版权声明:原创作品,谢绝转载!否则将追究法律责任。
Disruptor是一个优秀的并发框架,可以实现单个或多个生产者生产消息,单个或多个消费者消息,且消费者之间可以存在消费消息的依赖关系。网上其他博客往往仅针对框架的一部分使用示例进行了介绍,对于某些场景下介绍并不完全:如多生产者间复杂的依赖关系的使用编码。
本文尽可能对Disruptor的所有使用场景进行总结,如有不全之处欢迎指出,请谅解。
具体关于Disruptor的原理,参见:http://ifeve.com/disruptor/,本文不在赘述。
Disruptor类的handleEventsWith,handleEventsWithWorkerPool方法的联系及区别
在disruptor框架调用start方法之前,往往需要将消息的消费者指定给disruptor框架。
常用的方法是:disruptor.handleEventsWith(EventHandler ... handlers),将多个EventHandler的实现类传入方法,封装成一个EventHandlerGroup,实现多消费者消费。
disruptor的另一个方法是:disruptor.handleEventsWithWorkerPool(WorkHandler ... handlers),将多个WorkHandler的实现类传入方法,封装成一个EventHandlerGroup实现多消费者消费。
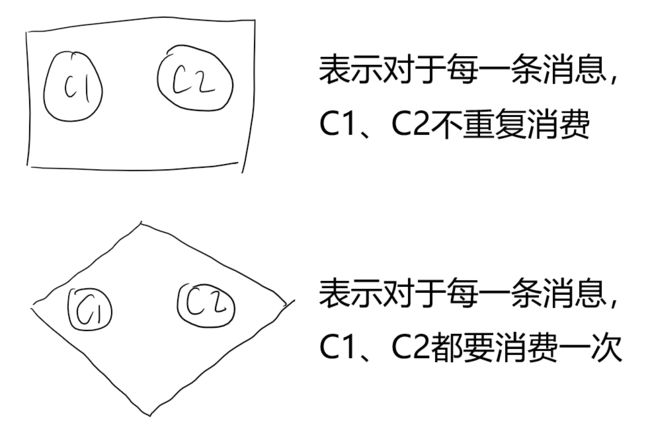
两者共同点都是,将多个消费者封装到一起,供框架消费消息。
不同点在于,
1. 对于某一条消息m,handleEventsWith方法返回的EventHandlerGroup,Group中的每个消费者都会对m进行消费,各个消费者之间不存在竞争。handleEventsWithWorkerPool方法返回的EventHandlerGroup,Group的消费者对于同一条消息m不重复消费;也就是,如果c0消费了消息m,则c1不再消费消息m。
2. 传入的形参不同。对于独立消费的消费者,应当实现EventHandler接口。对于不重复消费的消费者,应当实现WorkHandler接口。
因此,根据消费者集合是否独立消费消息,可以对不同的接口进行实现。也可以对两种接口同时实现,具体消费流程由disruptor的方法调用决定。
在进行场景分析之前,首先定义公共的生产者Producer,消费者OrderHandler1,消息Order,消息工厂OrderFactory。定义分别如下:
package liuqiang.complex.common; public class Order { private String id; public String getId() { return id; } public void setId(String id) { this.id = id; } }
package liuqiang.complex.common; import com.lmax.disruptor.EventFactory; public class OrderFactory implements EventFactory{ @Override public Order newInstance() { return new Order(); } }
package liuqiang.complex.common; import com.lmax.disruptor.EventHandler; import com.lmax.disruptor.WorkHandler; //EventHandler用于EventHandlerGroup,WorkHandler用于WorkPool。同时实现两接口,该类对象可同时用于EventHandlerGroup和WorkPool public class OrderHandler1 implements EventHandler, WorkHandler { private String consumerId; public OrderHandler1(String consumerId){ this.consumerId = consumerId; } //EventHandler的方法 @Override public void onEvent(Order order, long sequence, boolean endOfBatch) throws Exception { System.out.println("OrderHandler1 " + this.consumerId + ",消费信息:" + order.getId()); } //WorkHandler的方法 @Override public void onEvent(Order order) throws Exception { System.out.println("OrderHandler1 " + this.consumerId + ",消费信息:" + order.getId()); } }
package liuqiang.complex.common; import com.lmax.disruptor.RingBuffer; public class Producer { private final RingBufferringBuffer; public Producer(RingBuffer ringBuffer){ this.ringBuffer = ringBuffer; } public void onData(String data){ long sequence = ringBuffer.next(); try { Order order = ringBuffer.get(sequence); order.setId(data); } finally { ringBuffer.publish(sequence); } } }
下面定义两种不同的消费者集合关系:
场景一:单生产者单消费者
