SparseArray源码来自:android-25/java/util/SparseArray
ArrayMap源码来自:25.3.1/support-compat-25.3.1/android/android.support.v4.util.ArrayMap
一、SparseArray实现源码学习
SparseArray采用时间换取空间的方式来提高手机App的运行效率,这也是其与HashMap的区别;HashMap通过空间换取时间,查找迅速;HashMap中当table数组中内容达到总容量0.75时,则扩展为当前容量的两倍,关于HashMap可查看HashMap实现原理学习)
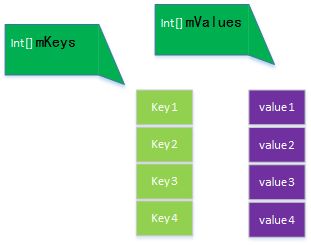
- SparseArray的key为int,value为Object。
- 在Android中,数据长度小于千时,用于替换HashMap
- 相比与HashMap,其采用 时间换空间 的方式,使用更少的内存来提高手机APP的运行效率(HashMap中当table数组中内容达到总容量0.75时,则扩展为当前容量的两倍,关于HashMap可查看HashMap实现原理学习)
下边对其源码进行简单学习。
1、构造方法
// 构造方法
public SparseArray() {
this(10);
}
// 构造方法
public SparseArray(int initialCapacity) {
if (initialCapacity == 0) {
mKeys = EmptyArray.INT;
mValues = EmptyArray.OBJECT;
} else {
// key value各自为一个数组,默认长度为10
mValues = ArrayUtils.newUnpaddedObjectArray(initialCapacity);
mKeys = new int[mValues.length];
}
mSize = 0;
}
ps:
SparseArray构造方法中,创建了两个数组mKeys、mValues分别存放int与Object,其默认长度为10
2、 put(int key, E value)
public void put(int key, E value) {
// 二分查找,key在mKeys列表中对应的index
int i = ContainerHelpers.binarySearch(mKeys, mSize, key);
// 如果找到,则直接赋值
if (i >= 0) {
mValues[i] = value;
}
// 找不到
else {
// binarySearch方法中,找不到时,i取了其非,这里再次取非,则非非则正
i = ~i;
// 如果该位置的数据正好被删除,则赋值
if (i < mSize && mValues[i] == DELETED) {
mKeys[i] = key;
mValues[i] = value;
return;
}
// 如果有数据被删除了,则gc
if (mGarbage && mSize >= mKeys.length) {
gc();
// Search again because indices may have changed.
i = ~ContainerHelpers.binarySearch(mKeys, mSize, key);
}
// 插入数据,增长mKeys与mValues列表
mKeys = GrowingArrayUtils.insert(mKeys, mSize, i, key);
mValues = GrowingArrayUtils.insert(mValues, mSize, i, value);
mSize++;
}
}
ps:
- 因为key为int,不存在hash冲突
- mKeys为有序列表,通过二分查找,找到要插入的key对应的index (这里相对于查找hash表应该算是费时间吧,但节省了内存,所以是 时间换取了空间)
- 通过二分查找到的index,将Value插入到mValues数组的对应位置
3、get(int key)
// 通过key查找对应的value
public E get(int key) {
return get(key, null);
}
// 通过key查找对应的value
public E get(int key, E valueIfKeyNotFound) {
// mKeys数组中采用二分查找,找到key对应的index
int i = ContainerHelpers.binarySearch(mKeys, mSize, key);
// 没有找到,则返回空
if (i < 0 || mValues[i] == DELETED) {
return valueIfKeyNotFound;
} else {
// 找到则返回对应的value
return (E) mValues[i];
}
}
ps:
每次调用get,则需经过一次mKeys数组的二分查找,因此mKeys数组越大则二分查找的时间就越长,因此SparseArray在大量数据,千以上时,会效率较低
3、ContainerHelpers.binarySearch(mKeys, mSize, key)二分查找
// array为有序数组
// size数组中内容长度
// value要查找的值
static int binarySearch(int[] array, int size, int value) {
int lo = 0;
int hi = size - 1;
// 循环查找
while (lo <= hi) {
// 取中间位置元素
final int mid = (lo + hi) >>> 1;
final int midVal = array[mid];
// 如果中间元素小于要查找元素,则midIndex赋值给 lo
if (midVal < value) {
lo = mid + 1;
}
// 如果中间元素大于要查找元素,则midIndex赋值给 hi
else if (midVal > value) {
hi = mid - 1;
}
// 找到则返回
else {
return mid; // value found
}
}
// 找不到,则lo 取非
