一、声明:
操作系统:cenots 6.4
server IP: 192.168.0.199
应老男孩老师的要求,做一次NTP服务的科普,由于NTP属于外围知识,没必要占用宝贵的课堂时间进行讲解,特此在课下进行科普.
其他声明:文章内容知识本人的一点理解,未必100%准确,更多资料请查看NTP官网:
http://www.ntp.org/ntpfaq/NTP-s-config.htm
http://linux.vbird.org/linux_server/0440ntp.php 鸟哥讲解
二、NTP相关知识
1) 时间和时区
date :查看当前系统时间(具体用法这里不啰嗦)
时区 :按照地球所在经度划分。自己可以去查查地球仪了解先关知识。
常见时区:CST(chinese stardard time)中国标准时区
UTC(Coordinated Universal Time)世界统一时间
GMT 格林威治时间,也就是0时区
2)设置时间和时区
# cp /usr/share/zoneinfo/posix/Asia/Shanghai /etc/localtime 设置为上海时间
# cp /usr/share/zoneinfo/posix/UTC /etc/localtime 设置为UTC时间
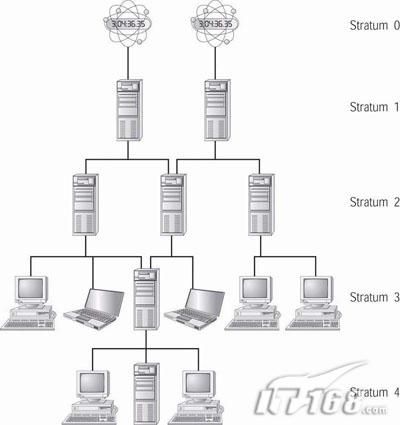
三、NTP服务简易原理
1)分层管理的类树形结构。网络中的节点有两种可能:时钟源或客户
2)所有服务器归入不同的Stratun(层)中。Stratum-1在顶层,有外部UTC接入,而Stratum-2则从Stratum-1获取时间,Stratum-3从Stratum-2获取时间,以此类推,但Stratum层的总数限制在15以内。所有这些服务器在逻辑上形成阶梯式的架构相互连接,而Stratum-1的时间服务器是整个系统的基础,也是顶端!
3)NTP的工作模式为典型的C/S模型
四、重要性
NTP服务器在普通行业里,由于对时间的精度要求不高,所以几乎很少搭建,但是对于一些科研机构,对于时间的精度要求非常高,据悉,网上有位牛人修改ntp源代码,可以实现比微秒更小的时间计量单位。
………………………………………………………………………………………………
NTP服务器的安装、调试
一、安装
安装方法有两种:yum 和source包安装,这里以yum安装为例:
首先查看系统是否安装ntp包
[root@gang test]# rpm -q ntp || yum -y install ntp
ntp-4.2.6p5-1.el6.centos.x86_64
############源码包安装方法如下############
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
以源代码为例
# wget http://ntp.buptnet.edu.cn/ntp_chinese/down/server/ntp-4.2.0.tar.gz
# tar -zxvf ntp-4.2.0.tar.gz –C /usr/local/src;cd /usr/local/src/ntp-4.2.0
2. 开始设定参数、编译与安装:
#./configure --prefix=/usr/local/ntp --enable-all-clocks --enable-parse-clocks
# make clean ; make
# make check
# make install
|
############ END ##################
二、配置NTP配置文件/etc/ntp.conf
1. 不得不提的几个经典问题
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
6.1.2.1. Can I use my system clock as reference clock? YES,as you do
like so #server 127.127.1.1 #LCL,local clock,最好不要这样。引发时间混乱
6.1.3.1. How can I configure the amount of logging information?
6.1.3.2. How can I speed up initial Synchronization?
6.1.3.3. How do
I configure remote administration?
6.1.3.4. How do
I use authentication keys?
6.1.3.5. What are all the different Keys used for?
6.1.3.6. How do
I use the new autokey feature?
