Dagger2是Google提供的依赖注入框架,依赖注入为Android中组件之间的解耦提供了很好的解决方案。
Retrofit2是一套RESTful架构的Android(Java)客户端实现,基于注解,提供多种数据交互类型(JSON、protobuf、XML等),网络请求(POST,GET,PUT,DELETE等)封装。
RxJava是一个在 Java VM上使用可观测的序列来组成异步的、基于事件的程序的库。
相关链接
Dagger2: https://github.com/google/dagger
Retrofit2:http://square.github.io/retrofit/
RxJava:https://github.com/ReactiveX/RxJava
本文旨在将目前在项目中实践出的这套网络框架整理出来,和广大读者一起交流共同提升。本文以Retrofit2的使用、RxJava的封装、和Dagger2的注入顺序讲述该网络交互框架。
Retrofit2的使用
讲述Retrofit2在项目中的应用之前,在此简要描述其基本使用知识。
Retrofit2的使用遵循两个基本步骤,先定义网络接口,并通过接口指定执行机制;使用时通过Retrofit Builder构建实例,并通过Retrofit.create() 方法创建接口实例,并使用之。
Retrofit 2 网络请求接口定义
Retrofit2支持通过网络接口来指定执行机制,默认是支持Call和Future类型的,RxJava的支持需要在Retrofit2的构造器中额外的指定适配器进行转换。网络接口定义如下:
interface GitHubService {
@GET("/repos/{owner}/{repo}/contributors")
Call> repoContributors(..);
@GET("/repos/{owner}/{repo}/contributors")
Observable> repoContributors2(..);
@GET("/repos/{owner}/{repo}/contributors")
Future> repoContributors3(..);
}
对于其同步调用和异步调用,以Call类型为例,如下:
Call> call =
gitHubService.repoContributors("square", "retrofit");
// 同步调用
response = call.execute();
// 异步调用
call.enqueue(new Callback>() {
@Override void onResponse(/* ... */) {
// ...
}
@Override void onFailure(Throwable t) {
// ...
}
});
Retrofit 2 初始化
Retrofit的构造器可以指定OkHttp支持,并且指明特定的 converter 或者 execute 机制。converter即网络交互数据解析器,包括JSON、protobuf、XML等,executer可以理解成Call Adapter Factory ,RxJava的支持要求在构造器中指定RxJavaCallAdapterFactory。
还是以GitHubService的使用为例。
Retrofit retrofit = new Retrofit.Builder()
.baseUrl("https://api.github.com")
.client(client)
.addConverterFactory(ProtoConverterFactory.create())
.addConverterFactory(GsonConverterFactory.create())
.addCallAdapterFactory(RxJavaCallAdapterFactory.create())
.build();
GitHubService gitHubService = retrofit.create(GitHubService.class);
添加 converter 的顺序很重要。按照这个顺序,SDK将依次询问每一个 converter 能否处理一个类型,并且SDK遵循first-come first-serve原则进行转换。Call Adapter Factory 是一个知道如何将 call 实例转换成其他类型的工厂类。目前,只有 RxJava 的类型,也就是将 Call 类型转换成 Observable 类型。Client是一个配置好的 OkHttp 实例的,比如:配置 interceptors, 或者一个 SSL socket 工厂类,或者 timeouts 的具体数值。
Retrofit 封装
基于以上的基本知识,本项目对Retrofit做了如下封装。
1、 网络接口封装
按照接口返回类型封装成不同的Api Service类
public interface SyncApiService {
@POST("/logon/refresh/{id}")
retrofit2.Call refreshToken(
@Path("id") String id, @Body HashMap map);
}
public interface ApiService {
@GET("/doctors/{id}")
Observable getDoctorinfo(@Path("id") String id);
...
