一级标题
文本处理工具和正则表达式
二级标题
1.文本编辑工具VIM
文本编辑工具之神VIM
vi
Visual editor,文本编辑器,是 Linux 必备工具之一,功能强大,学习曲线较陡峭,学习难度大
vim
VIsual editor iMproved ,和 vi 使用方法一致,但功能更为强大,不是必备软件
官网:www.vim.org
其他相关编辑器:gvim 一个Vim编辑器的图形版本
1.1使用 vim 初步
常用选项
+# 打开文件后,让光标处于第#行的行首,+默认行尾
+/PATTERN 让光标处于第一个被PATTERN匹配到的行行首
-b file 二进制方式打开文件
-d file1 file2… 比较多个文件,相当于 vimdiff
-m file 只读打开文件
-e file 直接进入ex模式,相当于执行ex file
说明:
如果该文件存在,文件被打开并显示内容
如果该文件不存在,当编辑后第一次存盘时创建它
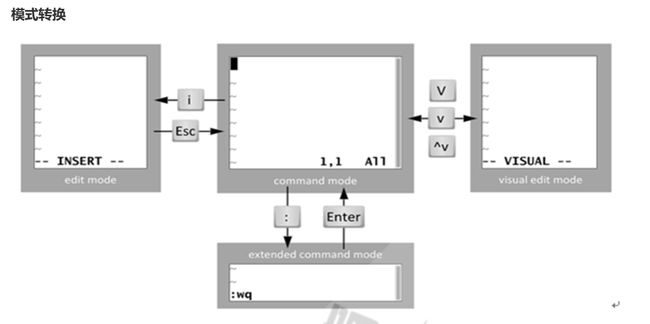
1.2三种常见模式:
命令或普通(Normal)模式:默认模式,可以实现移动光标,剪切/粘贴文本
插入(Insert)或编辑模式:用于修改文本
扩展命令(extended command )或命令(末)行模式:保存,退出等
命令模式 --> 插入模式
i insert, 在光标所在处输入
I 在当前光标所在行的行首输入
a append, 在光标所在处后面输入
A 在当前光标所在行的行尾输入
o 在当前光标所在行的下方打开一个新行
O 在当前光标所在行的上方打开一个新行
插入模式 --- ESC-----> 命令模式
命令模式 ---- : ----> 扩展命令模式
扩展命令模式 ----ESC,enter----> 命令模式
1.3 扩展命令模式
按“:”进入Ex模式 ,创建一个命令提示符: 处于底部的屏幕左侧
扩展命令模式基本命令
w 写(存)磁盘文件
wq 写入并退出
x 写入并退出
X 加密
q 退出
q! 不存盘退出,即使更改都将丢失
r filename 读文件内容到当前文件中
w filename 将当前文件内容写入另一个文件
!command 执行命令
r!command 读入命令的输出
地址定界格式
# #具体第#行,例如2表示第2行
#,# #从左侧#表示起始行,到右侧#表示结尾行
#,+# #从左侧#表示的起始行,加上右侧#表示的行数,范例:2,+3 表示2到5行
. #当前行
$ #最后一行
.,$-1 #当前行到倒数第二行
% #全文, 相当于1,$
/pattern/ #从当前行向下查找,直到匹配pattern的第一行,即:正则表达式
/pat1/,/pat2/ #从第一次被pat1模式匹配到的行开始,一直到第一次被pat2匹配到的行结束
#,/pat/ #从指定行开始,一直找到第一个匹配patttern的行结束
/pat/,$ #向下找到第一个匹配patttern的行到整个文件的结尾的所有行
地址定界后跟一个编辑命令
d #删除
y #复制
w file #将范围内的行另存至指定文件中
r file #在指定位置插入指定文件中的所有内容
查找并替换
格式
s/要查找的内容/替换为的内容/修饰符
说明
要查找的内容:可使用基末正则表达式模式
替换为的内容:不能使用模式,但可以使用\1, \2, ...等后向引用符号;还可以使用“&”引用前面查找时查
找到的整个内容
修饰符:
i #忽略大小写
g #全局替换,默认情况下,每一行只替换第一次出现
gc #全局替换,每次替换前询问
查找替换中的分隔符/可替换为其它字符,如:#,@
定制vim的工作特性
扩展命令模式的配置只是对当前vim进程有效,可将配置存放在文件中持久保存
配置文件:
/etc/vimrc #全局
~/.vimrc #个人
行号
显示:set number,简写 set nu
取消显示:set nonumber, 简写 set nonu
忽略字符的大小写
启用:set ignorecase,简写 set ic
不忽略:set noic
自动缩进
启用:set autoindent,简写 set ai
禁用:set noai
复制保留格式
启用:set paste
禁用:set nopaste
显示Tab和换行符 ^I 和$显示
启用:set list
禁用:set nolist
高亮搜索
启用:set hlsearch
禁用:set nohlsearch
语法高亮
启用:syntax on
禁用:syntax off
文件格式
