hbase源码系列(九)StoreFile存储格式
从这一章开始要讲Region Server这块的了,但是在讲Region Server这块之前得讲一下StoreFile,否则后面的不好讲下去,这块是基础,Region Sever上面的操作,大部分都是基于它来进行的。
HFile概述
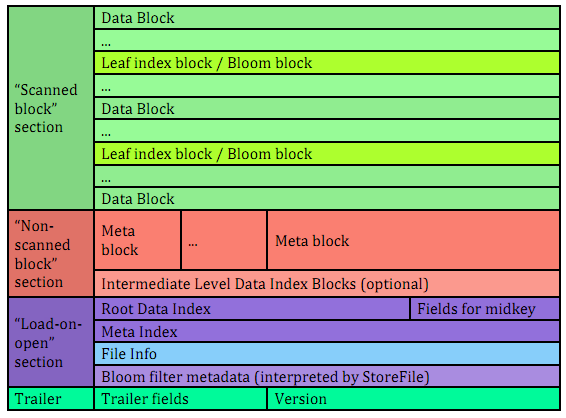
HFile是HBase中实际存数据的文件,为HBase提供高效快速的数据访问。它是基于Hadoop的TFile,模仿Google Bigtable 架构中的SSTable格式。文件格式如下:
文件是变长的,唯一固定的块是File Info和Trailer,如图所示,Trailer有指向其它块的指针,这些指针也写在了文件里,Index块记录了data和meta块的偏移量,meta块是可选的。
下面我们从原来上来一个一个的看它们到底是啥样的,先从入口看起,那就是StoreFile.Writer的append方法,先看怎么写入的,然后它就怎么读了,不知道怎么使用这个类的,可以看看我写的这篇文章《非mapreduce生成Hfile,然后导入hbase当中》。
往HFile追加KeyValue
不扯这些了,看一下StoreFile里面的append方法。
public void append(final KeyValue kv) throws IOException { //如果是新的rowkey的value,就追加到Bloomfilter里面去 appendGeneralBloomfilter(kv); //如果是DeleteFamily、DeleteFamilyVersion类型的kv appendDeleteFamilyBloomFilter(kv); writer.append(kv); //记录最新的put的时间戳,更新时间戳范围 trackTimestamps(kv); }
在用writer进行append之前先把kv写到generalBloomFilterWriter里面,但是我们发现generalBloomFilterWriter是HFile.Writer里面的InlineBlockWriter。
generalBloomFilterWriter = BloomFilterFactory.createGeneralBloomAtWrite( conf, cacheConf, bloomType, (int) Math.min(maxKeys, Integer.MAX_VALUE), writer); //在createGeneralBloomAtWriter方法发现了以下代码 ...... CompoundBloomFilterWriter bloomWriter = new CompoundBloomFilterWriter(getBloomBlockSize(conf), err, Hash.getHashType(conf), maxFold, cacheConf.shouldCacheBloomsOnWrite(), bloomType == BloomType.ROWCOL ? KeyValue.COMPARATOR : KeyValue.RAW_COMPARATOR); writer.addInlineBlockWriter(bloomWriter);
我们接下来看HFileWriterV2的append方法吧。
public void append(final KeyValue kv) throws IOException { append(kv.getMvccVersion(), kv.getBuffer(), kv.getKeyOffset(), kv.getKeyLength(), kv.getBuffer(), kv.getValueOffset(), kv.getValueLength()); this.maxMemstoreTS = Math.max(this.maxMemstoreTS, kv.getMvccVersion()); }
为什么贴这段代码,注意这个参数maxMemstoreTS,它取kv的mvcc来比较,mvcc是用来实现MemStore的原子性操作的,在MemStore flush的时候同一批次的mvcc都是一样的,失败的时候,把mvcc相同的全部干掉,这里提一下,以后应该还会说到,继续追杀append方法。方法比较长,大家展开看看。

private void append(final long memstoreTS, final byte[] key, final int koffset, final int klength, final byte[] value, final int voffset, final int vlength) throws IOException { boolean dupKey = checkKey(key, koffset, klength); checkValue(value, voffset, vlength); if (!dupKey) { //在写每一个新的KeyValue之间,都要检查,到了BlockSize就重新写一个HFileBlock checkBlockBoundary(); } //如果当前的fsBlockWriter的状态不对,就重新写一个新块 if (!fsBlockWriter.isWriting()) newBlock(); // 把值写入到ouputStream当中,怎么写入的自己看啊 { DataOutputStream out = fsBlockWriter.getUserDataStream(); out.writeInt(klength); totalKeyLength += klength; out.writeInt(vlength); totalValueLength += vlength; out.write(key, koffset, klength); out.write(value, voffset, vlength); if (this.includeMemstoreTS) { WritableUtils.writeVLong(out, memstoreTS); } } // 记录每个块的第一个key 和 上次写的key if (firstKeyInBlock == null) { firstKeyInBlock = new byte[klength]; System.arraycopy(key, koffset, firstKeyInBlock, 0, klength); } lastKeyBuffer = key; lastKeyOffset = koffset; lastKeyLength = klength; entryCount++; }