package liuqiang.complex.single; import com.lmax.disruptor.EventFactory; import com.lmax.disruptor.RingBuffer; import com.lmax.disruptor.YieldingWaitStrategy; import com.lmax.disruptor.dsl.Disruptor; import com.lmax.disruptor.dsl.ProducerType; import liuqiang.complex.common.Order; import liuqiang.complex.common.OrderFactory; import liuqiang.complex.common.OrderHandler1; import liuqiang.complex.common.Producer; import java.util.concurrent.Executors; public class Main1 { //单生产者模式,单消费者模式 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { EventFactoryfactory = new OrderFactory(); int ringBufferSize = 1024 * 1024; Disruptor disruptor = new Disruptor (factory, ringBufferSize, Executors.defaultThreadFactory(), ProducerType.SINGLE, new YieldingWaitStrategy()); //设置一个消费者 disruptor.handleEventsWith(new OrderHandler1("1")); disruptor.start(); RingBuffer ringBuffer = disruptor.getRingBuffer(); Producer producer = new Producer(ringBuffer); //单生产者,生产3条数据 for (int l = 0; l < 3; l++) { producer.onData(l + ""); } //为了保证消费者线程已经启动,留足足够的时间。具体原因详见另一篇博客:disruptor的shutdown失效问题 Thread.sleep(1000); disruptor.shutdown(); } }
这种情况最为简单,单生产者,仅需在Disruptor初始化时,传入ProducerType.SINGLE即可。使用disruptor.handleEventsWith传入单消费者。Thread.sleep方法调用是为了保证,在调用disruptor.shutdown方法前,所有的消费者线程都已经启动,防止shutdown失效的问题。具体问题详见本人另一篇博客:Disruptor中shutdown方法失效,及产生的不确定性源码分析。
输出结果如下:
OrderHandler1 1,消费信息:0
OrderHandler1 1,消费信息:1
OrderHandler1 1,消费信息:2
场景二:单生产者多消费者,多消费者间形成依赖关系,每个依赖节点只有一个消费者。
package liuqiang.complex.single; import com.lmax.disruptor.EventFactory; import com.lmax.disruptor.RingBuffer; import com.lmax.disruptor.YieldingWaitStrategy; import com.lmax.disruptor.dsl.Disruptor; import com.lmax.disruptor.dsl.EventHandlerGroup; import com.lmax.disruptor.dsl.ProducerType; import liuqiang.complex.common.*; import java.util.concurrent.Executors; public class Main2 { //单生产者,多消费者,但多消费者间形成依赖关系,每个依赖节点单线程。 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { EventFactoryfactory = new OrderFactory(); int ringBufferSize = 1024 * 1024; Disruptor disruptor = new Disruptor (factory, ringBufferSize, Executors.defaultThreadFactory(), ProducerType.SINGLE, new YieldingWaitStrategy()); //多个消费者间形成依赖关系,每个依赖节点的消费者为单线程。 disruptor.handleEventsWith(new OrderHandler1("1")).then(new OrderHandler1("2"), new OrderHandler1("3")).then(new OrderHandler1("4")); disruptor.start(); RingBuffer ringBuffer = disruptor.getRingBuffer(); Producer producer = new Producer(ringBuffer); //单生产者,生产3条数据 for (int l = 0; l < 3; l++) { producer.onData(l + ""); } //为了保证消费者线程已经启动,留足足够的时间。具体原因详见另一篇博客:disruptor的shutdown失效问题 Thread.sleep(1000); disruptor.shutdown(); } }
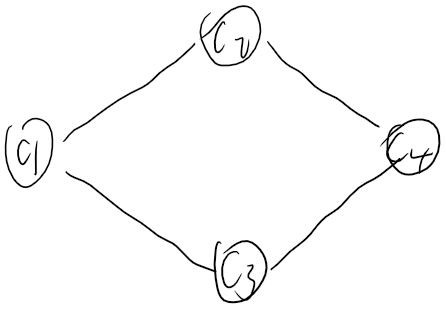
四个消费者之间的依赖图如下:
消费者C2、C3只有在C1消费完消息m后,才能消费m。消费者C4只有在C2、C3消费完m后,才能消费该消息。
可能的输出结果如下(可能因为线程执行先后顺序不同略有区别,但输出一定满足相关依赖约束):
OrderHandler1 1,消费信息:0
OrderHandler1 1,消费信息:1
OrderHandler1 2,消费信息:0
OrderHandler1 3,消费信息:0
OrderHandler1 1,消费信息:2
OrderHandler1 2,消费信息:1
OrderHandler1 2,消费信息:2
OrderHandler1 3,消费信息:1
OrderHandler1 3,消费信息:2
OrderHandler1 4,消费信息:0
OrderHandler1 4,消费信息:1
OrderHandler1 4,消费信息:2
场景三:单生产者,多消费者模式。多消费者对于消息不重复消费。