启用windows格式:set fileformat=dos
启用unix格式:set fileformat=unix
简写 set ff=dos|unix
设置文本宽度
set textwidth=65 (vim only)
设置光标所在行的标识线
启用:set cursorline,简写 set cul
禁用:set nocursorline
加密
启用: set key=password
禁用: set key=
1.4 命令模式
命令模式,又称为Normal模式,功能强大,只是此模式输入指令并在屏幕上显示,所以需要记忆大量的快捷按键才能更好的使用
1.退出VIM
ZZ 保存退出
ZQ 不保存退出
2. 光标跳转
字符间跳转:
h: 左 L: 右 j: 下 k: 上
#COMMAND:跳转由#指定的个数的字符
单词间跳转:
w:下一个单词的词首
e:当前或下一单词的词尾
b:当前或前一个单词的词首
#COMMAND:由#指定一次跳转的单词数
当前页跳转:
H:页首 M:页中间行 L:页底
zt:将光标所在当前行移到屏幕顶端
zz:将光标所在当前行移到屏幕中间
zb:将光标所在当前行移到屏幕底端
行首行尾跳转:
^ 跳转至行首的第一个非空白字符
0 跳转至行首
$ 跳转至行尾
行间移动:
#G 或者扩展命令模式下 :# 跳转至由第#行
G 最后一行
1G, gg 第一行
句间移动:
) 下一句 ( 上一句
段落间移动:
} 下一段 { 上一段
命令模式翻屏操作
Ctrl+f 向文件尾部翻一屏
Ctrl+b 向文件首部翻一屏
Ctrl+d 向文件尾部翻半屏
Ctrl+u 向文件首部翻半屏
3.字符编辑
x 删除光标处的字符
#x 删除光标处起始的#个字符
xp 交换光标所在处的字符及其后面字符的位置
~ 转换大小写
J 删除当前行后的换行符
4.替换命令(replace)
r 只替换光标所在处的一个字符
R 切换成REPLACE模式(在末行出现-- REPLACE -- 提示),按ESC回到命令模式
5.删除命令(delete)
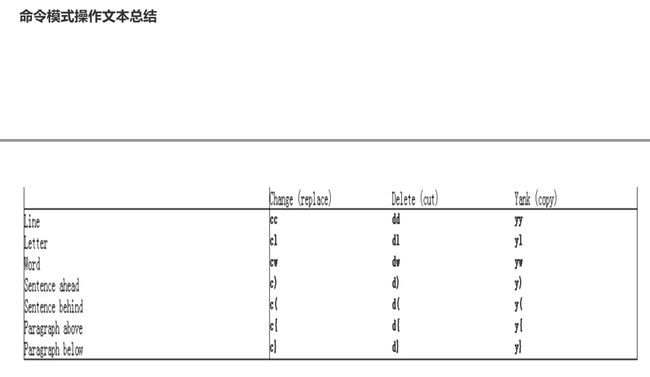
d 删除命令,可结合光标跳转字符,实现范围删除
d$ 删除到行尾
d^ 删除到非空行首
d0 删除到行首
dw
de
db
#COMMAND
dd: 剪切光标所在的行
#dd 多行删除
D:从当前光标位置一直删除到行尾,等同于d$
6.复制命令(yank)
y 复制,行为相似于d命令
y$
y0
y^
ye
yw
yb
#COMMAND
yy:复制行
#yy 复制多行
Y:复制整行
7.粘贴命令(paste)
p 缓冲区存的如果为整行,则粘贴当前光标所在行的下方;否则,则粘贴至当前光标所在处的后面
P 缓冲区存的如果为整行,则粘贴当前光标所在行的上方;否则,则粘贴至当前光标所在处的前面
8. 改变命令(change)
c: 删除后切换成插入模式
c$
c^
c0
cb
ce
cw
#COMMAND
cc:删除当前行并输入新内容,相当于S
#cc
C:删除当前光标到行尾,并切换成插入模式,相当于c$
9. 查找
/PATTERN:从当前光标所在处向文件尾部查找
?PATTERN:从当前光标所在处向文件首部查找
n:与命令同方向
N:与命令反方向
10. 撤消更改
u 撤销最近的更改,相当于windows中ctrl+z
#u 撤销之前多次更改
U 撤消光标落在这行后所有此行的更改
Ctrl - r 重做最后的“撤消”更改,相当于windows中crtl+y
. 重复前一个操作
#. 重复前一个操作#次
高级用法
常见Command:y 复制、d 删除、gU 变大写、gu 变小写
0y$ 命令
0 → 先到行头
y → 从这里开始拷贝
$ → 拷贝到本行最后一个字符
粘贴“wang”100次
100iwang [ESC]
di" 光标在” “之间,则删除” “之间的内容
yi( 光标在()之间,则复制()之间的内容
vi[ 光标在[]之间,则选中[]之间的内容
dtx 删除字符直到遇见光标之后的第一个 x 字符
ytx 复制字符直到遇见光标之后的第一个 x 字符
1.5 可视化模式
在末行有”-- VISUAL -- “指示,表示在可视化模式
允许选择的文本块
v 面向字符,-- VISUAL --
V 面向整行,-- VISUAL LINE --
ctrl-v 面向块,-- VISUAL BLOCK --
可视化键可用于与移动键结合使用
w ) } 箭头等
突出显示的文字可被删除,复制,变更,过滤,搜索,替换等
范例:在文件行首插入#
输入ctrl+v 进入可视化模式