从上面我们可以看到来,HFile写入的时候,是分一个块一个块的写入的,每个Block块64KB左右,这样有利于数据的随机访问,不利于连续访问,连续访问需求大的,可以把Block块的大小设置得大一点。好,我们继续看checkBlockBoundary方法。
private void checkBlockBoundary() throws IOException { if (fsBlockWriter.blockSizeWritten() < blockSize) return; finishBlock(); writeInlineBlocks(false); newBlock(); }
简单交代一下
1、结束一个block的时候,把block的所有数据写入到hdfs的流当中,记录一些信息到DataBlockIndex(块的第一个key和上一个块的key的中间值,块的大小,块的起始位置)。
2、writeInlineBlocks(false)给了一个false,是否要关闭,所以现在什么都没干,它要等到最后才会输出的。
3、newBlock方法就是重置输出流,做好准备,读写下一个块。
Close的时候
close的时候就有得忙咯,从之前的图上面来看,它在最后的时候是最忙的,因为它要写入一大堆索引信息、附属信息啥的。
public void close() throws IOException { boolean hasGeneralBloom = this.closeGeneralBloomFilter(); boolean hasDeleteFamilyBloom = this.closeDeleteFamilyBloomFilter(); writer.close(); }
在调用writer的close方法之前,close了两个BloomFilter,把BloomFilter的类型写进FileInfo里面去,把BloomWriter添加到Writer里面。下面进入正题吧,放大招了,我折叠吧。。。

public void close() throws IOException { if (outputStream == null) { return; } // 经过编码压缩的,把编码压缩方式写进FileInfo里面 blockEncoder.saveMetadata(this); //结束块 finishBlock(); //输出DataBlockIndex索引的非root层信息 writeInlineBlocks(true); FixedFileTrailer trailer = new FixedFileTrailer(2,HFileReaderV2.MAX_MINOR_VERSION); // 如果有meta块的存在的话 if (!metaNames.isEmpty()) { for (int i = 0; i < metaNames.size(); ++i) { long offset = outputStream.getPos(); // 输出meta的内容,它是meta的名字的集合,按照名字排序 DataOutputStream dos = fsBlockWriter.startWriting(BlockType.META); metaData.get(i).write(dos); fsBlockWriter.writeHeaderAndData(outputStream); totalUncompressedBytes += fsBlockWriter.getUncompressedSizeWithHeader(); // 把meta块的信息加到meta块的索引里 metaBlockIndexWriter.addEntry(metaNames.get(i), offset, fsBlockWriter.getOnDiskSizeWithHeader()); } } //下面这部分是打开文件的时候就加载的部分,是前面部分的索引 //HFileBlockIndex的根层次的索引 long rootIndexOffset = dataBlockIndexWriter.writeIndexBlocks(outputStream); trailer.setLoadOnOpenOffset(rootIndexOffset); //Meta块的索引 metaBlockIndexWriter.writeSingleLevelIndex(fsBlockWriter.startWriting( BlockType.ROOT_INDEX), "meta"); fsBlockWriter.writeHeaderAndData(outputStream); totalUncompressedBytes += fsBlockWriter.getUncompressedSizeWithHeader(); //如果需要写入Memstore的最大时间戳到FileInfo里面 if (this.includeMemstoreTS) { appendFileInfo(MAX_MEMSTORE_TS_KEY, Bytes.toBytes(maxMemstoreTS)); appendFileInfo(KEY_VALUE_VERSION, Bytes.toBytes(KEY_VALUE_VER_WITH_MEMSTORE)); } //把FileInfo的起始位置写入trailer,然后输出 writeFileInfo(trailer, fsBlockWriter.startWriting(BlockType.FILE_INFO)); fsBlockWriter.writeHeaderAndData(outputStream); totalUncompressedBytes += fsBlockWriter.getUncompressedSizeWithHeader(); // 