常用的自定义View例子一( FlowLayout)
在Android开发中,我们经常会遇到流布式的布局,经常会用来一些标签的显示,比如qq中个人便签,搜索框下方提示的词语,这些是指都是流布式的布局,今天我就我们日常开放中遇到的流布式布局坐一些总结
转载请注明博客地址:http://blog.csdn.net/gdutxiaoxu/article/details/51765428
**源码下载地址:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/CustomViewDemo.git **
1. 先给大家看一下效果
- 图一
- 图二
仔细观察,我们可以知道图二其实是图一效果的升级版,图一当我们控件的宽度超过这一行的时候,剩余的宽度它不会自动分布到每个控件中,而图二的效果当我们换行的时候,如控件还没有占满这一行的时候,它会自动把剩余的宽度分布到每个控件中
2.废话不多说了,大家来直接看来看一下图一的源码
1)代码如下
/**
* 博客地址:http://blog.csdn.net/gdutxiaoxu
* @author xujun
* @time 2016/6/20 23:49.
*/
public class SimpleFlowLayout extends ViewGroup {
private int verticalSpacing = 20;
public SimpleFlowLayout(Context context ) {
super(context);
}
/**
* 重写onMeasure方法是为了确定最终的大小
* @param widthMeasureSpec
* @param heightMeasureSpec
*/
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
int widthSpecMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec);
int widthSpecSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
int heightSpecMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec);
int heightSpecSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec);
int paddingLeft = getPaddingLeft();
int paddingRight = getPaddingRight();
int paddingTop = getPaddingTop();
int paddingBottom = getPaddingBottom();
//处理Padding属性,让当前的ViewGroup支持Padding
int widthUsed = paddingLeft + paddingRight;
int heightUsed = paddingTop + paddingBottom;
int childMaxHeightOfThisLine = 0;
int childCount = getChildCount();
for (int i = 0; i < childCount; i++) {
View child = getChildAt(i);
if (child.getVisibility() != GONE) {
// 已用的宽度
int childUsedWidth = 0;
// 已用的高度
int childUsedHeight = 0;
// 调用ViewGroup自身的方法测量孩子的宽度和高度,我们也可以自己根据MeasureMode来测量
measureChild(child,widthMeasureSpec,heightMeasureSpec);
childUsedWidth += child.getMeasuredWidth();
childUsedHeight += child.getMeasuredHeight();
//处理Margin,支持孩子的Margin属性
Rect marginRect = getMarginRect(child);
int leftMargin=marginRect.left;
int rightMargin=marginRect.right;
int topMargin=marginRect.top;
int bottomMargin=marginRect.bottom;
childUsedWidth += leftMargin + rightMargin;
childUsedHeight += topMargin + bottomMargin;
//总宽度没有超过本行
if (widthUsed + childUsedWidth < widthSpecSize) {
widthUsed += childUsedWidth;
if (childUsedHeight > childMaxHeightOfThisLine) {
childMaxHeightOfThisLine = childUsedHeight;
}
} else {//总宽度已经超过本行
heightUsed += childMaxHeightOfThisLine + verticalSpacing;
widthUsed = paddingLeft + paddingRight + childUsedWidth;
childMaxHeightOfThisLine = childUsedHeight;
}
}
}
//加上最后一行的最大高度
heightUsed += childMaxHeightOfThisLine;
setMeasuredDimension(widthSpecSize, heightUsed);
}
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) {
int paddingLeft = getPaddingLeft();
int paddingRight = getPaddingRight();
int paddingTop = getPaddingTop();
int paddingBottom = getPaddingBottom();
/**
* 为了 支持Padding属性
*/
int childStartLayoutX = paddingLeft;
int childStartLayoutY = paddingTop;
int widthUsed = paddingLeft + paddingRight;
int childMaxHeight = 0;
int childCount = getChildCount();
//摆放每一个孩子的高度
for (int i = 0; i < childCount; i++) {
View child = getChildAt(i);
if (child.getVisibility() != GONE) {
int childNeededWidth, childNeedHeight;
int left, top, right, bottom;
int childMeasuredWidth = child.getMeasuredWidth();
int childMeasuredHeight = child.getMeasuredHeight();
