内容:自定义view实现
自定义View
View的三大流程:测量流程measure,布局流程layout,绘制流程draw
自定义View的分类
分类标准不唯一
- 继承View重写onDraw方法
主要用于实现一些不规则效果,即这种效果不方便通过布局的组合方式来达到,往往需要静态或动态地显示一些不规则图形。这需要重写onDraw方法。采用这种方式需要自己支持wrap_content,并且padding也需要自己处理。 - 继承ViewGroup派生特殊的Layout
主要用于实现自定义布局,除LinearLayout、RelativeLayout、FrameLayout这几种系统的布局之外,重新定义一个新的布局,当某种效果看起来像几个view组合在一起的时候,可以采用这种方法来实现。这种方式稍微复杂些,需要合适的处理ViewGroup的测量、布局两个过程,并同时处理子元素的测量和布局过程。 - 继承特定的View(例TextView)
常见方法,一般用于扩展某种已有的View的功能,比如TextView,这种方法比较容易实现。不需要自己支持wrap_content和padding等。 - 继承特定的ViewGroup(例LinearLayout)
常见方法,当某种效果看起来像几个view组合在一起的时候,可以采用这种方法来实现。这种方法不需要自己处理ViewGroup的测量、布局。方法2与4的差别主要是2更接近View底层。
自定义View须知
自定义View的注意事项
- 让View支持wrap_content
因为直接继承View或ViewGroup的控件,如果不在onMeasure中对wrap_content做处理,当外界在布局中使用wrap_content时无法达到预期效果。 - 如果有必要,让你的View支持padding
因为直接继承View的控件,如果不在draw方法中处理padding,那么padding属性无效。直接继承ViewGroup的控件需要在onMeasure和onLayout中考虑padding和子元素的margin对其造成的影响,不然padding和子元素的margin会失效。 - 尽量不在View中使用Handler
因为View内部本身就提供了post系列方法,完全代替Handler的作用,除非很明确要使用Handler来发送消息。 - View中如果有线程或者动画,需要及时停止,参考View#onDetachedFromWindow
当包含此View的Activity退出或者当前View被remove时,View的onDetachedFromWindow方法会被调用,当包含此View的Activity启动时,View的onAttachedToWindow方法会被调用。当View变的不可见时我们也需要停止线程和动画,不及时处理可能会造成内存泄漏。 - View带有滑动嵌套情形时,需要处理好滑动冲突
自定义View示例
1.继承View重写onDraw方法
这个例子是绘制一个红心圆,代码:
public class CustomView extends View {
private int mColor = Color.RED;
private Paint mPaint = new Paint(Paint.ANTI_ALIAS_FLAG);
public CustomView(Context context) {
super(context);
init();
}
public CustomView(Context context, @Nullable AttributeSet attrs) {
this(context, attrs, 0);
}
public CustomView(Context context, @Nullable AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
init();
}
public CustomView(Context context, @Nullable AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr, int defStyleRes) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr, defStyleRes);
}
private void init() {
mPaint.setColor(mColor);
}
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
//进行绘制使wrap_content为200的宽高
int widthSpecMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec);
int widthSpecSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
int heightSpecMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec);
int heightSpecSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec);
if (widthSpecMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST
&& heightSpecMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST) {
setMeasuredDimension(200, 200);
} else if (widthSpecMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST) {
setMeasuredDimension(200, heightSpecSize);
} else if (heightSpecMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST) {
setMeasuredDimension(widthSpecSize, 200);
}
}
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
super.onDraw(canvas);
//这里对padding进行处理否则无效
final int paddingLeft = getPaddingLeft();
final int paddingRight = getPaddingRight();
final int paddingTop = getPaddingTop();
final int paddingBottom = getPaddingBottom();
int width = getWidth() - paddingLeft - paddingRight;
int height = getHeight() - paddingTop - paddingBottom;
//取宽高的最小值绘制圆
int radius = Math.min(width, height) / 2;
canvas.drawCircle(paddingLeft + width / 2, paddingTop + height / 2,
radius, mPaint);
}
Activity中没有新增代码,布局代码
添加自定义属性
- 在values目录下创建自定义属性xml,比如attrs.xml(完整代码属性)
- 在View的构造方法中解析自定义属性的值并做相应处理。本例解析circle_color属性
public CustomView(Context context, @Nullable AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
//加载自定义属性集合CircleView
TypedArray a = context.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, R.styleable.CircleView);
//解析CircleView集合中的circle_color属性,如果没有指定则记载默认色值红色
mColor = a.getColor(R.styleable.CircleView_circle_color, Color.RED);
//实现资源
a.recycle();
init();
}
- 在布局文件中使用自定义属性(完整代码布局)
注意:使用自定义属性,必须在布局文件中添加schemas声明:xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto "。app是自定义属性前缀,可以换成其它名字,但是必须与布局中CircleView的自定义属性的前缀保持一致。也有按照如下方式声明schemas的:xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/com.example.ceshiactivity "没有区别。
下面给出完整代码:
public class CustomView extends View {
private int mColor = Color.RED;
private Paint mPaint = new Paint(Paint.ANTI_ALIAS_FLAG);
public CustomView(Context context) {
super(context);
init();
}
public CustomView(Context context, @Nullable AttributeSet attrs) {
this(context, attrs, 0);
}
