版本:
for (int i = 0; i < API_COMPATIBILITY_LIST.length; i++) {
if (requested.startsWith(API_COMPATIBILITY_LIST[i])) {
match = true;
}
}
if (!match) {.....}
} catch (java.lang.NoSuchFieldError nsfe) {
} catch (Throwable e) {}
}
}
org.slf4j.impl.StaticLoggerBinder类:
public class StaticLoggerBinder implements LoggerFactoryBinder {
//StaticLoggerBinder构造方法:private修饰,单例;
private StaticLoggerBinder() {
//创建Log4jLoggerFactory对象:
loggerFactory = new Log4jLoggerFactory();
....
}
//单例对象:
private static final StaticLoggerBinder SINGLETON = new StaticLoggerBinder();
//供外部调用,得到单例的StaticLoggerBinder对象:
public static final StaticLoggerBinder getSingleton() {
return SINGLETON;
}
//获取ILoggerFactory对象,实际为Log4jLoggerFactory;
public ILoggerFactory getLoggerFactory() {
return loggerFactory;
}
}
org.slf4j.impl.Log4jLoggerFactory类:
public class Log4jLoggerFactory implements ILoggerFactory {
// 线程安全的ConcurrentHashMap对象,保存日志对象;
ConcurrentMap loggerMap;
public Log4jLoggerFactory() {
loggerMap = new ConcurrentHashMap();
}
//创造Logger对象:实际返回的是与slf4j相结合的日志对象;
public Logger getLogger(String name) {
//通过类名称获取日志对象:
Logger slf4jLogger = loggerMap.get(name);
//不为空,则返回:
if (slf4jLogger != null) {
return slf4jLogger;
} else {
//log4j日志对象:
org.apache.log4j.Logger log4jLogger;
if (name.equalsIgnoreCase(Logger.ROOT_LOGGER_NAME)) {
//开始log4j的初始化过程:
log4jLogger = LogManager.getRootLogger();
}else {
//开始log4j的初始化过程:
log4jLogger = LogManager.getLogger(name);
}
//通过Log4jLoggerAdapter对象,对log4j的日志对象进行封装,使用了适配器模式:
Logger newInstance = new Log4jLoggerAdapter(log4jLogger);
Logger oldInstance = loggerMap.putIfAbsent(name, newInstance);
return oldInstance == null ? newInstance : oldInstance;
}
}
}
具体流程总结如下:
1.结合上面的例子,当slf4j_log4jDemo测试类被加载的时候,slf4j开始了初始化操作:
Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(slf4j_log4jDemo.class);
2.slf4j初始化操作分为2个阶段,第一阶段获取日志工厂,第二阶段通过日志工厂获取日志对象;
3.在第一阶段中,首先通过classloader查找classpath下存在的org/slf4j/impl/StaticLoggerBinder.class类,可能有多个。在我们的测试例子中,实际上找到的是slf4j-log4j12包下的org.slf4j.impl.StaticLoggerBinder类
4.其次,实例化StaticLoggerBinder对象,调用getLoggerFactory方法获取对应的loggerFactory,也就是slf4j-log4j12包下的org.slf4j.impl.Log4jLoggerFactory,并返回;
5.上面过程结束后,loggerFactory被创建,紧接着通过Log4jLoggerFactory的getLogger方法获取log4j的日志对象,使用的是最原生的方法log4j的LogManager来实现,最终返回org.apache.log4j.Logger.log4jLogger对象;
6.由于log4j的日志对象org.apache.log4j.Logger.log4jLogger与slf4j的org.slf4j.Logger日志接口并无多态关系,所以此时slf4j引入了一个org.slf4j.impl.Log4jLoggerAdapter类,该类实现了slf4j的Logger接口,再其内部维护一个log4j的日志对象log4jLogger,使用的是适配器模式,进而达到了整合;在程序中,我们使用日志api的时候,实际上都是Log4jLoggerAdapter类来完成的。
3.4 slf4j静态绑定原理
虽然commons-logging和slf4j都是日志服务接口,但是两者对于底层日志框架绑定的方式相差甚远。在第一篇日志系统的文章中,笔者已经介绍过,commons-logging是基于动态绑定来实现与日志框架的结合,也就是说在编译期间我们的程序并不知道底层的实现是什么,只有在运行期间才进行获取;
与commons-logging不同的是,slf4j是基于静态绑定来实现与日志框架的结合,在编译期间我们的程序就已经知道使用了哪种日志实现。在上面的源码中已有所提及,下面再回顾下。
具体源码,如下:
public final class LoggerFactory {
private static String STATIC_LOGGER_BINDER_PATH = "org/slf4j/impl/StaticLoggerBinder.class";
//静态绑定操作:找到与slf4j相结合的日志框架,在编译期间完成日志绑定操作;
private final static void bind() {
try {
//在类路径下,查找org.slf4j.impl.StaticLoggerBinder类:
Set staticLoggerBinderPathSet = findPossibleStaticLoggerBinderPathSet();
。。。。。
}
//在类路径下,查找org.slf4j.impl.StaticLoggerBinder类:
private static Set findPossibleStaticLoggerBinderPathSet() {
Set staticLoggerBinderPathSet = new LinkedHashSet();
try {
//获取LoggerFactory的类加载器:
ClassLoader loggerFactoryClassLoader = LoggerFactory.class.getClassLoader();
Enumeration paths;
//判断类加载器是否为null:
if (loggerFactoryClassLoader == null) {
//查找org.slf4j.impl.StaticLoggerBinder类:
paths = ClassLoader.getSystemResources(STATIC_LOGGER_BINDER_PATH);
} else {
//查找org.slf4j.impl.StaticLoggerBinder类:
paths = loggerFactoryClassLoader.getResources(STATIC_LOGGER_BINDER_PATH);
}
......
