POJ 1145 Tree Summing
Tree Summing
| Time Limit: 1000MS | Memory Limit: 10000K | |
| Total Submissions: 7698 | Accepted: 1737 |
Description
LISP was one of the earliest high-level programming languages and, with FORTRAN, is one of the oldest languages currently being used. Lists, which are the fundamental data structures in LISP, can easily be adapted to represent other important data structures such as trees.
This problem deals with determining whether binary trees represented as LISP S-expressions possess a certain property.
Given a binary tree of integers, you are to write a program that determines whether there exists a root-to-leaf path whose nodes sum to a specified integer. For example, in the tree shown below there are exactly four root-to-leaf paths. The sums of the paths are 27, 22, 26, and 18.
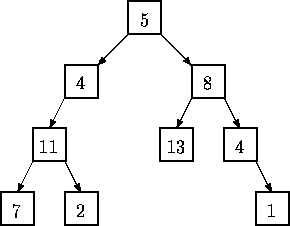
Binary trees are represented in the input file as LISP S-expressions having the following form.
The tree diagrammed above is represented by the expression (5 (4 (11 (7 () ()) (2 () ()) ) ()) (8 (13 () ()) (4 () (1 () ()) ) ) )
Note that with this formulation all leaves of a tree are of the form (integer () () )
Since an empty tree has no root-to-leaf paths, any query as to whether a path exists whose sum is a specified integer in an empty tree must be answered negatively.
This problem deals with determining whether binary trees represented as LISP S-expressions possess a certain property.
Given a binary tree of integers, you are to write a program that determines whether there exists a root-to-leaf path whose nodes sum to a specified integer. For example, in the tree shown below there are exactly four root-to-leaf paths. The sums of the paths are 27, 22, 26, and 18.

Binary trees are represented in the input file as LISP S-expressions having the following form.
empty tree ::= ()
tree ::= empty tree (integer tree tree)
The tree diagrammed above is represented by the expression (5 (4 (11 (7 () ()) (2 () ()) ) ()) (8 (13 () ()) (4 () (1 () ()) ) ) )
Note that with this formulation all leaves of a tree are of the form (integer () () )
Since an empty tree has no root-to-leaf paths, any query as to whether a path exists whose sum is a specified integer in an empty tree must be answered negatively.
Input
The input consists of a sequence of test cases in the form of integer/tree pairs. Each test case consists of an integer followed by one or more spaces followed by a binary tree formatted as an S-expression as described above. All binary tree S-expressions will be valid, but expressions may be spread over several lines and may contain spaces. There will be one or more test cases in an input file, and input is terminated by end-of-file.
Output
There should be one line of output for each test case (integer/tree pair) in the input file. For each pair I,T (I represents the integer, T represents the tree) the output is the string yes if there is a root-to-leaf path in T whose sum is I and no if there is no path in T whose sum is I.
Sample Input
22 (5(4(11(7()())(2()()))()) (8(13()())(4()(1()()))))
20 (5(4(11(7()())(2()()))()) (8(13()())(4()(1()()))))
10 (3
(2 (4 () () )
(8 () () ) )
(1 (6 () () )
(4 () () ) ) )
5 ()
Sample Output
yes no yes no
题目大意:输入一个整数sum,后面是一串字符,代表一颗二叉树,二叉树结点类型为(integer () () ),问是否存在一条从根节点到叶子节点的路径上数字之和为sum.
