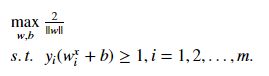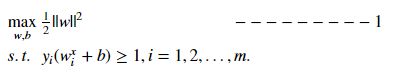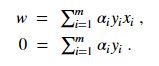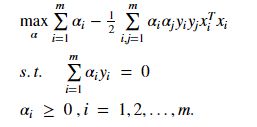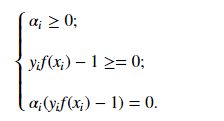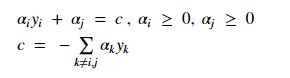概念
SVM(Support Vector Machine)支持 向量 的机器 简化 支持向量机。
那什么又是支持向量呢?距离超平面(在之前的感知机说过)最近的几个训练样本使得
如果你要问为什么要设置1为临界值呢。这个其实很简单,可以从两个方面讲:
a.分割线的斜率只和w有关
b.下面将要用到SMO算法,需要控制变量,所以我们固定一个因子,来最大化另一个因子,方便又有效。
这里我认为只要是大于零的数基本都可以。因为间隔(这里指支持向量到分割线的距离)必须得大于0吧起码。
2/||w||是距离公式 自己算算就出来了
大致流程
细化过程
想要找到具有“最大间隔”的划分超平面,也就是要找到能满足下面式子中约束的参数w和b,使得gama最大,即
(s.t. 使得。。。满足。。。)
显然,为了最大化1/||w||,这等价于最小化||w||(这里为了计算方便,选择最小化||w||^2).于是,重写为
这就是支持向量机的基本模型。
我们注意到1式是一个凸二次规划问题,在这里我们用拉格朗日乘子法。
拓展(了解就行,想深入了解还是查查相关资料吧):
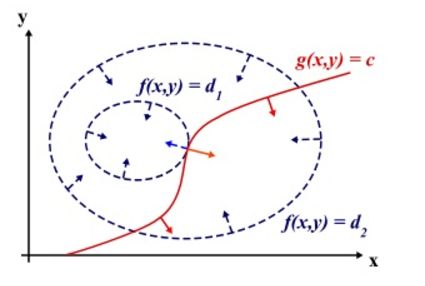
为什么要用拉格朗日乘子法得到最优值?设想我们的目标函数z = f(x), x是向量, z取不同的值,相当于可以投影在x构成的平面(曲面)上,即成为等高线,如下图,目标函数是f(x, y),这里x是标量,虚线是等高线,现在假设我们的约束g(x)=0,x是向量,在x构成的平面或者曲面上是一条曲线,假设g(x)与等高线相交,交点就是同时满足等式约束条件和目标函数的可行域的值,但肯定不是最优值,因为相交意味着肯定还存在其它的等高线在该条等高线的内部或者外部,使得新的等高线与目标函数的交点的值更大或者更小,只有到等高线与目标函数的曲线相切的时候,可能取得最优值,如下图所示,即等高线和目标函数的曲线在该点的法向量必须有相同方向,所以最优值必须满足:f(x)的梯度 = a* g(x)的梯度,a是常数,表示左右两边同向。这个等式就是L(a,x)对参数求导的结果。(上述描述,我不知道描述清楚没,如果与我物理位置很近的话,直接找我,我当面讲好理解一些,注:下图来自wiki)。
回归正题。
这里对每条约束添加拉格朗日乘子alpha_i >= 0, 则该问题的拉格朗日可写为:
令L对w,b的偏导为零可得:
带入L式中得:
上面的式子需要KKT约束(想要具体了解的可以 点这里),即要求:
于是,对于样本(xi, yi),总是有alpha_i = 0 or yif(xi) = 1.这里,显然可以看出当alpha_i = 0,则不会出现在上述的求和公式中。若alpha_i > 0,则必有yif(xi) = 1,所对应的样本点位于最大间隔边界上,是一个支持向量。一般支持向量只占数据的一小部分,所以也就表示训练过程中,大部分数据都不保留。保留下来的仅仅是支持向量。
那么若何求解改写后的式子L呢?目前应用广泛的是SMO(Sequential Minimal Optimization 序列最小优化算法)
SMO基本思路是先固定alpha_i之外的所有参数 (这里就是刚开始为什么要设置成1的问题的一个原因)然后求alpha_i上的极值。则alpha_i可有其他变量导出。于是,SMO每次选择两个变量alpha_i and alpha_j ,并固定其他参数。这样,在参数初始化后不断执行如下两部分:
这里仅仅考虑alpha_i and alpha_j时,约束可以重写:
那么如何确定偏移量b呢?这里用的是支持向量求解的平均。
上代码 没有再度优化的SMO,仅仅为了实现。
train.txt
-1 1 1
-1 0.9 1.8
-1 2.3 1
-1 2.8 2.5
1 1.3 4
1 6 4.6
1 4.2 5.1
1 5.1 6.6
1 5.2 5.6
1 4.6 5.2
载入数据
import random
from numpy import *
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def loadDataSet(fileName):
dataMat = []
labelMat = []
fr = open(fileName)
for line in fr.readlines():
line = line.strip().split()
dataMat.append([float(line[1]), float(line[2])])
labelMat.append(float(line[0]))
return dataMat, labelMat
选取不同的alpha_i,alpha_j
def selectJrand(i,m):
j = i
while j == i:
j = int(random.uniform(0, m))
return j
用于调整大于H or 小于L的 alpha值
def clipAlpha(aj,H,L):
if aj > H:
aj = H
if aj < L:
aj = L
return aj
简化版SMO
(数据集,类别标签,常数C,容错率。最大循环)
alphaPairsChanged记录alpha是否进行优化。
fXi预测
Ei误差
Eta是alpha的最优修改值
def smoSimple(dataMatIn,classLabels,C,toler,maxIter):
dataMatrix = mat(dataMatIn)
labelMat = mat(classLabels).transpose()
b = 0
m, n = shape(dataMatrix)
alphas = mat(zeros((m,1)))
iter = 0