} catch (IOException ioe) {}
return staticLoggerBinderPathSet;
}
}
3.5 slf4j和commons-logging比较
(1)slf4j使用了静态绑定方式,实现了与底层日志框架的结合, 避免了commons-logging中由于类加载器不同导致的日志加载失败情况的发生;
(2)slf4j支持参数化日志打印,也就是占位符{}的方式。去除了commons-logging中的isDebugEnabled(), isInfoEnabled()等方法的日志级别检查代码,极大的提高了代码可读性;并且,占位符的方式也延缓了构建日志信息(String的开销),提高了内存的使用性;
在commons-logging中,我们经常需要些这样的代码:
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("我是: " + name);
}
而在slf4j中,我们可以这样写:
logger.debug("我是: {}",name);
在commons-logging中,是要符合日记级别,我们就进行字符串的拼接;而在slf4j中,我们不进行字符串拼接操作,而是使用StringBuffer来完成的替换。这不仅降低了内存消耗而且预先降低了CPU去处理字符串连接命令的时间,提高了程序的性能。
3.6 slf4j搭配commons-logging使用原理
在前面的小节中,我们提到了slf4j为了兼容老代码,是可以跟commons-logging结合使用的,需要在pom.xml文件中引入jcl-over-slf4j.jar包。具体实现过程如下:
测试代码:(引入的依旧为commons-logging对象,无需改变)
import org.apache.commons.logging.Log;
import org.apache.commons.logging.LogFactory;
import org.junit.Test;
public class commons_loggingDemo {
Log log= LogFactory.getLog(commons_loggingDemo.class);
@Test
public void test() throws IOException {
log.debug("Debug info.");
log.info("Info info");
log.warn("Warn info你好");
log.error("Error info");
log.fatal("Fatal info");
}
}
引入pom依赖:(除了原有的commons-logging和log4j依赖外,还需要添加slf4j-api、jcl-over-slf4j、slf4j-log4j12依赖)
!-- commons-logging -->
commons-logging
commons-logging
1.1.3
org.slf4j
jcl-over-slf4j
1.7.20
log4j
log4j
1.2.17
org.slf4j
slf4j-log4j12
1.7.12
org.slf4j
slf4j-api
1.7.20
日志配置文件: (均为commons-logging时期配置,无需为slf4j做任何改变)
commons-logging.properties配置文件:
#日志对象:
org.apache.commons.logging.Log=org.apache.log4j.Logger
#日志工厂:
org.apache.commons.logging.LogFactory=org.apache.commons.logging.impl.LogFactoryImpl
log4j.xml配置文件:
实现原理:
将commons-logging的输出引入到jcl-over-slf4j中,再转向slf4j,紧接着进入到slf4j-log4j12,最终进入到log4j;
源码分析:(请结合commons-logging初始化过程进行学习)
commons-logging中的org.apache.commons.logging.LogFactory类:
public abstract class LogFactory {
protected static final String SERVICE_ID = "META-INF/services/org.apache.commons.logging.LogFactory";
public static LogFactory getFactory() throws LogConfigurationException {
ClassLoader contextClassLoader = getContextClassLoaderInternal();
if (factory == null) {
。。。忽略
try {
//在classpath下寻找 META-INF/services/org.apache.commons.logging.LogFactory 文件:(在jcl-over-slf4j.jar中)
final InputStream is = getResourceAsStream(contextClassLoader, SERVICE_ID);
if( is != null ) {
BufferedReader rd;
try {
rd = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(is, "UTF-8"));
} catch (java.io.UnsupportedEncodingException e) {
rd = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(is));
}
//读取该文件中的第一行信息:org.apache.commons.logging.impl.SLF4JLogFactory
String factoryClassName = rd.readLine();
rd.close();
if (factoryClassName != null && ! "".equals(factoryClassName)) {
。。。。忽略
//SLF4JLogFactory进行实例化(在jcl-over-slf4j.jar中)
factory = newFactory(factoryClassName, baseClassLoader, contextClassLoader );
}
} else {
。。。。。忽略
}
} catch (Exception ex) { 。。。。。忽略}
}
。。。。。忽略
return factory;
}
}
jcl-over-slf4j的org.apache.commons.logging.impl.SLF4JLogFactory中:
public class SLF4JLogFactory extends LogFactory {
//获取日志对象:
public Log getInstance(Class clazz) throws LogConfigurationException {
return (getInstance(clazz.getName()));
}
public Log getInstance(String name) throws LogConfigurationException {
Log instance = loggerMap.get(name);
if (instance != null) {
return instance;
} else {
Log newInstance;
//此处使用的是slf4j中的LoggerFactory进行日志对象获取,此时已经完全将commons-logging引入到了slf4j中来;
Logger slf4jLogger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(name);
if (slf4jLogger instanceof LocationAwareLogger) {
newInstance = new SLF4JLocationAwareLog((LocationAwareLogger) slf4jLogger);
} else {
newInstance = new SLF4JLog(slf4jLogger);
}
Log oldInstance = loggerMap.putIfAbsent(name, newInstance);
return oldInstance == null ? newInstance : oldInstance;
}
}
}
以上便完成了,commons-logging结合slf4j的过程,后续获取日志对象的逻辑与3.3节中完全一致,可参考上面的讲解。