return ~lo; // value not present
}
二、android.support.v4.util.ArrayMap
ArrayMap和SparseArray有点类似;其中含有两个数组,一个是mHashes(key的hash值数组,为一个有序数组),另一个数组存储的是key和value,其中key和value是成对出现的,key存储在数组的偶数位上,value存储在数组的奇数位上。
1、构造方法
public SimpleArrayMap() {
// key的hash值数组,为一个有序数组
mHashes = ContainerHelpers.EMPTY_INTS;
// key 与 value数组
mArray = ContainerHelpers.EMPTY_OBJECTS;
mSize = 0;
}
ps:
构造方法中初始化了两个数组mHashes、mArray,其中mHashes为key的Hash值对应的数组
2、put(K key, V value)
public V put(K key, V value) {
// key 对应的hash值
final int hash;
// hash对应的mHashes列表的index
int index;
// key为空,hash为0
if (key == null) {
hash = 0;
index = indexOfNull();
}
//
else {
// 计算key的hashcode
hash = key.hashCode();
// 查找key对应mHashes中的index,大于0则找到了,否则为未找到
// 这里涉及到hash冲突,如果hash冲突,则在index的相邻位置插入数据
index = indexOf(key, hash);
}
// 找到key对应mHashes中的index
if (index >= 0) {
// 取出基数位置原有的Value
index = (index<<1) + 1;
final V old = (V)mArray[index];
// 将新数据放到基数index位置
mArray[index] = value;
return old;
}
// indexOf中取了反,这里反反则正
index = ~index;
// 如果满了就扩容
if (mSize >= mHashes.length) {
final int n = mSize >= (BASE_SIZE*2) ? (mSize+(mSize>>1))
: (mSize >= BASE_SIZE ? (BASE_SIZE*2) : BASE_SIZE);
final int[] ohashes = mHashes;
final Object[] oarray = mArray;
// 扩容
allocArrays(n);
// 把原来的数据拷贝到扩容后的数组中
if (mHashes.length > 0) {
if (DEBUG) Log.d(TAG, "put: copy 0-" + mSize + " to 0");
System.arraycopy(ohashes, 0, mHashes, 0, ohashes.length);
System.arraycopy(oarray, 0, mArray, 0, oarray.length);
}
freeArrays(ohashes, oarray, mSize);
}
// 根据上面的二分法查找,如果index小于mSize,说明新的数据是插入到数组之间index位置,插入之前需要把后面的移位
if (index < mSize) {
if (DEBUG) Log.d(TAG, "put: move " + index + "-" + (mSize-index)
+ " to " + (index+1));
System.arraycopy(mHashes, index, mHashes, index + 1, mSize - index);
System.arraycopy(mArray, index << 1, mArray, (index + 1) << 1, (mSize - index) << 1);
}
// 保存数据
mHashes[index] = hash;
mArray[index<<1] = key;
mArray[(index<<1)+1] = value;
mSize++;
return null;
}
// 根据key 与key的hash,查找key对应的index
int indexOf(Object key, int hash) {
final int N = mSize;
// Important fast case: if nothing is in here, nothing to look for.
if (N == 0) {
return ~0;
}
// 二分查找mHashes有序数组,查找hash对应的index
int index = ContainerHelpers.binarySearch(mHashes, N, hash);
// 没有找到
if (index < 0) {
return index;
}
// 偶数位为对应的key,则找到了
if (key.equals(mArray[index<<1])) {
return index;
}
// index之后查找
// 这里涉及到hash冲突,如果hash冲突,则在index的相邻位置插入数据
// Search for a matching key after the index.
int end;
for (end = index + 1; end < N && mHashes[end] == hash; end++) {
if (key.equals(mArray[end << 1])) return end;
}
// index之前查找
// Search for a matching key before the index.
for (int i = index - 1; i >= 0 && mHashes[i] == hash; i--) {
if (key.equals(mArray[i << 1])) return i;
}
// 没有找到
return ~end;
}