Rect marginRect = getMarginRect(child);
int leftMargin=marginRect.left;
int rightMargin=marginRect.right;
int topMargin=marginRect.top;
int bottomMargin=marginRect.bottom;
childNeededWidth = leftMargin + rightMargin + childMeasuredWidth;
childNeedHeight = topMargin + topMargin + childMeasuredHeight;
// 没有超过本行
if (widthUsed + childNeededWidth <= r - l) {
if (childNeedHeight > childMaxHeight) {
childMaxHeight = childNeedHeight;
}
left = childStartLayoutX + leftMargin;
top = childStartLayoutY + topMargin;
right = left + childMeasuredWidth;
bottom = top + childMeasuredHeight;
widthUsed += childNeededWidth;
childStartLayoutX += childNeededWidth;
} else {
childStartLayoutY += childMaxHeight + verticalSpacing;
childStartLayoutX = paddingLeft;
widthUsed = paddingLeft + paddingRight;
left = childStartLayoutX + leftMargin;
top = childStartLayoutY + topMargin;
right = left + childMeasuredWidth;
bottom = top + childMeasuredHeight;
widthUsed += childNeededWidth;
childStartLayoutX += childNeededWidth;
childMaxHeight = childNeedHeight;
}
child.layout(left, top, right, bottom);
}
}
}
private Rect getMarginRect(View child) {
LayoutParams layoutParams = child.getLayoutParams();
int leftMargin = 0;
int rightMargin = 0;
int topMargin = 0;
int bottomMargin = 0;
if (layoutParams instanceof MarginLayoutParams) {
MarginLayoutParams marginLayoutParams = (MarginLayoutParams) layoutParams;
leftMargin = marginLayoutParams.leftMargin;
rightMargin = marginLayoutParams.rightMargin;
topMargin = marginLayoutParams.topMargin;
bottomMargin = marginLayoutParams.bottomMargin;
}
return new Rect(leftMargin, topMargin, rightMargin, bottomMargin);
}
}
2)思路解析
首先我们重写onMeasure方法,在OnMeasure方法里面我们调用measureChild()这个方法去获取每个孩子的宽度和高度,每次增加一个孩子我们执行 widthUsed += childUsedWidth;
-
添加完一个孩子以后我们判断widthUsed是够超出控件本身的最大宽度widthSpecSize,
若没有超过执行widthUsed += childUsedWidth; if (childUsedHeight > childMaxHeightOfThisLine) { childMaxHeightOfThisLine = childUsedHeight; }
超过控件的宽度执行
heightUsed += childMaxHeightOfThisLine + verticalSpacing;
widthUsed = paddingLeft + paddingRight + childUsedWidth;
childMaxHeightOfThisLine = childUsedHeight;
最后调用 setMeasuredDimension(widthSpecSize, heightUsed);这个方法去设置它的大小
3.在OnLayout方法里面,所做的工作就是去摆放每一个孩子的位置 ,判断需不需要换行,不需要更改left值,需要换行,更改top值
3)注意事项
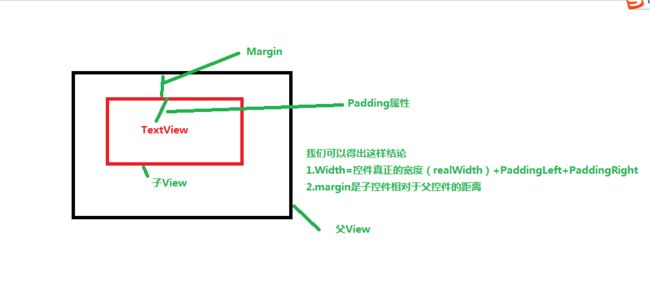
讲解之前,我们先来了解一下一个基本知识
从这张图片里面我们可以得出这样结论
- Width=控件真正的宽度(realWidth)+PaddingLeft+PaddingRight
- margin是子控件相对于父控件的距离
注意事项
- 为了支持控件本身的padding属性,我们做了处理,主要代码如下
int widthUsed = paddingLeft + paddingRight;
int heightUsed = paddingTop + paddingBottom;
----------
if (widthUsed + childUsedWidth < widthSpecSize) {
widthUsed += childUsedWidth;
if (childUsedHeight > childMaxHeightOfThisLine) {
childMaxHeightOfThisLine = childUsedHeight;
}
}
- 为了支持子控件的margin属性,我们同样也做了处理
Rect marginRect = getMarginRect(child);
int leftMargin=marginRect.left;
int rightMargin=marginRect.right;
int topMargin=marginRect.top;
int bottomMargin=marginRect.bottom;
childUsedWidth += leftMargin + rightMargin;
childUsedHeight += topMargin + bottomMargin;
即我们在计算孩子所占用的宽度和高度的时候加上margin属性的高度,接着在计算需要孩子总共用的宽高度的时候加上每个孩子的margin属性的宽高度,这样自然就支持了孩子的margin属性了
4.缺陷
如下图所见,在控件宽度参差不齐的情况下,控件换行会留下一些剩余的宽度,作为想写出鲁棒性的代码的我们会觉得别扭,于是我们相处了解决办法。
解决方法见下面
图二源码解析
废话不多说,先看源码
/**
* 博客地址:http://blog.csdn.net/gdutxiaoxu
* @author xujun
* @time 2016/6/26 22:54.
