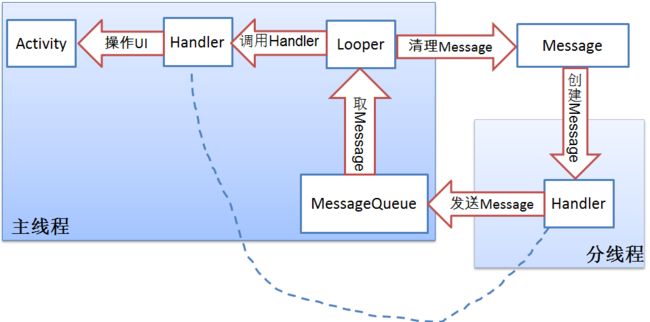
一、Message分析
1.创建对象
通过调用Message的静态方法obtain(),从内部提供的消息池中获取一个消息。
final Message obtain = Message.obtain();
2.Message参数
long when:记录消息何时被处理
Handler target:记录的消息被处理的handler对象
Message sPool:反应了消息池的概念
Runnable callback:优先级最高的消息处理的方式。
Message next:形成消息的链表
二、Handler分析源码
发送消息 sendMessage
public final boolean sendMessage(Message msg)
{
return sendMessageDelayed(msg, 0);
}
调用sendMessageDelayed
public final boolean sendMessageDelayed(Message msg, long delayMillis)
{
if (delayMillis < 0) {
delayMillis = 0;
}
return sendMessageAtTime(msg, SystemClock.uptimeMillis() + delayMillis);
}
delayMillis 延迟时间
SystemClock.uptimeMillis() + delayMillis 执行时间
最终调用sendMessageAtTime
public boolean sendMessageAtTime(Message msg, long uptimeMillis) {
MessageQueue queue = mQueue;
if (queue == null) {
RuntimeException e = new RuntimeException(
this + " sendMessageAtTime() called with no mQueue");
Log.w("Looper", e.getMessage(), e);
return false;
}
return enqueueMessage(queue, msg, uptimeMillis);
}
MessageQueue 存储消息,链表结构(插入快,数组查询快),以被处理的时间顺序存储
public Handler(Looper looper, Callback callback, boolean async) {
mLooper = looper;
mQueue = looper.mQueue;
mCallback = callback;
mAsynchronous = async;
}
mQueue = looper.mQueue;Looper中使用的同一个MessageQueue 对象
private boolean enqueueMessage(MessageQueue queue, Message msg, long uptimeMillis) {
msg.target = this;
if (mAsynchronous) {
msg.setAsynchronous(true);
}
return queue.enqueueMessage(msg, uptimeMillis);
}
msg.target = this; 数明处理和发送的是同一个handle对象
三、MessageQueue分析源码
主要enqueueMessage方法 按照when时间(被处理时间)排序
boolean enqueueMessage(Message msg, long when) {
if (msg.target == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Message must have a target.");
}
if (msg.isInUse()) {
throw new IllegalStateException(msg + " This message is already in use.");
}
synchronized (this) {
if (mQuitting) {
IllegalStateException e = new IllegalStateException(
msg.target + " sending message to a Handler on a dead thread");
Log.w(TAG, e.getMessage(), e);
msg.recycle();
return false;
}
msg.markInUse();
msg.when = when;
Message p = mMessages;
boolean needWake;
if (p == null || when == 0 || when < p.when) {
// New head, wake up the event queue if blocked.
msg.next = p;
mMessages = msg;
needWake = mBlocked;
} else {
// Inserted within the middle of the queue. Usually we don't have to wake
// up the event queue unless there is a barrier at the head of the queue
// and the message is the earliest asynchronous message in the queue.
needWake = mBlocked && p.target == null && msg.isAsynchronous();
Message prev;
for (;;) {
prev = p;
p = p.next;
if (p == null || when < p.when) {
break;
}
if (needWake && p.isAsynchronous()) {
needWake = false;
}
}
msg.next = p; // invariant: p == prev.next
prev.next = msg;
}
// We can assume mPtr != 0 because mQuitting is false.
if (needWake) {
nativeWake(mPtr);
}
}
return true;
}
通过死循环进行排序
四、MessageQueue分析源码
loop方法:
public static void loop() {
final Looper me = myLooper();
if (me == null) {
throw new RuntimeException("No Looper; Looper.prepare() wasn't called on this thread.");
}
final MessageQueue queue = me.mQueue;
// Make sure the identity of this thread is that of the local process,
// and keep track of what that identity token actually is.
Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
final long ident = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
for (;;) {
Message msg = queue.next(); // might block
if (msg == null) {
// No message indicates that the message queue is quitting.
return;
}
// This must be in a local variable, in case a UI event sets the logger
Printer logging = me.mLogging;
if (logging != null) {
logging.println(">>>>> Dispatching to " + msg.target + " " +
msg.callback + ": " + msg.what);
}
msg.target.dispatchMessage(msg);
if (logging != null) {
logging.println("<<<<< Finished to " + msg.target + " " + msg.callback);
}
// Make sure that during the course of dispatching the
// identity of the thread wasn't corrupted.
final long newIdent = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
if (ident != newIdent) {
Log.wtf(TAG, "Thread identity changed from 0x"
+ Long.toHexString(ident) + " to 0x"
+ Long.toHexString(newIdent) + " while dispatching to "
+ msg.target.getClass().getName() + " "
+ msg.callback + " what=" + msg.what);
}
msg.recycleUnchecked();
}
}
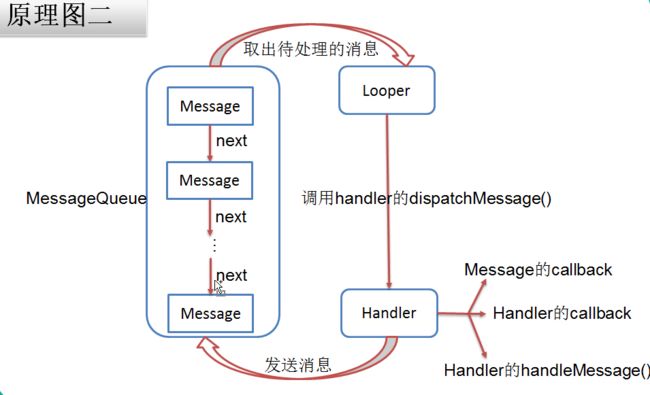
循环取msg,取出之后调用
msg.target.dispatchMessage(msg);
分发消息
handle中的
public void dispatchMessage(Message msg) {
if (msg.callback != null) {
handleCallback(msg);
} else {
if (mCallback != null) {
if (mCallback.handleMessage(msg)) {
return;
}
}
handleMessage(msg);
}
}
可以看出只有当msg.callback=null,mCallback=null或者msg.callback=null,mCallback.handleMessage(msg)=false时,才会执行回调handleMessage(msg);