输出GENERAL_BLOOM_META、DELETE_FAMILY_BLOOM_META类型的BloomFilter的信息 for (BlockWritable w : additionalLoadOnOpenData){ fsBlockWriter.writeBlock(w, outputStream); totalUncompressedBytes += fsBlockWriter.getUncompressedSizeWithHeader(); } //HFileBlockIndex的二级实体的层次 trailer.setNumDataIndexLevels(dataBlockIndexWriter.getNumLevels()); //压缩前的HFileBlockIndex的大小 trailer.setUncompressedDataIndexSize( dataBlockIndexWriter.getTotalUncompressedSize()); //第一个HFileBlock的起始位置 trailer.setFirstDataBlockOffset(firstDataBlockOffset); //最后一个HFileBlock的起始位置 trailer.setLastDataBlockOffset(lastDataBlockOffset); //比较器的类型 trailer.setComparatorClass(comparator.getClass()); //HFileBlockIndex的根实体的数量,应该是和HFileBlock的数量是一样的 //它每次都把HFileBlock的第一个key加进去 trailer.setDataIndexCount(dataBlockIndexWriter.getNumRootEntries()); //把Trailer的信息写入硬盘,关闭输出流 finishClose(trailer); fsBlockWriter.release(); }
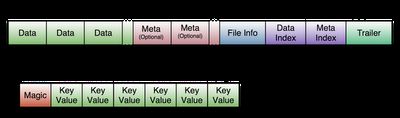
和图片上写的有些出入。
1、输出HFileBlocks
2、输出HFileBlockIndex的二级索引(我叫它二级索引,我也不知道对不对,HFileBlockIndex那块我有点儿忘了,等我再重新调试的时候再看看吧)
3、如果有的话,输出MetaBlock
下面的部分是打开文件的时候就加载的
4、输出HFileBlockIndex的根索引
5、如果有的话,输出MetaBlockIndex的根索引(它比较小,所以只有一层)
6、输出文件信息(FileInfo)
7、输出文件尾巴(Trailer)
Open的时候
这部分打算讲一下实例化Reader的时候,根据不同类型的文件是怎么实例化Reader的,在StoreFile里面搜索open方法。
this.reader = fileInfo.open(this.fs, this.cacheConf, dataBlockEncoder.getEncodingInCache()); // 加载文件信息到map里面去,后面部分就不展开讲了 metadataMap = Collections.unmodifiableMap(this.reader.loadFileInfo());
我们进入F3进入fileInfo.open这个方法里面去。
FSDataInputStreamWrapper in; FileStatus status; if (this.link != null) { // HFileLink in = new FSDataInputStreamWrapper(fs, this.link); status = this.link.getFileStatus(fs); } else if (this.reference != null) { // HFile Reference 反向计算出来引用所指向的位置的HFile位置 Path referencePath = getReferredToFile(this.getPath()); in = new FSDataInputStreamWrapper(fs, referencePath); status = fs.getFileStatus(referencePath); } else { in = new FSDataInputStreamWrapper(fs, this.getPath()); status = fileStatus; } long length = status.getLen(); if (this.reference != null) { hdfsBlocksDistribution = computeRefFileHDFSBlockDistribution(fs, reference, status); //如果是引用的话,创建一个一半的reader return new HalfStoreFileReader( fs, this.getPath(), in, length, cacheConf, reference, dataBlockEncoding); } else { hdfsBlocksDistribution = FSUtils.computeHDFSBlocksDistribution(fs, status, 0, length); return new StoreFile.Reader(fs, this.getPath(), in, length, cacheConf, dataBlockEncoding); }
它一上来就判断它是不是HFileLink是否为空了,这是啥情况?找了一下,原来在StoreFile的构造函数的时候,就开始判断了。

