SPI简介
SPI是Service Provider Interface的缩写,即服务提供接口(翻译出来好绕口,还是不翻译的好),实质上是接口,作用是对外提供服务。
SPI是Java的一种插件机制,可以不用修改源代码实现新功能的扩展。
主要有如下几个步骤:
- 实现SPI接口
- 在项目的META-INF/services文件夹下,新建一个以SPI接口命名的文件, 文件里面配置上SPI接口的实现类
- 使用java.util.ServiceLoader加载。
由于本篇文章主要讲解Dubbo是如何使用SPI的,如果想要具体了解Java的SPI,可以参考下面两篇文章:
- JavaSPI机制学习笔记
- Introduction to the Service Provider Interfaces
当然还可以看 java.util.ServiceLoader 源码,注释中也有详细的说明。
Dubbo SPI
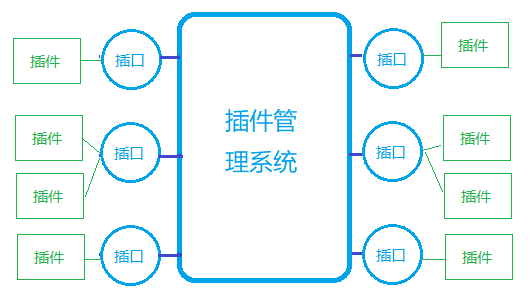
回到正题,SPI在dubbo应用的地方很多,专业一点讲叫做微内核机制;
如下图:
我们拿其中一个标签进行讲解,我们在使用dubbo框架时,会配置
我们来看下配置文件的内容:
dubbo=org.apache.dubbo.rpc.protocol.dubbo.DubboProtocol
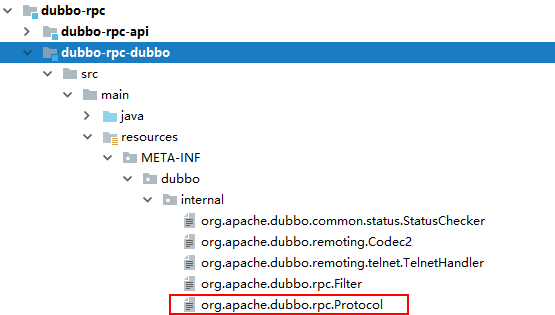
配置了一个键值对,key为dubbo,值为org.apache.dubbo.rpc.protocol.dubbo.DubboProtocol,在其它几个子包下,也有名称叫做org.apache.dubbo.rpc.Protocol的配置文件,说明Protocol插口有几个对应的插件
可以猜测一下,当
Dubbo为使用SPI做的准备工作:
三个注解
- SPI:这个注解使用在接口上,标识接口是否是extension(扩展或插口),可以接收一个默认的extension名称
- Adaptive: 这个注解可以使用在类或方法上,决定加载哪一个extension,值为字符串数组,数组中的字符串是key值,比如new String[]{"key1","key2"};先在URL中寻找key1的值,如果找到,则使用此值加载extension,如果key1没有,则寻找key2的值,如果key2也没有,则使用接口SPI注解的值,如果接口SPI注解,没有配置默认值,则将接口名按照首字母大写分成多个部分,然后以'.'分隔,例如org.apache.dubbo.xxx.YyyInvokerWrapper接口名会变成yyy.invoker.wrapper,然后以此名称做为key到URL寻找,如果仍没有找到,则抛出IllegalStateException异常;Adaptive注解用在类上,表示此类是它实现接口(插口)的自适应插件
- Activate:这个注解可以使用在类或方法上,用以根据URL的key值判断当前extension是否生效,当一个extension有多个实现时,可以加载特定的extension实现类,例如extension实现类上有注解@Activate("cache, validation"),则当URL上出现"cache”或“validation" key时,当前extension才会生效
ExtensionLoader
顾名思义,ExtensionLoader用于加载extension,它的作用有三点:1.自动加载extension;2.自动包装(wrap) extension;3.创建自适应的(adaptive)extension;
旅途开始
先看下上篇文章中Provider端的配置文件
还是先从ClassPathXmlApplicationContext加载spring配置文件说起,上回我们说到ClassPathXmlApplicationContext会使用XmlBeanDefinitionReader将xml文件解析成BeanDefiniton集合,当解析
ServiceBean是ServiceConfig的子类,所以在创建ServiceBean对象的时候,会去先实例化父类,ServiceConfig中有一个static final成员变量protocol
private static final Protocol protocol = ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(Protocol.class).getAdaptiveExtension();
ExtensionLoader终于出场了,想要获取插件,得分两步走,第一步得到Protocol的插件加载对象extensionLoader,然后由这个加载对象获得对应的插件。
先来看第一步:
public static ExtensionLoader getExtensionLoader(Class type) {
//一些检查的代码,省略
ExtensionLoader loader = (ExtensionLoader) EXTENSION_LOADERS.get(type);
if (loader == null) {
EXTENSION_LOADERS.putIfAbsent(type, new ExtensionLoader(type));
loader = (ExtensionLoader) EXTENSION_LOADERS.get(type);
}
return loader;
}
EXTENSION_LOADERS保存的是目前已经保存的插口的加载类,显然第一次加载的时候,Protocol还没有自己的插件加载类,那么需要实例化一个。实例化加载对象之后,用这个对象去加载插件。
public T getAdaptiveExtension() {
//从已经缓存的自适应对象中获得,第一次调用时还没有创建自适应类,所以instance为null
Object instance = cachedAdaptiveInstance.get();
if (instance == null) {
if (createAdaptiveInstanceError == null) {
synchronized (cachedAdaptiveInstance) {
instance = cachedAdaptiveInstance.get();
if (instance == null) {
try {
//创建一个自适应类
instance = createAdaptiveExtension();
cachedAdaptiveInstance.set(instance);
} catch (Throwable t) {
createAdaptiveInstanceError = t;