*/
public class PrefectFlowLayout extends ViewGroup {
public PrefectFlowLayout(Context context) {
super(context);
}
public PrefectFlowLayout(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
}
public PrefectFlowLayout(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
}
//父容器宽度
private int parentWidthSize;
//水平间距
private int horizontalSpacing = 16;
//垂直间距
private int verticalSpacing = 16;
//当前行
private Line currentLine;
//所有行的集合
private List mLines = new ArrayList<>();
//当前行已使用宽度
private int userWidth = 0;
/**
* 行对象
*/
private class Line {
//一行里面所添加的子View集合
private List children;
//当前行高度
private int height;
//当前行已使用宽度
private int lineWidth = 0;
public Line() {
children = new ArrayList<>();
}
/**
* 添加一个子控件
*
* @param child
*/
private void addChild(View child) {
children.add(child);
if (child.getMeasuredHeight() > height) {
//当前行高度以子控件最大高度为准
height = child.getMeasuredHeight();
}
//将每个子控件宽度进行累加,记录使用的宽度
lineWidth += child.getMeasuredWidth();
}
/**
* 获取行的高度
*
* @return
*/
public int getHeight() {
return height;
}
/**
* 获取子控件的数量
*
* @return
*/
public int getChildCount() {
return children.size();
}
/**
* 放置每一行里面的子控件的位置
*
* @param l 距离最左边的距离
* @param t 距离最顶端的距离
*/
public void onLayout(int l, int t) {
//当前行使用的宽度,等于每个子控件宽度之和+子控件之间的水平距离
lineWidth += horizontalSpacing * (children.size() - 1);
int surplusChild = 0;
int surplus = parentWidthSize - lineWidth;//剩余宽度
if (surplus > 0) {
//如果有剩余宽度,则将剩余宽度平分给每一个子控件
surplusChild = (int) (surplus / children.size()+0.5);
}
for (int i = 0; i < children.size(); i++) {
View child = children.get(i);
child.getLayoutParams().width=child.getMeasuredWidth()+surplusChild;
if (surplusChild>0){
//如果长度改变了后,需要重新测量,否则布局中的属性大小还会是原来的大小
child.measure(MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(
child.getMeasuredWidth()+surplusChild,MeasureSpec.EXACTLY)
,MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(height,MeasureSpec.EXACTLY));
}
child.layout(l, t, l + child.getMeasuredWidth(), t + child.getMeasuredHeight());
l += child.getMeasuredWidth() + horizontalSpacing;
}
}
}
// getMeasuredWidth() 控件实际的大小
// getWidth() 控件显示的大小
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
//将之前测量的数据进行清空,以防复用时影响下次测量
mLines.clear();
currentLine = null;
userWidth = 0;
//获取父容器的宽度和模式
int widthMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec);
parentWidthSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec)
- getPaddingLeft() - getPaddingRight();
//获取父容器的高度和模式
int heigthMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec);
int heightSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec)
- getPaddingTop() - getPaddingBottom();
int childWidthMode, childHeightMode;
//为了测量每个子控件,需要指定每个子控件的测量规则
//子控件设置为WRAP_CONTENT,具体测量规则详见,ViewGroup的getChildMeasureSpec()方法
if (widthMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY) {
childWidthMode = MeasureSpec.AT_MOST;
} else {
childWidthMode = widthMode;
}
if (heigthMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY) {
childHeightMode = MeasureSpec.AT_MOST;
} else {
childHeightMode = heigthMode;
}