输入 G 跳到最后1行,选中每一行的第一个字符
输入 I 切换至插入模式
输入 #
按 ESC 键
1.6 多文件模式
vim FILE1 FILE2 FILE3 ...
:next 下一个
:prev 前一个
:first 第一个
:last 最后一个
:wall 保存所有
:qall 不保存退出所有
:wqall保存退出所有
1.7 多窗口模式
多文件分割
vim -o|-O FILE1 FILE2 ...
-o: 水平或上下分割
-O: 垂直或左右分割(vim only)
在窗口间切换:Ctrl+w, Arrow
单文件窗口分割
Ctrl+w,s:split, 水平分割,上下分屏
Ctrl+w,v:vertical, 垂直分割,左右分屏
ctrl+w,q:取消相邻窗口
ctrl+w,o:取消全部窗口
:wqall 退出
1.8 vim的寄存器
有26个命名寄存器和1个无命名寄存器,常存放不同的剪贴版内容,可以在同一个主机的不同会话(终端窗口)间共享
寄存器名称a,b,…,z,格式: ”寄存器 放在数字和命令之间
范例:
3"tyy 表示复制3行到t寄存器中 ,末行显示 3 lines yanked into "t
"tp 表示将t寄存器内容粘贴未指定,将使用无命名寄存器
有10个数字寄存器,用0,1,…,9表示,0存放最近复制内容,1存放最近删除内容。当新的文本变更和删除时,1转存到2,2转存到3,以此类推。数字寄存器不能在不同会话间共享
1.9 标记和宏(macro)
ma 将当前位置标记为a,26个字母均可做标记, mb 、 mc 等等
'a 跳转到a标记的位置,实用的文档内标记方法,文档中跳跃编辑时很有用
qa 录制宏 a,a为宏的名称,末行提示: recording @a
q 停止录制宏
@a 执行宏 a
@@ 重新执行上次执行的宏
二级标题
2.各种文本工具
查看文本文件内容
cat 可以查看文本内容
常见选项
-E:显示行结束符$
-A:显示所有控制符
-n:对显示出的每一行进行编号
-b:非空行编号
-s:压缩连续的空行成一行
范例:
[root@centos8 ~]#cat -A /data/fa.txt
a b$
c $
dIbIc$
[root@centos8 ~]#cat /data/fa.txt
a b
c
d b c
[root@centos8 ~]#cat /data/fb.txt
a
b
c
[root@centos8 ~]#hexdump -C /data/fb.txt
00000000 61 0d 0a 62 0d 0a 63 0d 0a |a..b..c..|
00000009
[root@centos8 ~]#cat -A /data/fb.txt
a^M$
b^M$
c^M$
[root@centos8 ~]#file /data/fb.txt
/data/fb.txt: ASCII text, with CRLF line terminators
显示行号nl
[root@centos8 ~]#cat /data/f1.txt
a
b
c
d
e
f
tac逆向显示文本内容
[root@centos8 ~]#cat /data/fa.txt
1
2
3
4
5
[root@centos8 ~]#tac /data/fa.txt
5
4
3
2
1
rev将同一行的内容逆向显示
[root@centos8 ~]#rev
abcdef
fedcba
[root@centos8 ~]#echo {1..10} |rev
01 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1
查看非文本文件内容
hexdump
hexdump -C -n 512 /dev/sda
00000000 eb 63 90 10 8e d0 bc 00 b0 b8 00 00 8e d8 8e c0 |.c..............|
echo {a..z} | tr -d ' '|hexdump -C
00000000 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 6a 6b 6c 6d 6e 6f 70 |abcdefghijklmnop|
00000010 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 7a 0a |qrstuvwxyz.|
0000001b
od
root@centos8 ~]#echo {a..z} | tr -d ' '|od -t x
