Adaptively Parametric ReLU是一种动态ReLU(Dynamic ReLU),在2019年5月3日投稿至IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics,2020年1月24日录用, 2020年2月13日在IEEE官网公布。
本文在调参记录15的基础上,将第一个残差模块的卷积核数量,从16个增加到32个,同时将Adaptively Parametric ReLU激活函数中第一个全连接层的神经元个数改成原先的1/16,继续测试其在Cifar10数据集上的效果。
Adaptively Parametric ReLU激活函数的基本原理如下: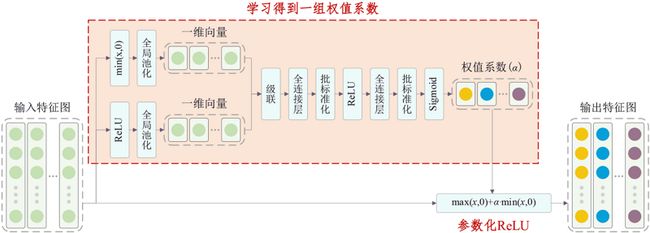
Keras程序:
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Created on Tue Apr 14 04:17:45 2020
Implemented using TensorFlow 1.0.1 and Keras 2.2.1
Minghang Zhao, Shisheng Zhong, Xuyun Fu, Baoping Tang, Shaojiang Dong, Michael Pecht,
Deep Residual Networks with Adaptively Parametric Rectifier Linear Units for Fault Diagnosis,
IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2020, DOI: 10.1109/TIE.2020.2972458,
Date of Publication: 13 February 2020
@author: Minghang Zhao
"""
from __future__ import print_function
import keras
import numpy as np
from keras.datasets import cifar10
from keras.layers import Dense, Conv2D, BatchNormalization, Activation, Minimum
from keras.layers import AveragePooling2D, Input, GlobalAveragePooling2D, Concatenate, Reshape
from keras.regularizers import l2
from keras import backend as K
from keras.models import Model
from keras import optimizers
from keras.preprocessing.image import ImageDataGenerator
from keras.callbacks import LearningRateScheduler
K.set_learning_phase(1)
# The data, split between train and test sets
(x_train, y_train), (x_test, y_test) = cifar10.load_data()
x_train = x_train.astype('float32') / 255.
x_test = x_test.astype('float32') / 255.
x_test = x_test-np.mean(x_train)
x_train = x_train-np.mean(x_train)
print('x_train shape:', x_train.shape)
print(x_train.shape[0], 'train samples')
print(x_test.shape[0], 'test samples')
# convert class vectors to binary class matrices
y_train = keras.utils.to_categorical(y_train, 10)
y_test = keras.utils.to_categorical(y_test, 10)
# Schedule the learning rate, multiply 0.1 every 1500 epoches
def scheduler(epoch):
if epoch % 1500 == 0 and epoch != 0:
lr = K.get_value(model.optimizer.lr)
K.set_value(model.optimizer.lr, lr * 0.1)
print("lr changed to {}".format(lr * 0.1))
return K.get_value(model.optimizer.lr)
# An adaptively parametric rectifier linear unit (APReLU)
def aprelu(inputs):
# get the number of channels
channels = inputs.get_shape().as_list()[-1]
# get a zero feature map
zeros_input = keras.layers.subtract([inputs, inputs])
# get a feature map with only positive features
pos_input = Activation('relu')(inputs)
# get a feature map with only negative features
neg_input = Minimum()([inputs,zeros_input])
# define a network to obtain the scaling coefficients
scales_p = GlobalAveragePooling2D()(pos_input)
scales_n = GlobalAveragePooling2D()(neg_input)
scales = Concatenate()([scales_n, scales_p])
scales = Dense(channels//16, activation='linear', kernel_initializer='he_normal', kernel_regularizer=l2(1e-4))(scales)
scales = BatchNormalization(momentum=0.9, gamma_regularizer=l2(1e-4))(scales)
scales = Activation('relu')(scales)
scales = Dense(channels, activation='linear', kernel_initializer='he_normal', kernel_regularizer=l2(1e-4))(scales)
scales = BatchNormalization(momentum=0.9, gamma_regularizer=l2(1e-4))(scales)
scales = Activation('sigmoid')(scales)
scales = Reshape((1,1,channels))(scales)
# apply a paramtetric relu
neg_part = keras.layers.multiply([scales, neg_input])
return keras.layers.add([pos_input, neg_part])
# Residual Block
def residual_block(incoming, nb_blocks, out_channels, downsample=False,
downsample_strides=2):
residual = incoming
in_channels = incoming.get_shape().as_list()[-1]
for i in range(nb_blocks):
identity = residual
if not downsample:
downsample_strides = 1
residual = BatchNormalization(momentum=0.9, gamma_regularizer=l2(1e-4))(residual)
residual = aprelu(residual)
residual = Conv2D(out_channels, 3, strides=(downsample_strides, downsample_strides),
padding='same', kernel_initializer='he_normal',