//获取到子控件高和宽的测量规则
int childWidthMeasureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(parentWidthSize, childWidthMode);
int childHeightMeasureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(heightSize, childHeightMode);
currentLine = new Line();//创建第一行
for (int i = 0; i < getChildCount(); i++) {
View child = getChildAt(i);
//测量每一个孩子
child.measure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
//获取当前子控件的实际宽度
int childMeasuredWidth = child.getMeasuredWidth();
//让当前行使用宽度加上当前子控件宽度
userWidth += childMeasuredWidth;
if (userWidth <= parentWidthSize) {
//如果当前行使用宽度小于父控件的宽度,则加入该行
currentLine.addChild(child);
//当前行使用宽度加上子控件之间的水平距离
userWidth += horizontalSpacing;
//如果当前行加上水平距离后超出父控件宽度,则换行
if (userWidth > parentWidthSize) {
newLine();
}
} else {
//以防出现一个子控件宽度超过父控件的情况出现
if (currentLine.getChildCount() == 0) {
currentLine.addChild(child);
}
newLine();
//并将超出范围的当前的子控件加入新的行中
currentLine.addChild(child);
//并将使用宽度加上子控件的宽度;
userWidth = child.getMeasuredWidth()+horizontalSpacing;
}
}
//加入最后一行,因为如果最后一行宽度不足父控件宽度时,就未换行
if (!mLines.contains(currentLine)) {
mLines.add(currentLine);
}
int totalHeight = 0;//总高度
for (Line line : mLines) {
//总高度等于每一行的高度+垂直间距
totalHeight += line.getHeight() + verticalSpacing;
}
//resolveSize(),将实际高度与父控件高度进行比较,选取最合适的
setMeasuredDimension(parentWidthSize + getPaddingLeft() + getPaddingRight(),
resolveSize(totalHeight + getPaddingTop() + getPaddingBottom(), heightMeasureSpec));
}
/**
* 换行
*/
private void newLine() {
mLines.add(currentLine);//记录之前行
currentLine = new Line();//重新创建新的行
userWidth = 0;//将使用宽度初始化
}
/**
* 放置每个子控件的位置
*
* @param changed
* @param l
* @param t
* @param r
* @param b
*/
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) {
l += getPaddingLeft();
t += getPaddingTop();
for (int i = 0; i < mLines.size(); i++) {
Line line = mLines.get(i);
//设置每一行的位置,每一行的子控件由其自己去分配
line.onLayout(l, t);
//距离最顶端的距离,即每一行高度和垂直间距的累加
t += line.getHeight() + verticalSpacing;
}
}
/**
* 获取子控件的测量规则
*
* @param mode 父控件的测量规则
* @return 子控件设置为WRAP_CONTENT,具体测量规则详见,ViewGroup的getChildMeasureSpec()方法
*/
private int getMode(int mode) {
int childMode = 0;
if (mode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY) {
childMode = MeasureSpec.AT_MOST;
} else {
childMode = mode;
}
return childMode;
}
}
2.思路解析
- 对比图一的实现思路,我们封装了Line这个内部类,看到这个名字,相信大家都猜到是什么意思了,其实就是一个Line实例对象代表一行,Line里面的List
children用来存放孩子
private List children;//一行里面所添加的子View集合
- Line里面还封装了void onLayout(int l, int t)方法,即自己去拜访每个孩子的位置,
实现剩余的宽度平均分配,主要体现在这几行代码
if (surplus > 0) {
//如果有剩余宽度,则将剩余宽度平分给每一个子控件
surplusChild = (int) (surplus / children.size()+0.5);
}
-------
//重新分配每个孩子的大小
child.measure(MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(
child.getMeasuredWidth()+surplusChild,MeasureSpec.EXACTLY)
,MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(height,MeasureSpec.EXACTLY));
今天就写到这里了,有时间再来补充,最近考试比较忙,已经好久没有更新博客了。
源码下载地址:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/CustomViewDemo.git
最后的最后,卖一下广告,欢迎大家关注我的微信公众号,扫一扫下方二维码或搜索微信号 stormjun,即可关注。 目前专注于 Android 开发,主要分享 Android开发相关知识和一些相关的优秀文章,包括个人总结,职场经验等。