0000000 64636261 68676665 6c6b6a69 706f6e6d
0000020 74737271 78777675 000a7a79
0000033
[root@centos8 ~]#echo {a..z} | tr -d ' '|od -t x1
0000000 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 6a 6b 6c 6d 6e 6f 70
0000020 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 7a 0a
0000033
[root@centos8 ~]#echo {a..z} | tr -d ' '|od -t x1z
0000000 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 6a 6b 6c 6d 6e 6f 70 >abcdefghijklmnop<
0000020 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 7a 0a >qrstuvwxyz.<
0000033
xxd
echo {a..z} | tr -d ' '|xxd
0000000: 6162 6364 6566 6768 696a 6b6c 6d6e 6f70 abcdefghijklmnop
0000010: 7172 7374 7576 7778 797a 0a qrstuvwxyz.
分页查看文件内容
more
可以实现分页查看文件,可以配合管道实现输出信息的分页
选项:
-d: 显示翻页及退出提示
less 也可以实现分页查看文件或STDIN输出
查看时有用的命令包括:
/文本 搜索 文本
n/N 跳到下一个 或 上一个匹配
less
[root@centos8 ~]#cat /etc/init.d/functions |less
# -*-Shell-script-*-
#
# functions This file contains functions to be used by most or all
# shell scripts in the /etc/init.d directory.
#
TEXTDOMAIN=initscripts
# Make sure umask is sane
umask 022
# Set up a default search path.
PATH="/sbin:/usr/sbin:/bin:/usr/bin"
export PATH
...省略..
显示文本前或后行内容
head
可以显示文件或标准输入的前面行
选项:
-c # 指定获取前#字节
-n # 指定获取前#行
-# 同上
[root@centos8 ~]#head -n 3 /etc/passwd
root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash
bin:x:1:1:bin:/bin:/sbin/nologin
daemon:x:2:2:daemon:/sbin:/sbin/nologin
[root@centos8 ~]#head -3 /etc/passwd
root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash
bin:x:1:1:bin:/bin:/sbin/nologin
daemon:x:2:2:daemon:/sbin:/sbin/nologin
[root@centos8 ~]#echo a我b | head -c4
a我[root@centos8 ~]#
[root@centos8 ~]#cat /dev/urandom | tr -dc '[:alnum:]'| head -c10
G755MlZatW[root@centos8 ~]#cat /dev/urandom | tr -dc '[:alnum:]'| head -c10
ASsax6DeBz[root@centos8 ~]#cat /dev/urandom | tr -dc '[:alnum:]'| head -c10 |
tes.txt | passwd --stdin mage
Changing password for user mage.
passwd: all authentication tokens updated successfully.