package liuqiang.complex.multi; import com.lmax.disruptor.EventFactory; import com.lmax.disruptor.RingBuffer; import com.lmax.disruptor.YieldingWaitStrategy; import com.lmax.disruptor.dsl.Disruptor; import com.lmax.disruptor.dsl.EventHandlerGroup; import com.lmax.disruptor.dsl.ProducerType; import liuqiang.complex.common.*; import java.util.concurrent.Executors; public class Main3 { //单生产者,多消费者模式。多消费者对于消息不重复消费。例如:1线程消费了消息0,则2线程只能从0后面的消息消费,不能对消息0进行消费。 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { EventFactoryfactory = new OrderFactory(); int ringBufferSize = 1024 * 1024; Disruptor disruptor = new Disruptor (factory, ringBufferSize, Executors.defaultThreadFactory(), ProducerType.SINGLE, new YieldingWaitStrategy()); /* * 该方法传入的消费者需要实现WorkHandler接口,方法的内部实现是:先创建WorkPool,然后封装WorkPool为EventHandlerPool返回。 * 消费者1、2对于消息的消费有时有竞争,保证同一消息只能有一个消费者消费 */ disruptor.handleEventsWithWorkerPool(new OrderHandler1("1"), new OrderHandler1("2")); disruptor.start(); RingBuffer ringBuffer = disruptor.getRingBuffer(); Producer producer = new Producer(ringBuffer); //单生产者,生产3条数据 for (int l = 0; l < 3; l++) { producer.onData(l + ""); } //为了保证消费者线程已经启动,留足足够的时间。具体原因详见另一篇博客:disruptor的shutdown失效问题 Thread.sleep(1000); disruptor.shutdown(); } }
调用handleEventsWithWorkerPool形成WorkerPool,并进一步封装成EventHandlerGroup。对于同一条消息,两消费者不重复消费。
可能输出结果如下:
OrderHandler1 1,消费信息:0
OrderHandler1 2,消费信息:1
OrderHandler1 1,消费信息:2
场景四:单生产者多消费者,多消费者对于消息m独立消费。
package liuqiang.complex.multi; import com.lmax.disruptor.EventFactory; import com.lmax.disruptor.RingBuffer; import com.lmax.disruptor.YieldingWaitStrategy; import com.lmax.disruptor.dsl.Disruptor; import com.lmax.disruptor.dsl.ProducerType; import liuqiang.complex.common.Order; import liuqiang.complex.common.OrderFactory; import liuqiang.complex.common.OrderHandler1; import liuqiang.complex.common.Producer; import java.util.concurrent.Executors; public class Main4 { //单生产者,多消费者模式。多消费者对于消息独立消费。例如:对于消息m,两个消费者都要对其进行消费。 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { EventFactoryfactory = new OrderFactory(); int ringBufferSize = 1024 * 1024; Disruptor disruptor = new Disruptor (factory, ringBufferSize, Executors.defaultThreadFactory(), ProducerType.SINGLE, new YieldingWaitStrategy()); /* * 两个消费者创建EventHandlerGroup。该消费者需要实现EventHandler类。两个消费者对于RingBuffer中的每个消息,都独立消费一次。 * 两个消费者在消费消息的过程中,各自独立,不产生竞争。 */ disruptor.handleEventsWith(new OrderHandler1("1"), new OrderHandler1("2")); disruptor.start(); RingBuffer ringBuffer = disruptor.getRingBuffer(); Producer producer = new Producer(ringBuffer); //单生产者,生产3条数据 for (int l = 0; l < 3; l++) { producer.onData(l + ""); } //为了保证消费者线程已经启动,留足足够的时间。具体原因详见另一篇博客:disruptor的shutdown失效问题 Thread.sleep(1000); disruptor.shutdown(); } }
可能输出结果如下:
OrderHandler1 1,消费信息:0
OrderHandler1 2,消费信息:0
OrderHandler1 2,消费信息:1
OrderHandler1 2,消费信息:2
OrderHandler1 1,消费信息:1
OrderHandler1 1,消费信息:2
场景五:单生产者,多消费者间存在依赖关系的模式。消费者1、2消息独立消费。消费者3、4仅能消费1、2均消费过的消息,消费者5仅能消费3、4均消费过的消息