解题方法:先通过字符串构造一颗二叉树,然后通过二叉树的非递归后序遍历判断是否存在解,这道题费了我九牛二虎之力,终于AC了。
#include <stdio.h> #include <iostream> #include <string.h> using namespace std; char str[1005]; typedef struct node { int data; node *lchild; node *rchild; bool bleftvisted;//用于标记左孩子是否访问过 node() { lchild = rchild = NULL; bleftvisted = false; } }TreeNode; //删除二叉树 void DeleteNode(TreeNode *pRoot) { if (pRoot != NULL) { DeleteNode(pRoot->lchild); DeleteNode(pRoot->rchild); } delete pRoot; } //创建一颗二叉树 void CreateTree(TreeNode *&pRoot) { TreeNode *StackNode[1005], *p;//StackNode为保存二叉树节点的栈 char StackCh[1005];//保存字符的栈 int topnode = -1, topch = -1, num, flag = 1, j = 0; bool isnum = false; char ch; num = 0; isnum = false ; while(str[j] != '\0') { ch = str[j]; switch(ch) { case ')'://如果是右括号则把相应配对的左括号和他们之间的数字出栈 { bool bflag = false; while(StackCh[topch] != '(') { //如果遇见了数字,则必须让保存二叉树节点的栈退栈, //表明该节点已经构造完了 if (isdigit(StackCh[topch])) { bflag = true; } --topch; } if (bflag) { --topnode; } j++; --topch; //如果某个节点的左孩子节点为空,则把左孩子访问标记为true if (topnode >= 0) { StackNode[topnode]->bleftvisted = true; } break; } case '('://遇到左括号,直接入栈 StackCh[++topch] = ch; j++; break; case '-': flag = -1; j++; break; default://遇到数字,新建一个节点,然后插入到相应的位置 num = num * 10 + (ch - '0'); StackCh[++topch] = ch; while(isdigit(ch = str[++j])) { num = num * 10 + (ch - '0'); StackCh[++topch] = ch; } p = new TreeNode; p->data = num * flag; flag = 1; num = 0; if (pRoot == NULL)//如果根节点为空,则把新节点赋给根节点 { pRoot = p; } else { //如果左孩子节点未被访问,则先插入左孩子节点 if (StackNode[topnode]->bleftvisted == false) { StackNode[topnode]->lchild = p; StackNode[topnode]->bleftvisted = true; } else//否则插入到右孩子节点 { StackNode[topnode]->rchild = p; } } StackNode[++topnode] = p;//新节点入栈 break; } } } //二叉树的非递归后序遍历查找是否满足条件 bool Postorder(TreeNode *pRoot, int sum) { TreeNode *Stack[1005]; int top = -1; TreeNode *p = pRoot, *q; if (pRoot != NULL) { do { while(p != NULL) { Stack[++top] = p; p = p->lchild; } q = NULL; while(top != -1) { p = Stack[top]; //如果q == NULL则表示p的右孩子不存在,而左子树不存在或者已经访问,所以可以访问p节点, //如果q != NULL则表示p的右子树已经被访问了,所以访问p节点 if (q == p->rchild) { if (p->lchild == NULL && p->rchild == NULL) { int temp = 0; //因为在后序遍历中,栈中保存的节点即为当前节点和它的所有父节点, //所以便利一遍相加所得的和就是根节点到当前节点路径上所有节点之和 for (int i = 0; i <= top; i++) { temp += Stack[i]->data; } if (temp == sum) { return true; } } top--; q = p; } else { p = p->rchild; break; } } } while (top != -1); } return false; } int main() { int sum; while(scanf("%d", &sum) != EOF) { TreeNode *pRoot = NULL; char ch; int nCount = -1; while ((ch = getchar()) != '('); str[++nCount] = ch; int mark = 1; while(mark != 0) { ch = getchar(); switch(ch) { case ')': mark--; str[++nCount] = ch; break; case '(': mark++; str[++nCount] = ch; break; case '-': str[++nCount] = ch; break; case ' ': break; case '\0': break; case '\n': break; default: str[++nCount] = ch; break; } } str[nCount + 1] = '\0'; CreateTree(pRoot); if (pRoot == NULL) { printf("no\n"); continue; } if (Postorder(pRoot, sum)) { printf("yes\n"); } else { printf("no\n"); } DeleteNode(pRoot); } return 0; }