[root@centos8 ~]#cat pass.txt
AGT952Essg[root@centos8 ~]#su - wang
[wang@centos8 ~]$su - mage
Password:
tail
tail 和head 相反,查看文件或标准输入的倒数行
-c # 指定获取后#字节
-n # 指定获取后#行
# 同上
-f 跟踪显示文件fd新追加的内容,常用日志监控,相当于 --follow=descriptor,当文件删除再新建同名
文件,将无法继续跟踪文件
-F 跟踪文件名,相当于--follow=name --retry,当文件删除再新建同名文件,将可以继续跟踪文件
tailf 类似 tail –f,当文件不增长时并不访问文件
[root@centos8 ~]#cat /data/f1.txt
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
[root@centos8 ~]#tail -n 3 /data/f1.txt
8
9
10
#只查看最新发生的日志
[root@centos8 ~]#tail -fn0 /var/log/messages
[root@centos8 ~]#tail -0f /var/log/messages
[root@centos8 data]#ifconfig | head -2 | tail -1
inet 10.0.0.8 netmask 255.255.255.0broadcast 10.0.0.255
按列抽取文本cut
cut 命令可以提取文本文件或STDIN数据的指定列
选项
-d DELIMITER: 指明分隔符,默认tab
-f FILEDS:
#: 第#个字段,例如:3
#,#[,#]:离散的多个字段,例如:1,3,6
#-#:连续的多个字段, 例如:1-6
混合使用:1-3,7
-c 按字符切割
--output-delimiter=STRING指定输出分隔符
[root@centos8 ~]#cut -d: -f1,3-4,7 /etc/passwd
[root@centos8 ~]#ifconfig |head -n2 |tail -n1|cut -d" " -f10
10.0.0.8
[root@centos8 ~]#ifconfig |head -n2 |tail -n1|tr -s " " |cut -d " " -f3
10.0.0.8
[root@centos8 ~]#cut -d: -f1,3,7 --output-delimiter="---" /etc/passwd
root---0---/bin/bash
bin---1---/sbin/nologin
daemon---2---/sbin/nologin
cat /etc/passwd | cut -d: -f7
cut -c2-5 /usr/share/dict/words
合并多个文件paste
-d 分隔符:指定分隔符,默认用TAB
-s : 所有行合成一行显示
[root@centos8 ~]#paste -s seq.log
1 2 3 4 5
[root@centos8 ~]#paste -s alpha.log
a b c d e f g h
[root@centos8 ~]#paste -s alpha.log seq.log
a b c d e f g h
1 2 3 4 5
2.6分析文本的工具
文本数据统计:wc
wc 命令可用于统计文件的行总数、单词总数、字节总数和字符总数
可以对文件或STDIN中的数据统计
常用选项
-l 只计数行数
-w 只计数单词总数
-c 只计数字节总数
-m 只计数字符总数
-L 显示文件中最长行的长度
范例:
[root@centos8 ~]#cat emp.txt
mage
zhang
wang
xu
[root@centos8 ~]#paste title.txt emp.txt
ceo mage
coo zhang
cto wang
xu
[root@centos8 ~]#paste -s title.txt emp.txt
ceo coo cto
mage zhang wang xu
wc story.txt
39 237 1901 story.txt
行数 单词数 字节数
[root@centos8 ~]#ll title.txt
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 30 Dec 20 11:05 title.txt
[root@centos8 ~]#ll title1.txt
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 28 Dec 20 11:06 title1.txt
[root@centos8 ~]#cat title.txt
ceo mage
coo zhang
cto 老王
[root@centos8 ~]#cat title1.txt
ceo mage
coo zhang
cto wang
[root@centos8 ~]#wc title.txt
3 6 30 title.txt
[root@centos8 ~]#wc title1.txt
3 6 28 title1.txt
[root@centos8 ~]#wc -l title.txt
3 title.txt
[root@centos8 ~]#cat title.txt | wc -l
3
[root@centos8 ~]#df | tail -n $(echo `df | wc -l`-1|bc)
devtmpfs 910220 0 910220 0% /dev
tmpfs 924728 0 924728 0% /dev/shm
tmpfs 924728 9224 915504 1% /run
tmpfs 924728 0 924728 0% /sys/fs/cgroup
/dev/sda2 104806400 4836160 99970240 5% /
/dev/sda3 52403200 398580 52004620 1% /data
/dev/sda1 999320 131764 798744 15% /boot
tmpfs 184944 4 184940 1% /run/user/0
整理文本:sort
把整理过的文本显示在STDOUT,不改变原始文件
常用选项
-r 执行反方向(由上至下)整理
-R 随机排序
-n 执行按数字大小整理
-f 选项忽略(fold)字符串中的字符大小写
-u 选项(独特,unique)删除输出中的重复行
-t c 选项使用c做为字段界定符
-k # 选项按照使用c字符分隔的 # 列来整理能够使用多次
范例:
[root@centos8 data]#cut -d: -f1,3 /etc/passwd|sort -t: -k2 -nr |head -n3
nobody:65534
xiaoming:1002
mage:1001
#统计日志访问量
[root@centos8 data]#cut -d" " -f1 /var/log/nginx/access_log |sort -u|wc -l
201
统计分区利用率
[root@centos8 ~]#df | tr -s " " %|cut -d% -f5|tr -d '[:alpha:]' | sort -nr|head
-n1
15
去重uniq
uniq命令从输入中删除前后相接的重复的行
-c: 显示每行重复出现的次数
-d: 仅显示重复过的行
-u: 仅显示不曾重复的行
范例:统计日志访问量最多的请求
[root@centos8 data]#cut -d" " -f1 access_log |sort |uniq -c|sort -nr |head -3
4870 172.20.116.228
3429 172.20.116.208
2834 172.20.0.222
[root@centos8 data]#lastb -f btmp-34 | tr -s ' ' |cut -d ' ' -f3|sort |uniq -c
|sort -nr | head -3
86294 58.218.92.37
43148 58.218.92.26
18036 112.85.42.201
范例:并发连接最多的远程主机IP
[root@centos8 ~]#ss -nt|tail -n+2 |tr -s ' ' : |cut -d: -f6|sort|uniq -c|sort -
nr |head -n2
7 10.0.0.1
2 10.0.0.7
范例:取两个文件的相同和不同的行
[root@centos8 data]#cat test1.txt
a
b
1
c
[root@centos8 data]#cat test2.txt
b
e
f
c
1
2
#取文件的共同行
[root@centos8 data]#cat test1.txt test2.txt | sort |uniq -d
1
b
c
#取文件的不同行
[root@centos8 data]#cat test1.txt test2.txt | sort |uniq -u
2
a
e
f
比较文件:diff和patch
diff 命令比较两个文件之间的区别
[root@centos8 ~]#cat f1.txt
mage
zhang
wang
xu
[root@centos8 ~]#cat f2.txt
magedu
zhang sir
wang
xu
shi
[root@centos8 ~]#diff f1.txt f2.txt
1,2c1,2
< mage
< zhang
---
> magedu
> zhang sir
4a5
> shi
[root@centos8 ~]#diff -u f1.txt f2.txt
--- f1.txt 2019-12-13 21:31:30.892775671 +0800
+++ f2.txt 2019-12-13 22:00:14.373677728 +0800
@@ -1,4 +1,5 @@
-mage
-zhang
+magedu
+zhang sir
wang
xu
+shi
[root@centos8 ~]#diff -u f1.txt f2.txt > f.patch
[root@centos8 ~]#rm -f f2.txt
[root@centos8 ~]#patch -b f1.txt f.patch
patching file f1.txt
[root@centos8 ~]#cat f1.txt
magedu
zhang sir
wang
xu
shi
[root@centos8 ~]#cat f1.txt.orig
mage
zhang
wang
patch
patch 复制在其它文件中进行的改变(要谨慎使用)
适用 -b 选项来自动备份改变了的文件
二级标题
3.基本正则表达式和扩展正则表达式
REGEXP: Regular Expressions,由一类特殊字符及文本字符所编写的模式,其中有些字符(元字符)
不表示字符字面意义,而表示控制或通配的功能,类似于增强版的通配符功能,但与通配符不同,通配
符功能是用来处理文件名,而正则表达式是处理文本内容中字符
正则表达式被很多程序和开发语言所广泛支持:vim, less,grep,sed,awk, nginx,mysql 等
正则表达式分两类
基本正则表达式:BRE
扩展正则表达式:ERE
正则表达式的元字符分类:字符匹配、匹配次数、位置锚定、分组
帮助:man 7 regex
基本正则表达式元字符
字符匹配
. 匹配任意单个字符,可以是一个汉字
[] 匹配指定范围内的任意单个字符,示例:[wang] [0-9] [a-z] [a-zA-Z]
[^] 匹配指定范围外的任意单个字符,示例:[^wang]
[:alnum:] 字母和数字
[:alpha:] 代表任何英文大小写字符,亦即 A-Z, a-z
[:lower:] 小写字母,示例:[[:lower:]],相当于[a-z]
[:upper:] 大写字母
[:blank:] 空白字符(空格和制表符)
[:space:] 水平和垂直的空白字符(比[:blank:]包含的范围广)
[:cntrl:] 不可打印的控制字符(退格、删除、警铃...)
[:digit:] 十进制数字
[:xdigit:]十六进制数字
[:graph:] 可打印的非空白字符
[:print:] 可打印字符
[:punct:] 标点符号
范例:
[root@centos8 ~]#ls /etc/ | grep 'rc[.0-6]'
rc0.d
rc1.d
rc2.d
rc3.d
rc4.d
rc5.d
rc6.d
rc.d
rc.local
[root@centos8 ~]#ls /etc/ | grep 'rc[.0-6].'
rc0.d
rc1.d
rc2.d
rc3.d
rc4.d
rc5.d
rc6.d
rc.d
rc.local
匹配次数
用在要指定次数的字符后面,用于指定前面的字符要出现的次数
* 匹配前面的字符任意次,包括0次,贪婪模式:尽可能长的匹配
.* 任意长度的任意字符
\? 匹配其前面的字符0或1次,即:可有可无
\+ 匹配其前面的字符至少1次,即:肯定有,>=1
\{n\} 匹配前面的字符n次
\{m,n\} 匹配前面的字符至少m次,至多n次
\{,n\} 匹配前面的字符至多n次,<=n
\{n,\} 匹配前面的字符至少n次
范例:
[root@centos8 ~]#echo /etc/ |grep "/etc/\?"