throw new IllegalStateException("fail to create adaptive instance: " + t.toString(), t);
}
}
}
} else {
throw new IllegalStateException("fail to create adaptive instance: " + createAdaptiveInstanceError.toString(), createAdaptiveInstanceError);
}
}
return (T) instance;
}
主要关注 instance = createAdaptiveExtension();这句,createAdaptiveExtension()方法是什么样的呢?
private T createAdaptiveExtension() {
try {
//得到自适应类并实现化,然后注入属性值
return injectExtension((T) getAdaptiveExtensionClass().newInstance());
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Can not create adaptive extension " + type + ", cause: " + e.getMessage(), e);
}
}
getAdaptiveExtensionClass():
private Class getAdaptiveExtensionClass() {
//1.获取所有实现Protocol插口的插件类
getExtensionClasses();
//2.如果有自适应插件类,则返回
if (cachedAdaptiveClass != null) {
return cachedAdaptiveClass;
}
//3.如果没有,则创建插件类
return cachedAdaptiveClass = createAdaptiveExtensionClass();
}
先来看上面的第1步,getExtensionClasses()
private Map> getExtensionClasses() {
//从缓存中获取插件类,第一次肯定没有
Map> classes = cachedClasses.get();
if (classes == null) {
synchronized (cachedClasses) {
classes = cachedClasses.get();
if (classes == null) {
//实际的加载插件类方法
classes = loadExtensionClasses();
cachedClasses.set(classes);
}
}
}
return classes;
}
//ExtensionLoader中的三个常量,加载插件的目录,第一个熟悉吧,是java spi的默认目录
private static final String SERVICES_DIRECTORY = "META-INF/services/";
private static final String DUBBO_DIRECTORY = "META-INF/dubbo/";
private static final String DUBBO_INTERNAL_DIRECTORY = DUBBO_DIRECTORY + "internal/";
private Map> loadExtensionClasses() {
//获取插口上SPI注解的值,默认值只能有一个,如果多于一个,则抛异常
final SPI defaultAnnotation = type.getAnnotation(SPI.class);
if (defaultAnnotation != null) {
String value = defaultAnnotation.value();
if ((value = value.trim()).length() > 0) {
String[] names = NAME_SEPARATOR.split(value);
if (names.length > 1) {
throw new IllegalStateException("more than 1 default extension name on extension " + type.getName()
+ ": " + Arrays.toString(names));
}
if (names.length == 1) cachedDefaultName = names[0];
}
}
//加载以上三个目录下的实现了相应插口的插件类(本例中插口是Protocol)
Map> extensionClasses = new HashMap>();
loadDirectory(extensionClasses, DUBBO_INTERNAL_DIRECTORY, type.getName());
loadDirectory(extensionClasses, DUBBO_INTERNAL_DIRECTORY, type.getName().replace("org.apache", "com.alibaba"));
loadDirectory(extensionClasses, DUBBO_DIRECTORY, type.getName());
loadDirectory(extensionClasses, DUBBO_DIRECTORY, type.getName().replace("org.apache", "com.alibaba"));
loadDirectory(extensionClasses, SERVICES_DIRECTORY, type.getName());
loadDirectory(extensionClasses, SERVICES_DIRECTORY, type.getName().replace("org.apache", "com.alibaba"));
return extensionClasses;
}
实现Protocol插口的共有四个插件:
再来看上面getAdaptiveExtensionClass方法的第2步,这一句是判断有没有自适应类,在加载配置的插件过程中,会判断此插件类是不是自适应插件类,判断的依据就是插件类上是否有注解@Adaptive,Protocol的这四个插件类上都没有此注解,所以没有自适应插件,则会走到第3步,创建一个自适应插件类
private Class createAdaptiveExtensionClass() {
//生成类代码