package liuqiang.complex.multi; import com.lmax.disruptor.EventFactory; import com.lmax.disruptor.RingBuffer; import com.lmax.disruptor.YieldingWaitStrategy; import com.lmax.disruptor.dsl.Disruptor; import com.lmax.disruptor.dsl.ProducerType; import liuqiang.complex.common.Order; import liuqiang.complex.common.OrderFactory; import liuqiang.complex.common.OrderHandler1; import liuqiang.complex.common.Producer; import java.util.concurrent.Executors; public class Main5 { //单生产者,多消费者间存在依赖关系的模式。消费者1、2组成EventHandlerGroup,消息独立消费。消费者3、4仅能消费1、2均消费过的消息,且独立消费。消费者5仅能消费3、4均消费过的消息 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { EventFactoryfactory = new OrderFactory(); int ringBufferSize = 1024 * 1024; Disruptor disruptor = new Disruptor (factory, ringBufferSize, Executors.defaultThreadFactory(), ProducerType.SINGLE, new YieldingWaitStrategy()); //相当于在各个EventHandlerGroup之间进行级联,形成依赖关系。 disruptor.handleEventsWith(new OrderHandler1("1"), new OrderHandler1("2")).then(new OrderHandler1("3"), new OrderHandler1("4")).then(new OrderHandler1("5")); disruptor.start(); RingBuffer ringBuffer = disruptor.getRingBuffer(); Producer producer = new Producer(ringBuffer); //单生产者,生产3条数据 for (int l = 0; l < 3; l++) { producer.onData(l + ""); } //为了保证消费者线程已经启动,留足足够的时间。具体原因详见另一篇博客:disruptor的shutdown失效问题 Thread.sleep(1000); disruptor.shutdown(); } }
消费者之间的依赖关系如下:
可能的输出结果如下:
OrderHandler1 2,消费信息:0
OrderHandler1 1,消费信息:0
OrderHandler1 1,消费信息:1
OrderHandler1 1,消费信息:2
OrderHandler1 2,消费信息:1
OrderHandler1 2,消费信息:2
OrderHandler1 3,消费信息:0
OrderHandler1 3,消费信息:1
OrderHandler1 3,消费信息:2
OrderHandler1 4,消费信息:0
OrderHandler1 4,消费信息:1
OrderHandler1 4,消费信息:2
OrderHandler1 5,消费信息:0
OrderHandler1 5,消费信息:1
OrderHandler1 5,消费信息:2
场景六:单生产者,多消费者。多消费者之间不重复消费,且不同的消费者WorkPool之间存在依赖关系。
package liuqiang.complex.multi; import com.lmax.disruptor.EventFactory; import com.lmax.disruptor.RingBuffer; import com.lmax.disruptor.YieldingWaitStrategy; import com.lmax.disruptor.dsl.Disruptor; import com.lmax.disruptor.dsl.ProducerType; import liuqiang.complex.common.Order; import liuqiang.complex.common.OrderFactory; import liuqiang.complex.common.OrderHandler1; import liuqiang.complex.common.Producer; import java.util.concurrent.Executors; public class Main6 { /* * 单生产者,多消费者。多消费者之间不重复消费,且不同的消费者WorkPool之间存在依赖关系。 * 消费者1、2不重复消费消息,消费者3、4不重复消费1或者2消费过的消息,消费者5消费消费者3或4消费过的消息。 */ public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { EventFactoryfactory = new OrderFactory(); int ringBufferSize = 1024 * 1024; Disruptor disruptor = new Disruptor (factory, ringBufferSize, Executors.defaultThreadFactory(), ProducerType.SINGLE, new YieldingWaitStrategy()); disruptor.handleEventsWithWorkerPool(new OrderHandler1("1"), new OrderHandler1("2")).thenHandleEventsWithWorkerPool(new OrderHandler1("3"), new OrderHandler1("4")).thenHandleEventsWithWorkerPool(new OrderHandler1("5")); disruptor.start(); RingBuffer ringBuffer = disruptor.getRingBuffer(); Producer producer = new Producer(ringBuffer); //单生产者,生产3条数据 for (int l = 0; l < 3; l++) { producer.onData(l + ""); } //为了保证消费者线程已经启动,留足足够的时间。具体原因详见另一篇博客:disruptor的shutdown失效问题 Thread.sleep(1000); disruptor.shutdown(); } }