public CustomView(Context context, @Nullable AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
//加载自定义属性集合CircleView
TypedArray a = context.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, R.styleable.CircleView);
//解析CircleView集合中的circle_color属性,如果没有指定则记载默认色值红色
mColor = a.getColor(R.styleable.CircleView_circle_color, Color.RED);
//实现资源
a.recycle();
init();
}
public CustomView(Context context, @Nullable AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr, int defStyleRes) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr, defStyleRes);
}
private void init() {
mPaint.setColor(mColor);
}
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
//进行绘制使wrap_content为200的宽高
int widthSpecMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec);
int widthSpecSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
int heightSpecMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec);
int heightSpecSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec);
if (widthSpecMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST
&& heightSpecMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST) {
setMeasuredDimension(200, 200);
} else if (widthSpecMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST) {
setMeasuredDimension(200, heightSpecSize);
} else if (heightSpecMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST) {
setMeasuredDimension(widthSpecSize, 200);
}
}
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
super.onDraw(canvas);
//这里对padding进行处理否则无效
final int paddingLeft = getPaddingLeft();
final int paddingRight = getPaddingRight();
final int paddingTop = getPaddingTop();
final int paddingBottom = getPaddingBottom();
int width = getWidth() - paddingLeft - paddingRight;
int height = getHeight() - paddingTop - paddingBottom;
//取宽高的最小值绘制圆
int radius = Math.min(width, height) / 2;
canvas.drawCircle(paddingLeft + width / 2, paddingTop + height / 2,
radius, mPaint);
}
}
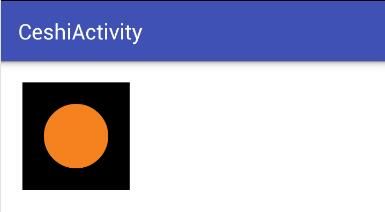
效果图:
2.继承ViewGroup派生特殊的Layout
使用滑动冲突的HorizontalScrollViewEx(外部拦截)类继承于ViewGroup,分析它的measure和layout过程。
注意:使用此种方法实现一个很规范的自定义View,是有一定的代价的,因为比较复杂,这里只完成主要功能。
- 看下measure的代码:
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
int measuredWidth = 0;
int measuredHeight = 0;
final int childCount = getChildCount();
measureChildren(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
int widthSpaceSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
int widthSpecMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec);
int heightSpaceSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec);
int heightSpecMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec);
//判断是否有子元素如果没有则宽高设置为0
if (childCount == 0) {
setMeasuredDimension(0, 0);
} else if (heightSpecMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST) {
//判断高是否是wrap_content,是则高度就是第一个子元素的高度
final View childView = getChildAt(0);
measuredHeight = childView.getMeasuredHeight();
setMeasuredDimension(widthSpaceSize, childView.getMeasuredHeight());
} else if (widthSpecMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST) {
//判断宽是否是wrap_content,是宽度取所有子元素的宽度之和
final View childView = getChildAt(0);
measuredWidth = childView.getMeasuredWidth() * childCount;
setMeasuredDimension(measuredWidth, heightSpaceSize);
} else {
final View childView = getChildAt(0);
measuredWidth = childView.getMeasuredWidth() * childCount;
measuredHeight = childView.getMeasuredHeight();
setMeasuredDimension(measuredWidth, measuredHeight);
}
}
以上代码不规范的地方:第一点没有子元素的时候不应该直接把宽高设置为0,而是应该根据LayoutParams中的宽高来做相应处理;第二点在测量HorizontalScrollViewEx的宽高时没有考虑到它的padding以及子元素的margin,这会影响到它的宽高。
- 看下onLayout方法
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) {
int childLeft = 0;
final int childCount = getChildCount();
mChildrenSize = childCount;
//遍历所有子元素
for (int i = 0; i < childCount; i++) {
final View childView = getChildAt(i);
//如果子元素不为gone,则通过layout方法放置在合适的位置上
if (childView.getVisibility() != View.GONE) {
final int childWidth = childView.getMeasuredWidth();
mChildWidth = childWidth;
childView.layout(childLeft, 0, childLeft + childWidth,
childView.getMeasuredHeight());
childLeft += childWidth;
}
}
}
不规范:放置子元素的过程没有考虑到它的padding以及子元素的margin。
自定义View的思想
- 首先掌握基本功,比如View的弹性滑动、滑动冲突、绘制原理,这些都是自定义View所必须的。
- 在面对新的自定义view时,要能够对其分类并选择合适的实现思路。
- 平时多积累自定义View相关经验,并逐渐做到融会贯通,通过这些慢慢提高自定义View的水平。