this.fileStatus = fileStatus; Path p = fileStatus.getPath(); if (HFileLink.isHFileLink(p)) { // HFileLink 被判断出来它是HFile this.reference = null; this.link = new HFileLink(conf, p); } else if (isReference(p)) { this.reference = Reference.read(fs, p); //关联的地址也可能是一个HFileLink,snapshot的时候介绍了 Path referencePath = getReferredToFile(p); if (HFileLink.isHFileLink(referencePath)) { // HFileLink Reference 如果它是一个HFileLink型的 this.link = new HFileLink(conf, referencePath); } else { // 只是引用 this.link = null; } } else if (isHFile(p)) { // HFile this.reference = null; this.link = null; } else { throw new IOException("path=" + p + " doesn't look like a valid StoreFile"); }
它有4种情况:
1、HFileLink
2、既是HFileLink又是Reference文件
3、只是Reference文件
4、HFile
说HFileLink吧,我们看看它的构造函数
public HFileLink(final Path rootDir, final Path archiveDir, final Path path) { Path hfilePath = getRelativeTablePath(path); this.tempPath = new Path(new Path(rootDir, HConstants.HBASE_TEMP_DIRECTORY), hfilePath); this.originPath = new Path(rootDir, hfilePath); this.archivePath = new Path(archiveDir, hfilePath); setLocations(originPath, tempPath, archivePath); }
尼玛,它计算了三个地址,原始位置,archive中的位置,临时目录的位置,按照顺序添加到一个locations数组里面。。接着看FSDataInputStreamWrapper吧,下面是三段代码
this.stream = (link != null) ? link.open(hfs) : hfs.open(path); //走的link.open(hfs) new FSDataInputStream(new FileLinkInputStream(fs, this)); //注意tryOpen方法 public FileLinkInputStream(final FileSystem fs, final FileLink fileLink, int bufferSize) throws IOException { this.bufferSize = bufferSize; this.fileLink = fileLink; this.fs = fs; this.in = tryOpen(); }
tryOpen的方法,会按顺序打开多个locations列表。。

for (Path path: fileLink.getLocations()) { if (path.equals(currentPath)) continue; try { in = fs.open(path, bufferSize); in.seek(pos); assert(in.getPos() == pos) : "Link unable to seek to the right position=" + pos; if (LOG.isTraceEnabled()) { if (currentPath != null) { LOG.debug("link open path=" + path); } else { LOG.trace("link switch from path=" + currentPath + " to path=" + path); } } currentPath = path; return(in); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { // Try another file location } }
恩,这回终于知道它是怎么出来的了,原来是尝试打开了三次,直到找到正确的位置。
StoreFile的文件格式到这里就结束了,有点儿遗憾的是HFileBlockIndex没给大家讲清楚。
补充:经网友"东岸往事"的提醒,有一个地方写错了,在结束一个块之后,会把它所有的BloomFilter全部输出,HFileBlockIndex的话,如果满了默认的128*1024个就输出二级索引。
具体的的内容在后面说查询的时候会说,下面先交代一下:
通过看继承InlineBlockWriter的类,发现了以下信息
1、BlockIndexWriter 不是关闭的情况下,没有超过默认值128*1024是不会输出的,每128*1024个HFileBlock 1个二级索引。
HFileBlockIndex包括2层,如果是MetaBlock的HFileBlock是1层。
二级索引 curInlineChunk 在结束了一个块之后添加一个索引的key(上一个块的firstKey和这个块的firstKey的中间值)。
byte[] indexKey = comparator.calcIndexKey(lastKeyOfPreviousBlock, firstKeyInBlock);
curInlineChunk.add(firstKey, blockOffset, blockDataSize);
一级索引 rootChunk 输出一次二级索引之后添加每个HFileBlock的第一个key,这样子其实二级索引里面是包括是一级索引的所有key的。
firstKey = curInlineChunk.getBlockKey(0);
rootChunk.add(firstKey, offset, onDiskSize, totalNumEntries);
2、CompoundBloomFilterWriter也就是Bloom Filter,在数据不为空的时候,就会输出。
对于HFileV2的正确的图,应该是下面这个,但是上面的那个图看起来好看一点,就保留了。