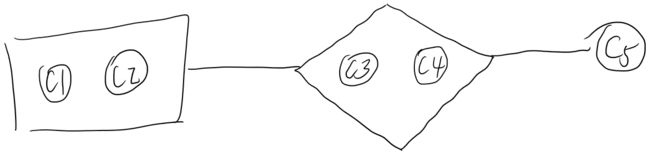
消费者之间的依赖图如下所示:
可能的输出结果如下:
OrderHandler1 2,消费信息:0
OrderHandler1 1,消费信息:1
OrderHandler1 2,消费信息:2
OrderHandler1 3,消费信息:0
OrderHandler1 3,消费信息:2
OrderHandler1 4,消费信息:1
OrderHandler1 5,消费信息:0
OrderHandler1 5,消费信息:1
OrderHandler1 5,消费信息:2
场景七:单生产者,多消费者模式。消费者1、2不重复消费消息,消费者3、4消费消费者1或2消费过的消息,且独立重复消费。消费者5消费消费者3、4均消费过的消息。
package liuqiang.complex.multi; import com.lmax.disruptor.EventFactory; import com.lmax.disruptor.RingBuffer; import com.lmax.disruptor.YieldingWaitStrategy; import com.lmax.disruptor.dsl.Disruptor; import com.lmax.disruptor.dsl.ProducerType; import liuqiang.complex.common.Order; import liuqiang.complex.common.OrderFactory; import liuqiang.complex.common.OrderHandler1; import liuqiang.complex.common.Producer; import java.util.concurrent.Executors; public class Main7 { //单生产者,多消费者模式。消费者1、2不重复消费消息,消费者3、4消费消费者1或2消费过的消息,且独立重复消费。消费者5消费消费者3、4均消费过的消息。 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { EventFactoryfactory = new OrderFactory(); int ringBufferSize = 1024 * 1024; Disruptor disruptor = new Disruptor (factory, ringBufferSize, Executors.defaultThreadFactory(), ProducerType.SINGLE, new YieldingWaitStrategy()); disruptor.handleEventsWithWorkerPool(new OrderHandler1("1"), new OrderHandler1("2")).then(new OrderHandler1("3"), new OrderHandler1("4")).then(new OrderHandler1("5")); disruptor.start(); RingBuffer ringBuffer = disruptor.getRingBuffer(); Producer producer = new Producer(ringBuffer); //单生产者,生产3条数据 for (long l = 0; l < 3; l++) { producer.onData(l + ""); } //为了保证消费者线程已经启动,留足足够的时间。具体原因详见另一篇博客:disruptor的shutdown失效问题 Thread.sleep(1000); disruptor.shutdown(); } }
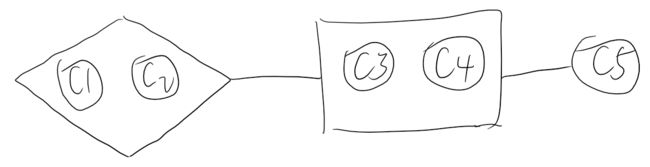
消费者之间的依赖图如下:
可能的输出结果如下:
OrderHandler1 1,消费信息:1
OrderHandler1 2,消费信息:0
OrderHandler1 1,消费信息:2
OrderHandler1 4,消费信息:0
OrderHandler1 4,消费信息:1
OrderHandler1 3,消费信息:0
OrderHandler1 4,消费信息:2
OrderHandler1 3,消费信息:1
OrderHandler1 3,消费信息:2
OrderHandler1 5,消费信息:0
OrderHandler1 5,消费信息:1
OrderHandler1 5,消费信息:2
场景八:单生产者,多消费者模式。消费者1、2独立消费每一条消息,消费者3、4不重复消费消费者1、2均处理过的消息,消费者5消费消费者3或4消费过的消息
package liuqiang.complex.multi; import com.lmax.disruptor.EventFactory; import com.lmax.disruptor.RingBuffer; import com.lmax.disruptor.YieldingWaitStrategy; import com.lmax.disruptor.dsl.Disruptor; import com.lmax.disruptor.dsl.ProducerType; import liuqiang.complex.common.Order; import liuqiang.complex.common.OrderFactory; import liuqiang.complex.common.OrderHandler1; import liuqiang.complex.common.Producer; import java.util.concurrent.Executors; public class Main8 { //单生产者,多消费者模式。