String code = createAdaptiveExtensionClassCode();
ClassLoader classLoader = findClassLoader();
//得到编辑器,并将类代码编译成字节码
org.apache.dubbo.common.compiler.Compiler compiler = ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(org.apache.dubbo.common.compiler.Compiler.class).getAdaptiveExtension();
return compiler.compile(code, classLoader);
}
//来看看生成类代码的过程,以生成Protocol插件类代码为例
private String createAdaptiveExtensionClassCode() {
StringBuilder codeBuilder = new StringBuilder();
//得到Protocol接口所有方法
Method[] methods = type.getMethods();
boolean hasAdaptiveAnnotation = false;
for (Method m : methods) {
if (m.isAnnotationPresent(Adaptive.class)) {
hasAdaptiveAnnotation = true;
break;
}
}
// // 如果方法上没有@Adaptive注解,则不能创建自适应插件类
if (!hasAdaptiveAnnotation)
throw new IllegalStateException("No adaptive method on extension " + type.getName() + ", refuse to create the adaptive class!");
codeBuilder.append("package ").append(type.getPackage().getName()).append(";");
codeBuilder.append("\nimport ").append(ExtensionLoader.class.getName()).append(";");
//类名为Protocol$Adaptive实现了Protocol接口
codeBuilder.append("\npublic class ").append(type.getSimpleName()).append("$Adaptive").append(" implements ").append(type.getCanonicalName()).append(" {");
for (Method method : methods) {
Class rt = method.getReturnType();
Class[] pts = method.getParameterTypes();
Class[] ets = method.getExceptionTypes();
Adaptive adaptiveAnnotation = method.getAnnotation(Adaptive.class);
StringBuilder code = new StringBuilder(512);
if (adaptiveAnnotation == null) {
code.append("throw new UnsupportedOperationException(\"method ")
.append(method.toString()).append(" of interface ")
.append(type.getName()).append(" is not adaptive method!\");");
} else {
int urlTypeIndex = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < pts.length; ++i) {
if (pts[i].equals(URL.class)) {
urlTypeIndex = i;
break;
}
}
// 如果发现方法中的参数有一个URL类型
if (urlTypeIndex != -1) {
// Null Point check
String s = String.format("\nif (arg%d == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException(\"url == null\");",
urlTypeIndex);
code.append(s);
s = String.format("\n%s url = arg%d;", URL.class.getName(), urlTypeIndex);
code.append(s);
}
// 如果没有发现,则会寻找每一个参数类型中的属性是否有为URL类型的
else {
String attribMethod = null;
// find URL getter method
LBL_PTS:
for (int i = 0; i < pts.length; ++i) {
Method[] ms = pts[i].getMethods();
for (Method m : ms) {
String name = m.getName();
if ((name.startsWith("get") || name.length() > 3)
&& Modifier.isPublic(m.getModifiers())
&& !Modifier.isStatic(m.getModifiers())
&& m.getParameterTypes().length == 0
&& m.getReturnType() == URL.class) {
urlTypeIndex = i;
attribMethod = name;
break LBL_PTS;
}
}
}
//如果没找到,则抛出异常
if (attribMethod == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("fail to create adaptive class for interface " + type.getName()
+ ": not found url parameter or url attribute in parameters of method " + method.getName());