具体解决方法,查看文首提示的官网链接
|
2. 编辑配置文件 /etc/ntp.conf
# vi /etc/ntp.conf
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
|
# write the server time and local BIOS time in it ,and count it.
driftfile /var/lib/ntp/drift
#restrict default kod nomodify notrap nopeer noquery
#restrict -6 default kod nomodify notrap nopeer noquery
# the Usage
# restrict [ your IP address ] mask [ netmask ] [ power ]
# power: ignore --> deny all of types NTP connection
# power: nomodify --> deny clients use ntpq or ntpc to change the time of NTP server
# power: noquery --> deny clients use ntpq or ntpc to checkout time , that means deny clients use the NTP server.
# power: notrap --> dont't support remote event logging.
# power: notrust --> deny clients that not be authored.
# if "[ power ]" is null , it means every client can use this host of NTP server.
restrict default nomodify notrap noquery
restrict 127.0.0.1
restrict 192.168.0.0 mask 255.255.255.0 nomodify
restrict -6 ::1
# Hosts on local network are less restricted.
#restrict 192.168.1.0 mask 255.255.255.0 nomodify notrap
# server 210.72.145.44 is BJ Time Station.
# source of ntp-server ; and prefer is priority
server asia.pool.ntp.org prefer
server 210.72.145.44
# local network lo interface
server 127.127.1.1
# LCL does't sync
fudge 127.127.1.1 stratum 10 refid NIST
# broadcast delay frequency
Broadcastdelay 0.008
#server 127.127.1.1
logfile /var/log/ntp.log
#broadcast 192.168.1.255 autokey # broadcast server
#broadcastclient # broadcast client
#broadcast 224.0.1.1 autokey # multicast server
#multicastclient 224.0.1.1 # multicast client
#manycastserver 239.255.254.254 # manycast server
#manycastclient 239.255.254.254 autokey # manycast client
# Enable public key cryptography.
#crypto
includefile /etc/ntp/crypto/pw
# Key file containing the keys and key identifiers used when operating
# with symmetric key cryptography.
keys /etc/ntp/keys
# Specify the key identifiers which are trusted.
#trustedkey 4 8 42
# Specify the key identifier to use with the ntpdc utility.
#requestkey 8
# Specify the key identifier to use with the ntpq utility.
#controlkey 8
# Enable writing of statistics records.
#statistics clockstats cryptostats loopstats peerstats
|
3. 启动ntp服务
|
1
2
|
[root@gang ~]# /etc/init.d/ntpd start
Starting ntpd: [ OK ]4. 一下为正常
|
4.以下为正常启动日志message
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
Mar 24 18:29:45 gang ntpd[3547]: ntpd [email protected] Sat Nov 23 18:21:48 UTC 2013 (1)
Mar 24 18:29:45 gang ntpd[3548]: proto: precision = 0.628 usec
Mar 24 18:29:45 gang ntpd[3548]: 0.0.0.0 c01d 0d kern kernel time
sync
enabled
Mar 24 18:29:45 gang ntpd[3548]: line 32 column 1 syntax error, unexpected T_String, expecting $end
Mar 24 18:29:45 gang ntpd[3548]: syntax error in
/etc/ntp.conf line 32, column 1
Mar 24 18:29:45 gang ntpd[3548]: Listen and drop on 0 v4wildcard 0.0.0.0 UDP 123
Mar 24 18:29:45 gang ntpd[3548]: Listen and drop on 1 v6wildcard :: UDP 123
Mar 24 18:29:45 gang ntpd[3548]: Listen normally on 2 lo 127.0.0.1 UDP 123
Mar 24 18:29:45 gang ntpd[3548]: Listen normally on 3 br0 192.168.0.199 UDP 123
Mar 24 18:29:45 gang ntpd[3548]: Listen normally on 4 eth0 fe80::eea8:6bff:fea4:912b UDP 123
Mar 24 18:29:45 gang ntpd[3548]: Listen normally on 5 br0 fe80::eea8:6bff:fea4:912b UDP 123
Mar 24 18:29:45 gang ntpd[3548]: Listen normally on 6 lo ::1 UDP 123
Mar 24 18:29:45 gang ntpd[3548]: peers refreshed
Mar 24 18:29:45 gang ntpd[3548]: Listening on routing socket on fd #23 for interface updates
|
……………………………………NTP 服务器配置完成………………………………
###################NTP 客户端的配置##################
网上有很多是在配置ntp.conf来进行客户端的同步,但是我觉得这个很没必要,就因为时间同步,就要开放一个端口?crontab计划任务完全可以胜任诶!单开个端口风险貌似很大的样纸...不过你们公司如果时间要求高,那也可以这么做. 具体配置如下:
# vi /etc/ntp.conf
添加一行
server 192.168.0.199
其次: 启动ntp服务
# /etc/init.d/ntpd start
##相关排错方式及讲解:
在server端,我只配置了上级服务器:asia.pool.ntp.org之后,发现启动日志正常,但是时间一直不同步。输入命令查看得知如下图提示:
|
1
2
3
4
|
[root@gang ~]# ntpq -p
remote refid st t when poll reach delay offset jitter
==============================================================================
proxy02.ispros. .INIT. 16 u - 256 0 0.000 0.000 0.000
|
发现pool 一直在增加,但是一直不同步,ping asia.pool.ntp.org发现延迟较高,甚至不通。
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
[root@gang ~]# ping asia.pool.ntp.org
PING asia.pool.ntp.org (78.111.50.2) 56(84) bytes of data.
^C
--- asia.pool.ntp.org ping
statistics ---
28 packets transmitted, 0 received, 100% packet loss, time
27241ms
|
解决方法:在配置文件中,添加多个server ,以防单一server连接不通时,时间同步异常。配置完成后,正常情况如下图:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
[root@gang ~]# ntpq -p
remote refid st t when poll reach delay offset jitter
==============================================================================
*time2.isu.net.s .GPS. 1 u 2 64 27 341.015 -64.352 16.181
210.72.145.44 .INIT. 16 u - 64 0 0.000 0.000 0.000
LOCAL(1) .NIST. 10 l 13 64 177 0.000 0.000 0.000
|
ntpq -p输出结果说明(摘录部分):
remote: 它指的就是本地机器所连接的远程NTP服务器
refid: 它指的是参考的上一层NTP主机的地址
st: 远程服务器的级别. 由于NTP是层型结构,有顶端的服务器,多层的Relay Server再到客户端. 所以服务器从高到低级别可以设定为1-16. 为了减缓负荷和网络堵塞,原则上应该避免直接连接到级别为1的服务器的.
when: 用做计时,用来告诉我们还有多久本地机器就需要和远程服务器进行一次时间同步
poll: 本地机和远程服务器多少时间进行一次同步(单位为秒). 在一开始运行NTP的时候这个poll值会比较小,那样和服务器同步的频率也就增加了,可以尽快调整到正确的时间范围.之后poll值会逐渐增大,同步的频率也就会相应减小
reach: 这是一个八进制值,表示已经向上层NTP伺服器要求更新的次数。每成功连接一次它的值就会增加。
delay: 网路传输过程当中延迟的时间,单位为 10^(-6) 秒
offset: 这是个最关键的值, 它告诉了我们本地机和服务器之间的时间差别. offset越接近于0,我们就和服务器的时间越接近。单位为10^(-3)秒
jitter: Linux系统时间与BIOS硬件时间的差异时间,单位为10^(-6)秒。简单地说这个数值的绝对值越小我们和服务器的时间就越精确。