消费者1、2独立消费每一条消息,消费者3、4不重复消费消费者1、2均处理过的消息,消费者5消费消费者3或4消费过的消息 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { EventFactoryfactory = new OrderFactory(); int ringBufferSize = 1024 * 1024; Disruptor disruptor = new Disruptor (factory, ringBufferSize, Executors.defaultThreadFactory(), ProducerType.SINGLE, new YieldingWaitStrategy()); disruptor.handleEventsWith(new OrderHandler1("1"), new OrderHandler1("2")).thenHandleEventsWithWorkerPool(new OrderHandler1("3"), new OrderHandler1("4")).then(new OrderHandler1("5")); disruptor.start(); RingBuffer ringBuffer = disruptor.getRingBuffer(); Producer producer = new Producer(ringBuffer); //单生产者,生产3条数据 for (int l = 0; l < 3; l++) { producer.onData(l + ""); } //为了保证消费者线程已经启动,留足足够的时间。具体原因详见另一篇博客:disruptor的shutdown失效问题 Thread.sleep(1000); disruptor.shutdown(); } }
消费者间的依赖图如下:
可能的输出结果如下:
OrderHandler1 2,消费信息:0
OrderHandler1 2,消费信息:1
OrderHandler1 2,消费信息:2
OrderHandler1 1,消费信息:0
OrderHandler1 1,消费信息:1
OrderHandler1 1,消费信息:2
OrderHandler1 3,消费信息:0
OrderHandler1 3,消费信息:1
OrderHandler1 3,消费信息:2
OrderHandler1 5,消费信息:0
OrderHandler1 5,消费信息:1
OrderHandler1 5,消费信息:2
场景九:多生产者,单消费者模式
该场景较为简单,只需将ProducerType.SINGLE改为ProducerType.MULTI,并且编写多线程生产者的相关代码即可。
package liuqiang.complex.multi; import com.lmax.disruptor.EventFactory; import com.lmax.disruptor.RingBuffer; import com.lmax.disruptor.YieldingWaitStrategy; import com.lmax.disruptor.dsl.Disruptor; import com.lmax.disruptor.dsl.ProducerType; import liuqiang.complex.common.Order; import liuqiang.complex.common.OrderFactory; import liuqiang.complex.common.OrderHandler1; import liuqiang.complex.common.Producer; import java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch; import java.util.concurrent.Executors; public class Main9 { //多生产者,单消费者版本。三个生产者独立生产消息。 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { EventFactoryfactory = new OrderFactory(); int ringBufferSize = 1024 * 1024; //ProducerType要设置为MULTI,后面才可以使用多生产者模式 Disruptor disruptor = new Disruptor (factory, ringBufferSize, Executors.defaultThreadFactory(), ProducerType.MULTI, new YieldingWaitStrategy()); //简化问题,设置为单消费者模式,也可以设置为多消费者及消费者间多重依赖。 disruptor.handleEventsWith(new OrderHandler1("1")); disruptor.start(); final RingBuffer ringBuffer = disruptor.getRingBuffer(); //判断生产者是否已经生产完毕 final CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(3); //单生产者,生产3条数据 for (int l = 0; l < 3; l++) { Thread thread = new Thread() { @Override public void run() { for(int i = 0; i < 3; i++) { new Producer(ringBuffer).onData(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "'s " + i + "th message"); } countDownLatch.countDown(); } }; thread.setName("producer thread " + l); thread.start(); } countDownLatch.await(); //为了保证消费者线程已经启动,留足足够的时间。具体原因详见另一篇博客:disruptor的shutdown失效问题 Thread.sleep(1000); disruptor.shutdown(); } }
以上是,对disruptor的各个使用场景的简单介绍。
后面会写博客针对Disruptor的各部分源码做一分析,详细介绍其消费者之间依赖关系的实现机制、单生产者、多生产者之间的不同实现方式等。