}
// Null point check
String s = String.format("\nif (arg%d == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException(\"%s argument == null\");",
urlTypeIndex, pts[urlTypeIndex].getName());
code.append(s);
s = String.format("\nif (arg%d.%s() == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException(\"%s argument %s() == null\");",
urlTypeIndex, attribMethod, pts[urlTypeIndex].getName(), attribMethod);
code.append(s);
s = String.format("%s url = arg%d.%s();", URL.class.getName(), urlTypeIndex, attribMethod);
code.append(s);
}
String[] value = adaptiveAnnotation.value();
// value is not set, use the value generated from class name as the key
if (value.length == 0) {
char[] charArray = type.getSimpleName().toCharArray();
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(128);
for (int i = 0; i < charArray.length; i++) {
if (Character.isUpperCase(charArray[i])) {
if (i != 0) {
sb.append(".");
}
sb.append(Character.toLowerCase(charArray[i]));
} else {
sb.append(charArray[i]);
}
}
value = new String[]{sb.toString()};
}
boolean hasInvocation = false;
for (int i = 0; i < pts.length; ++i) {
if (pts[i].getName().equals("org.apache.dubbo.rpc.Invocation")) {
// Null Point check
String s = String.format("\nif (arg%d == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException(\"invocation == null\");", i);
code.append(s);
s = String.format("\nString methodName = arg%d.getMethodName();", i);
code.append(s);
hasInvocation = true;
break;
}
}
String defaultExtName = cachedDefaultName;
String getNameCode = null;
for (int i = value.length - 1; i >= 0; --i) {
if (i == value.length - 1) {
if (null != defaultExtName) {
if (!"protocol".equals(value[i]))
if (hasInvocation)
getNameCode = String.format("url.getMethodParameter(methodName, \"%s\", \"%s\")", value[i], defaultExtName);
else
getNameCode = String.format("url.getParameter(\"%s\", \"%s\")", value[i], defaultExtName);
else
getNameCode = String.format("( url.getProtocol() == null ? \"%s\" : url.getProtocol() )", defaultExtName);
} else {
if (!"protocol".equals(value[i]))
if (hasInvocation)
getNameCode = String.format("url.getMethodParameter(methodName, \"%s\", \"%s\")", value[i], defaultExtName);
else
getNameCode = String.format("url.getParameter(\"%s\")", value[i]);
else
getNameCode = "url.getProtocol()";
}
} else {
if (!"protocol".equals(value[i]))
//如果方法参数类型名称为"org.apache.dubbo.rpc.Invocation"则从url获取以此参数类型名为key的值,获取不到则取默认扩展名,即Protocol接口上注解SPI的值“dubbo”
if (hasInvocation)
getNameCode = String.format("url.getMethodParameter(methodName, \"%s\", \"%s\")", value[i], defaultExtName);
else
//否则,取从url中取以方法上注解adaptive的值为key对应的值
getNameCode = String.format("url.getParameter(\"%s\", %s)", value[i], getNameCode);
else
getNameCode = String.format("url.getProtocol() == null ? (%s) : url.getProtocol()", getNameCode);
}
}
code.append("\nString extName = ").append(getNameCode).append(";");
// check extName == null?