/etc/
[root@centos8 ~]#echo /etc |grep "/etc/\?"
/etc
位置锚定
位置锚定可以用于定位出现的位置
^ 行首锚定,用于模式的最左侧
$ 行尾锚定,用于模式的最右侧
^PATTERN$ 用于模式匹配整行
^$ 空行
^[[:space:]]*$ 空白行
\< 或 \b 词首锚定,用于单词模式的左侧
\> 或 \b 词尾锚定,用于单词模式的右侧
\ 匹配整个单词
范例:
[root@centos8 ~]#grep -v '^$' /etc/profile|grep -v '^#'
分组其它
分组:() 将多个字符捆绑在一起,当作一个整体处理,如:\(root\)+
后向引用:分组括号中的模式匹配到的内容会被正则表达式引擎记录于内部的变量中,这些变量的命名
方式为: \1, \2, \3, ...
\1 表示从左侧起第一个左括号以及与之匹配右括号之间的模式所匹配到的字符
\(string1\(string2\)\)
\1 :string1\(string2\)
\2 :string2
注意: 后向引用 引用前面的分组括号中的模式所匹配字符,而非模式本身
或者\|
a\|b #a或b
C\|cat #C或cat
\(C\|c\)at #Cat或cat
范例:排除空行和#开头的行
[root@centos6 ~]#grep -v '^#' /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf |grep -v ^$
[root@centos6 ~]#grep -v '^#\|^$' /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
[root@centos6 ~]#grep -v '^\(#\|$\)' /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
[root@centos6 ~]#grep "^[^#]" /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
扩展正则表达式
字符匹配元字符
. 任意单个字符
[wang] 指定范围的字符
[^wang] 不在指定范围的字符
[:alnum:] 字母和数字
[:alpha:] 代表任何英文大小写字符,亦即 A-Z, a-z
[:lower:] 小写字母,示例:[[:lower:]],相当于[a-z]
[:upper:] 大写字母
[:blank:] 空白字符(空格和制表符)
[:space:] 水平和垂直的空白字符(比[:blank:]包含的范围广)
[:cntrl:] 不可打印的控制字符(退格、删除、警铃...)
[:digit:] 十进制数字
[:xdigit:]十六进制数字
[:graph:] 可打印的非空白字符
[:print:] 可打印字符
[:punct:] 标点符号
次数匹配
* 匹配前面字符任意次
? 0或1次
+ 1次或多次
{n} 匹配n次
{m,n} 至少m,至多n次
位置锚定
^ 行首
$ 行尾
\<, \b 语首
\>, \b 语尾
分组其它
() 分组
后向引用:\1, \2, ...
| 或者
a|b #a或b
C|cat #C或cat
(C|c)at #Cat或cat
二级标题
4.文本处理三剑客之grep
grep 命令主要对文本的(正则表达式)行基于模式进行过滤
grep: Global search REgular expression and Print out the line
作用:文本搜索工具,根据用户指定的“模式”对目标文本逐行进行匹配检查;打印匹配到的行
模式:由正则表达式字符及文本字符所编写的过滤条件
常见选项:
--color=auto 对匹配到的文本着色显示
-m # 匹配#次后停止
-v 显示不被pattern匹配到的行
-i 忽略字符大小写
-n 显示匹配的行号
-c 统计匹配的行数
-o 仅显示匹配到的字符串
-q 静默模式,不输出任何信息
-A # after, 后#行
-B # before, 前#行
-C # context, 前后各#行
-e 实现多个选项间的逻辑or关系,如:grep –e ‘cat ’ -e ‘dog’ file
-w 匹配整个单词
-E 使用ERE,相当于egrep
-F 不支持正则表达式,相当于fgrep
-f file 根据模式文件处理
-r 递归目录,但不处理软链接
-R 递归目录,但处理软链接
范例:
grep root /etc/passwd
grep "USER" /etc/passwd
grep 'USER' /etc/passwd
grep whoami /etc/passwd
取两个文件的相同行
[root@centos8 ~]#cat /data/f1.txt
a
b
1
c
[root@centos8 ~]#cat /data/f2.txt
b
e
f
c
1
2
[root@centos8 ~]#grep -f /data/f1.txt /data/f2.txt
b
c
1
df | grep '^/dev/sd' |tr -s ' ' %|cut -d% -f5|sort -n|tail -1
[root@centos8 ~]#ss -nt | grep "^ESTAB" |tr -s ' ' : |cut -d: -f6|sort |uniq -c|sort -nr|head -n3
3 10.0.0.1
1 172.16.4.100
1 172.16.31.188
[root@centos8 ~]#grep -v "^#" /etc/profile | grep -v '^$'