}
2、 Retrofit构造器封装
Retrofit构造器可以按照不同需求创建Retrofit,提供了converter、executer、和 HttpClient设置,并封装了网络错误和数据的统一处理机制。
@Singleton
public final class RestApi {
public static final long CONNECT_TIME_OUT = 30L;
public static final long READ_TIME_OUT = 30L;
public static final long WRITE_TIME_OUT = 30L;
private Context context;
private RxBus rxBus;
private OkHttpClient mOkHttpClient;
private Map dynamicHosts;
@Inject
public RestApi(Context context, RxBus rxBus) {
this.context = context;
this.rxBus = rxBus;
}
/**
* 指定 RxJavaCallAdapterFactory 为 Call Adapter
*/
public Retrofit retrofitStudio(String url) {
return new Retrofit.Builder()
.baseUrl(url)
.addConverterFactory(GsonConverterFactory.create())
.addCallAdapterFactory(RxJavaCallAdapterFactory.create())
.client(setupClient())
.build();
}
/**
* 自定义RxErrorHandlingCallAdapterFactory 为 Call Adapter
*/
public Retrofit retrofitDajia(String url) {
return new Retrofit.Builder()
.baseUrl(url)
.addConverterFactory(GsonConverterFactory.create())
.addCallAdapterFactory(RxErrorHandlingCallAdapterFactory.create(context))
.client(setupClient())
.build();
}
public OkHttpClient setupClient() {
if (mOkHttpClient == null) {
HttpLoggingInterceptor loggingInterceptor = getHttpLoggingInterceptor();
Interceptor layoutInterceptor = getLayoutInterceptor();
Interceptor hmacInterceptor = getHMACInterceptor();
Interceptor cookieInterceptor = getCookieInterceptor();
Interceptor dynamicHostInterceptor = getDynamicHostInterceptor();
Authenticator authenticator = new TokenAuthenticator(context);
mOkHttpClient = new OkHttpClient.Builder()
.dispatcher(new Dispatcher(GlobalConfig.HTTP_EXECUTOR))
.cache(getHttpCache())
.authenticator(authenticator)
.addInterceptor(loggingInterceptor)
.addInterceptor(dynamicHostInterceptor)
.addInterceptor(getCacheInterceptor())
.addNetworkInterceptor(getCacheInterceptor())
.addNetworkInterceptor(layoutInterceptor)
.addNetworkInterceptor(hmacInterceptor)
.addNetworkInterceptor(cookieInterceptor)
.connectTimeout(CONNECT_TIME_OUT, TimeUnit.SECONDS)
.readTimeout(READ_TIME_OUT, TimeUnit.SECONDS)
.writeTimeout(WRITE_TIME_OUT, TimeUnit.SECONDS)
.build();
}
return mOkHttpClient;
}
....
}
以上代码中关于自定义RxErrorHandlingCallAdapterFactory,以及OkHttpClient中的各种设置(Cache机制、动态Host设置、Cookie、URL加密等)我会在另外的文章中细讲,此处不展开。
3、 网络接口使用方法
SyncApiService apiService = RestApi.retrofitStudio([BaseApiUrl]).create(SyncApiService.class);
ApiService apiService = RestApi.retrofitDajia([BaseApiUrl]).create(ApiService.class);
RxJava的封装
对于返回Observable 的网络接口,可以用RxJava 进行处理。我重写了一个HttpResponseObserver,该类有两个目的:1、所有网络请求错误支持统一处理;2、接口返回的Observable 支持对 onNext、onError、onComplete的统一处理。该类的封装如下:
public abstract class HttpResponseObserver implements Observer {
private RxBus rxBus;
public HttpResponseObserver() {
}
public HttpResponseObserver(RxBus rxBus) {
this.rxBus = rxBus;
}
@Override
public void onNext(T t) {
}
@Override
public void onCompleted() {
}
@Override
public void onError(Throwable e) {
Logger.e(e, "error message : %s", e.getMessage());
ApiError error = new ApiError(e);
if (!onError(error)) {
handleError(error);
}
}
/**
* 错误处理回调
*
* @param error
* @return true:已经handle, false: 统一handle
*/
protected boolean onError(ApiError error) {
return false;
}
private void handleError(ApiError error) {
if (rxBus == null) {
rxBus = RxBus.getInstance();
}
rxBus.post(ApiError.class, error);
}
}
从代码中可以看到,Observable返回的错误会通过onError(Throwable e)方法统一转换成ApiError,onError(ApiError error)方法用于用户进行重载,根据其返回boolean决定是否进行统一 handleError(ApiError error)。handleError()方法会将错误通过RxBus 丢到统一的地方进行处理。