String s = String.format("\nif(extName == null) " +
"throw new IllegalStateException(\"Fail to get extension(%s) name from url(\" + url.toString() + \") use keys(%s)\");",
type.getName(), Arrays.toString(value));
code.append(s);
s = String.format("\n%s extension = (% 0) {
codeBuilder.append(", ");
}
codeBuilder.append(pts[i].getCanonicalName());
codeBuilder.append(" ");
codeBuilder.append("arg").append(i);
}
codeBuilder.append(")");
if (ets.length > 0) {
codeBuilder.append(" throws ");
for (int i = 0; i < ets.length; i++) {
if (i > 0) {
codeBuilder.append(", ");
}
codeBuilder.append(ets[i].getCanonicalName());
}
}
codeBuilder.append(" {");
codeBuilder.append(code.toString());
codeBuilder.append("\n}");
}
codeBuilder.append("\n}");
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug(codeBuilder.toString());
}
return codeBuilder.toString();
}
我们来看下生成的插件类Protocol$Adaptive代码:
package org.apache.dubbo.rpc;
import org.apache.dubbo.common.extension.ExtensionLoader;
public class Protocol$Adaptive implements org.apache.dubbo.rpc.Protocol {
public void destroy()
{throw new UnsupportedOperationException("method public abstract void org.apache.dubbo.rpc.Protocol.destroy() of interface org.apache.dubbo.rpc.Protocol is not adaptive method!");
}
public int getDefaultPort() {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("method public abstract int org.apache.dubbo.rpc.Protocol.getDefaultPort() of interface org.apache.dubbo.rpc.Protocol is not adaptive method!");
}
public org.apache.dubbo.rpc.Invoker refer(java.lang.Class arg0, org.apache.dubbo.common.URL arg1) throws org.apache.dubbo.rpc.RpcException {
if (arg1 == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("url == null");
org.apache.dubbo.common.URL url = arg1;
String extName = ( url.getProtocol() == null ? "dubbo" : url.getProtocol() );
if(extName == null) throw new IllegalStateException("Fail to get extension(org.apache.dubbo.rpc.Protocol) name from url(" + url.toString() + ") use keys([protocol])");
org.apache.dubbo.rpc.Protocol extension = (org.apache.dubbo.rpc.Protocol)ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(org.apache.dubbo.rpc.Protocol.class).getExtension(extName);
return extension.refer(arg0, arg1);
}
public org.apache.dubbo.rpc.Exporter export(org.apache.dubbo.rpc.Invoker arg0) throws org.apache.dubbo.rpc.RpcException {
if (arg0 == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("org.apache.dubbo.rpc.Invoker argument == null");
if (arg0.getUrl() == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("org.apache.dubbo.rpc.Invoker argument getUrl() == null");org.apache.dubbo.common.URL url = arg0.getUrl();
String extName = ( url.getProtocol() == null ? "dubbo" : url.getProtocol() );
if(extName == null) throw new IllegalStateException("Fail to get extension(org.apache.dubbo.rpc.Protocol) name from url(" + url.toString() + ") use keys([protocol])");
org.apache.dubbo.rpc.Protocol extension = (org.apache.dubbo.rpc.Protocol)ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(org.apache.dubbo.rpc.Protocol.class).getExtension(extName);
return extension.export(arg0);
}
}
可以看出此类可以根据url中参数protocol值加载对应的插件,如果url中没有,则加载名为"dubbo"对应的插件,而从前面加载的四个插件可以看出,名称为dubbo的插件类为org.apache.dubbo.rpc.protocol.dubbo.DubboProtocol.
写到这里总算将SPI加载的过程大体上讲述了一篇,Dubbo中还有许多类似的插件,原理基本相同;除了有的插口有自适应插件,比如org.apache.dubbo.common.compiler.Compiler和org.apache.dubbo.common.extension.ExtensionFactory,自适应插件类上都有注解@Adaptive,比如Compile的自适应插件AdaptiveCompiler,ExtensionFactory的自适应插件AdaptiveExtensionFactory.
为什么要提供自适应插件,而不是都在运行时生成?
答:
(1)解决鸡生蛋,蛋生鸡的问题,上面createAdaptiveExtensionClass方法中,在第1步生成Protocol$Adaptive类后,会使用编译器将其编译成字节码,但是编译器本身也是插件化的,可以有好几种编译器,所以需要提供一个已经存在的自适应编译器(AdaptiveCompiler),然后在编译的时候,使用此编译器找到Compile接口上SPI注解中配置的默认的编译器进行编译。
(2)解决对象生成方式不同导致的加载问题;Dubbo中对象的生成一类是由Spring容器创建,一类是根据插件文件的配置动态加载;所以要想获取这两部分对象,需要使用不同的方式;而AdaptiveExtensionFactory就是为了解决这个问题,在获取对象时,分别从Spring容器和ExtensionLoader中查找。