# print("alphas:", alphas,"shape:", shape(alphas))
# print("labelMat:",labelMat,"shape:", shape(labelMat))
# print("dataMatrix:", dataMatrix,"shape:", shape(dataMatrix))
# multiply(alphas, labelMat)
# (dataMatrix * dataMatrix[0:].T)
while iter < maxIter:
print("Step ", iter)
alphaPairsChanged = 0
for i in range(m):
fXi = float(multiply(alphas, labelMat).T * (dataMatrix * dataMatrix[i,:].T)) + b
Ei = fXi - float(labelMat[i])
if ((labelMat[i]*Ei < -toler) and (alphas[i] < C)) or ((labelMat[i]*Ei > toler) and (alphas[i] > 0)):
j = selectJrand(i,m)
fXj = float(multiply(alphas,labelMat).T * ((dataMatrix * dataMatrix[j,:].T))) + b
Ej = fXj - float(labelMat[j])
alphaIold = alphas[i].copy()
alphaJold = alphas[j].copy()
if labelMat[i] != labelMat[j]:
L = max(0, alphas[j] - alphas[i])
H = min(C, C + alphas[j] - alphas[i])
else:
L = max(0, alphas[j] + alphas[i] - C)
H = min(C, alphas[j] + alphas[i])
if L == H:
print("L == H")
continue
eta = 2.0 * dataMatrix[i,:] * dataMatrix[i,:].T - dataMatrix[j,:] * dataMatrix[j,:].T
if eta >= 0:
print("eta >= 0")
continue
alphas[j] -= labelMat[j] * (Ei - Ej)/eta
alphas[j] = clipAlpha(alphas[j],H,L)
if(abs(alphas[j] - alphaJold) < 0.00001):
print("j not moving enough")
continue
alphas[i] += labelMat[j] * labelMat[i] * (alphaJold - alphas[j])
b1 = b-Ei-labelMat[i]*(alphas[i]-alphaIold)*dataMatrix[i,:]*dataMatrix[i,:].T \
- labelMat[j] * (alphas[j]-alphaJold)*dataMatrix[i,:]*dataMatrix[j,:].T
b2 = b - Ej - labelMat[i] * (alphas[i] - alphaIold) * dataMatrix[i,:] * dataMatrix[j,:].T \
- labelMat[j] * (alphas[j] - alphaJold) * dataMatrix[i,:] * dataMatrix[j,:].T
if (0 < alphas[i]) and (C > alphas[i]):
b = b1
elif (0 < alphas[j]) and (C > alphas[j]):
b = b2
else:
b = (b1 + b2)/2.0
alphaPairsChanged += 1
print("iter: %d i:%d, pairs changed %d" %(iter, i, alphaPairsChanged))
if alphaPairsChanged == 0:
iter += 1
else:
iter = 0
print("iteration number : %d" %iter)
return b, alphas
计算w
def calcWs(alphas, dataArr, classLabels):
X = mat(dataArr)
labelMat = mat(classLabels).transpose()
m, n = shape(X)
w = zeros((n, 1))
for i in range(m):
w += multiply(alphas[i] * labelMat[i], X[i,:].T)
return w
主函数
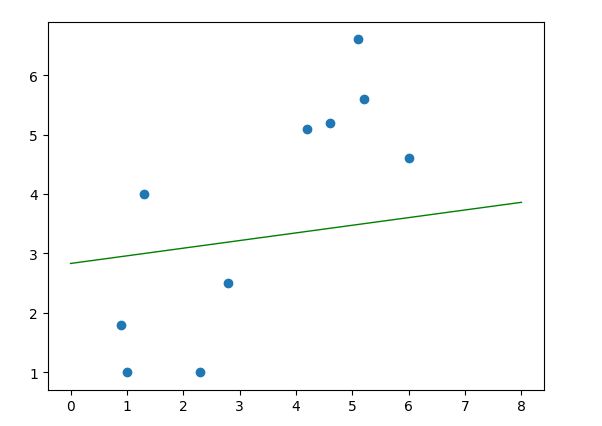
dataArr, labelArr = loadDataSet("train.txt")
b, alphas = smoSimple(dataArr, labelArr, 0.6, 0.001, 40)
w = calcWs(alphas, dataArr, labelArr)
print("b:", b)
print("W:", w)
# print("alphas:",alphas)
plt.scatter([l[0] for l in dataArr], [l[1] for l in dataArr])
s1 = (0, -b/w[1])
s2 = (8, (-b-8*w[0])/w[1])
print(float(s1[0]), float(s2[0]), s1[1], float(s2[1]))
plt.plot([float(s1[0]), float(s2[0])], [float(s1[1]), float(s2[1])], 'k-', linewidth=1.0, color='green')
plt.autoscale(True)
plt.show()
结果显示:
my github
my website
欢迎关注深度学习自然语言处理公众号