RxBus是我基于RxJava封装的,我会在另外篇幅中论述。
如此,网络接口的调用简化如下:
StudioApiService studioApiService; // 获取StudioApiService示例
studioApiService.getStudioAuth(doctorId).subscribeOn(Schedulers.io())
.observeOn(AndroidSchedulers.mainThread())
.subscribe(new HttpResponseObserver() {
@Override
public void onNext(StudioAuth studioAuth) {
// 网络请求成功,处理返回数据
}
@Override
protected boolean onError(ApiError error) {
// 此处作特殊的Error处理
return false; // 再将错误传递到统一错误处理
}
});
Dagger2 依赖注入
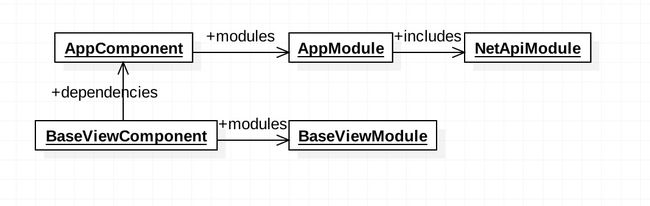
跟网络交互相关的Dagger组件依赖关系如下:
各组件代码如下:
@Scope
@Retention(RUNTIME)
public @interface PerView {
}
@Module
public class NetApiModule {
@Provides
@Singleton
StudioApiService provideStudioApiService(RestApi restApi) {
return restApi.retrofitStudio(GlobalConfig.STUDIO_API_BASE_URL).create(StudioApiService.class);
}
@Provides
@Singleton
RxBus provideRxBus() {
return RxBus.getInstance();
}
}
@Module(includes = NetApiModule.class)
public class AppModule {
private final Application application;
public AppModule(Application app) {
application = app;
}
@Provides
@Singleton
Application provideApplication() {
return application;
}
@Provides
@Singleton
Context provideContext() {
return application;
}
}
@Singleton
@Component(modules = {AppModule.class, AppManageModule.class})
public interface AppComponent {
void inject(DajiaApplication app);
StudioApiService studioApiService();
...
}
@Module
public class BaseViewModule {
private final Activity activity;
public BaseViewModule(Activity activity) {
this.activity = activity;
}
@Provides
@PerView
Activity provideActivity() {
return this.activity;
}
}
@PerView
@Component(dependencies = AppComponent.class, modules = BaseViewModule.class)
public interface BaseViewComponent {
Activity activity();
void inject(AbstractActivity activity);
void inject(MainActivity activity);
}
网络接口使用方法:
在Activity中注入使用
public class AbstractActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
@Inject
protected Lazy studioApiServiceLazy;
@Inject
protected Lazy fileUploadServiceLazy;
public BaseViewComponent component() {
if (mBaseViewComponent == null) {
mBaseViewComponent = DaggerBaseViewComponent.builder()
.appComponent(DajiaApplication.getInstance().component())
.baseViewModule(new BaseViewModule(this))
.build();
}
return mBaseViewComponent;
}
}
public class MainActivity extends BasePresenterActivity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(@Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
component().inject(this);
...
}
private void loadData() {
studioApiServiceLazy.get().getProfile(docId, params).subscribeOn(Schedulers.io())
.observeOn(AndroidSchedulers.mainThread())
.subscribe(new HttpResponseObserver(rxBus) {
@Override
public void onNext(Profile profile) {
// 处理返回数据
}
}
});
}
}
通过Application注入使用
public class MyApplication extends MultiDexApplication {
public AppComponent component() {
if (appComponent == null) {
appComponent = DaggerAppComponent.builder().appModule(new AppModule(this)).appManageModule(new AppManageModule(this)).build();
}
return appComponent;
}
}
在任何地方可以以下方法调用
StudioApiService apiService = DajiaApplication.getInstance().component().studioApiService();
思路梳理
- Retrofit构造类构造不同需求下的 Retrofit,配置好HttpClient各种属性;
- 以RxJava 来处理返回数据,并进行必要的封装,统一处理网络请求错误;
- Dagger2 实现依赖注入,实现在Activity、Fragment等组件中注入网络接口。
这样,结合Dagger2、Retrofit2与RxJava的网路框架就介绍结束了,有些论述可能不够详细,欢迎大家讨论。