kernel_regularizer=l2(1e-4))(residual)
residual = BatchNormalization(momentum=0.9, gamma_regularizer=l2(1e-4))(residual)
residual = aprelu(residual)
residual = Conv2D(out_channels, 3, padding='same', kernel_initializer='he_normal',
kernel_regularizer=l2(1e-4))(residual)
# Downsampling
if downsample_strides > 1:
identity = AveragePooling2D(pool_size=(1,1), strides=(2,2))(identity)
# Zero_padding to match channels
if in_channels != out_channels:
zeros_identity = keras.layers.subtract([identity, identity])
identity = keras.layers.concatenate([identity, zeros_identity])
in_channels = out_channels
residual = keras.layers.add([residual, identity])
return residual
# define and train a model
inputs = Input(shape=(32, 32, 3))
net = Conv2D(16, 3, padding='same', kernel_initializer='he_normal', kernel_regularizer=l2(1e-4))(inputs)
net = residual_block(net, 1, 32, downsample=False)
net = residual_block(net, 1, 32, downsample=True)
# net = residual_block(net, 2, 32, downsample=False)
net = residual_block(net, 1, 64, downsample=True)
# net = residual_block(net, 2, 64, downsample=False)
net = BatchNormalization(momentum=0.9, gamma_regularizer=l2(1e-4))(net)
net = aprelu(net)
net = GlobalAveragePooling2D()(net)
outputs = Dense(10, activation='softmax', kernel_initializer='he_normal', kernel_regularizer=l2(1e-4))(net)
model = Model(inputs=inputs, outputs=outputs)
sgd = optimizers.SGD(lr=0.1, decay=0., momentum=0.9, nesterov=True)
model.compile(loss='categorical_crossentropy', optimizer=sgd, metrics=['accuracy'])
# data augmentation
datagen = ImageDataGenerator(
# randomly rotate images in the range (deg 0 to 180)
rotation_range=30,
# Range for random zoom
zoom_range = 0.2,
# shear angle in counter-clockwise direction in degrees
shear_range = 30,
# randomly flip images
horizontal_flip=True,
# randomly shift images horizontally
width_shift_range=0.125,
# randomly shift images vertically
height_shift_range=0.125)
reduce_lr = LearningRateScheduler(scheduler)
# fit the model on the batches generated by datagen.flow().
model.fit_generator(datagen.flow(x_train, y_train, batch_size=100),
validation_data=(x_test, y_test), epochs=5000,
verbose=1, callbacks=[reduce_lr], workers=4)
# get results
K.set_learning_phase(0)
DRSN_train_score = model.evaluate(x_train, y_train, batch_size=100, verbose=0)
print('Train loss:', DRSN_train_score[0])
print('Train accuracy:', DRSN_train_score[1])
DRSN_test_score = model.evaluate(x_test, y_test, batch_size=100, verbose=0)
print('Test loss:', DRSN_test_score[0])
print('Test accuracy:', DRSN_test_score[1])实验结果如下:
Epoch 3335/5000
11s 23ms/step - loss: 0.3965 - acc: 0.8939 - val_loss: 0.4183 - val_acc: 0.8890
Epoch 3336/5000
12s 23ms/step - loss: 0.3979 - acc: 0.8945 - val_loss: 0.4120 - val_acc: 0.8892
Epoch 3337/5000
12s 23ms/step - loss: 0.3957 - acc: 0.8945 - val_loss: 0.4194 - val_acc: 0.8864
Epoch 3338/5000
12s 24ms/step - loss: 0.3987 - acc: 0.8936 - val_loss: 0.4174 - val_acc: 0.8869
Epoch 3339/5000
12s 24ms/step - loss: 0.4016 - acc: 0.8928 - val_loss: 0.4162 - val_acc: 0.8889
Epoch 3340/5000
12s 24ms/step - loss: 0.3999 - acc: 0.8931 - val_loss: 0.4098 - val_acc: 0.8924
Epoch 3341/5000
12s 24ms/step - loss: 0.3988 - acc: 0.8932 - val_loss: 0.4134 - val_acc: 0.8905
Epoch 3342/5000
12s 23ms/step - loss: 0.3974 - acc: 0.8928 - val_loss: 0.4153 - val_acc: 0.8893
Epoch 3343/5000
12s 23ms/step - loss: 0.3994 - acc: 0.8940 - val_loss: 0.4135 - val_acc: 0.8921
Epoch 3344/5000
12s 23ms/step - loss: 0.3994 - acc: 0.8925 - val_loss: 0.4181 - val_acc: 0.8890
Epoch 3345/5000
12s 24ms/step - loss: 0.3940 - acc: 0.8945 - val_loss: 0.4138 - val_acc: 0.8890程序没跑完,这次没有过拟合了,存在欠拟合。
后续可以继续稍微增加网络规模。
Minghang Zhao, Shisheng Zhong, Xuyun Fu, Baoping Tang, Shaojiang Dong, Michael Pecht, Deep Residual Networks with Adaptively Parametric Rectifier Linear Units for Fault Diagnosis, IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2020, DOI: 10.1109/TIE.2020.2972458, Date of Publication: 13 February 2020