[root@centos8 ~]#grep -v "^#\|^$" /etc/profile
[root@centos8 ~]#grep -v "^\(#\|$\)" /etc/profile
[root@centos8 ~]#grep -Ev "^(#|$)" /etc/profile
[root@centos8 ~]#egrep -v "^(#|$)" /etc/profile
[root@centos6 ~]#egrep -v '^(#|$)' /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
[root@centos8 ~]#ifconfig | grep -E '[0-9]{1,3}.[0-9]{1,3}.[0-9]{1,3}.[0-9]{1,3}'
inet 10.0.0.8 netmask 255. 255.255.0 broadcast 10.0.0.255
inet 172.16.0.123 netmask 255.255.0.0 broadcast 172.16.255.255
inet6 fe80::c11e:4792:7e77:12a4 prefixlen 64 scopeid 0x20
inet 127.0.0.1 netmask 255.0.0.0
[root@centos8 ~]#ifconfig | grep -E '([0-9]{1,3}.){3}[0-9]{1,3}'
inet 10.0.0.8 netmask 255.255.255.0 broadcast 10.0.0.255
inet 172.16.0.123 netmask 255.255.0.0 broadcast 172.16.255.255
inet6 fe80::c11e:4792:7e77:12a4 prefixlen 64 scopeid 0x20
inet 127.0.0.1 netmask 255.0.0.0
[root@centos8 ~]#ifconfig eth0 | grep -Eo '([0-9]{1,3}.){3}[0-9]{1,3}'|head -1
10.0.0.8
[root@centos8 ~]#cat regex.txt
([0-9]{1,3}.){3}[0-9]{1,3}
[root@centos8 ~]#ifconfig | grep -oEf regex.txt
10.0.0.8
255.255.255.0
10.0.0.255
127.0.0.1
255.0.0.0
[root@centos8 ~]#grep -E 'root|bash' /etc/passwd
root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash
operator:x:11:0:operator:/root:/sbin/nologin
wang:x:1000:1000:wang:/home/wang:/bin/bash
mage:x:1001:1001::/home/mage:/bin/bash
xiaoming:x:1002:1002::/home/xiaoming:/bin/bash
roob:x:1003:1003::/home/roob:/bin/bash
[root@centos8 ~]#grep -e 'root' -e 'bash' /etc/passwd
root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash
operator:x:11:0:operator:/root:/sbin/nologin
wang:x:1000:1000:wang:/home/wang:/bin/bash
mage:x:1001:1001::/home/mage:/bin/bash
xiaoming:x:1002:1002::/home/xiaoming:/b
[root@centos8 ~]#grep "^\(.*\)\>.*\<\1$" /etc/passwd
sync:x:5:0:sync:/sbin:/bin/sync
shutdown:x:6:0:shutdown:/sbin:/sbin/shutdown
halt:x:7:0:halt:/sbin:/sbin/halt
bash:x:1008:1008::/home/bash:/bin/bash
nologin:x:1011:1011::/home/nologin:/sbin/nologin
[root@centos8 ~]#grep -E "^(.*)\>.*\<\1$" /etc/passwd
sync:x:5:0:sync:/sbin:/bin/sync
shutdown:x:6:0:shutdown:/sbin:/sbin/shutdown
halt:x:7:0:halt:/sbin:/sbin/halt
bash:x:1008:1008::/home/bash:/bin/bash
nologin:x:1011:1011::/home/nologin:/sbin/nologin
[root@centos8 ~]#egrep "^(.*)\>.*\<\1$" /etc/passwd
sync:x:5:0:sync:/sbin:/bin/sync
shutdown:x:6:0:shutdown:/sbin:/sbin/shutdown
halt:x:7:0:halt:/sbin:/sbin/halt
bash:x:1008:1008::/home/bash:/bin/bash
nologin:x:1011:1011::/home/nologin:/sbin/nologin
二级标题
5.文本处理三剑客之sed
二级标题
6.文本处理三剑客之awk