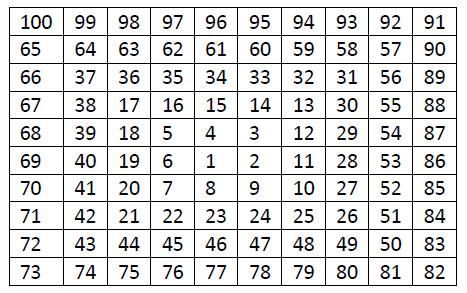
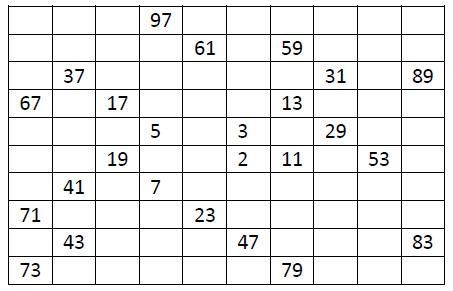
【题目】【分析】本题较为简单,设置一个计数器,当接收的字符为"("时候自增,为")"时自减,为B时候退出循环。AC的C++代码如下:#include#includeusingnamespacestd;intmain(){strings;intcount;while(getline(cin,s)){count=0;intlen=s.length();for(inti=0;i
【算法随笔:HDU 3333 Turing tree】(线段树 | 离线 | 离散化 | 贪心)
XNB's Not a Beginner
算法算法哈希算法leetcodec++排序算法
https://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=3333https://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=3333https://vjudge.net.cn/problem/HDU-3333https://vjudge.net.cn/problem/HDU-3333题目很简单,给出长度为N的数组,Q次询问,每次给出区间[x,
test_Time_2h
爱思考的小伙
#基础数据结构与算法图论算法c++
文章目录RelicDiscoveryHDU-5982TextReverseHDU-1062DownloadManagerHDU-3233看病要排队HDU-1873RedandBlackHDU-1312最短路HDU-2544https://vjudge.csgrandeur.cn/contest/499778RelicDiscoveryHDU-5982#include#includeusingnam
hdu 4408 Minimum Spanning Tree
luckycoding
hdu
题目连接:点击打开链接解法:利用kruskal算法把图划分成森林,同一点有相同最小的权值到别的点,通过determinant计算树的课数。总结:模板+自己不太懂=记录+重新学代码君:#include#include#include#defineLLlonglongusingnamespacestd;constintMAX=105;constintMAXE=1005;structnode{intse
2024/2/17 图论 最短路入门 dijkstra 1
极度的坦诚就是无坚不摧
寒假集训寒假算法图论算法c++c语言dijkstra
目录算法思路Dijkstra求最短路AcWing849.Dijkstra求最短路I-AcWing850.Dijkstra求最短路II-AcWing题库最短路最短路-HDU2544-VirtualJudge(vjudge.net)【模板】单源最短路径(弱化版)P3371【模板】单源最短路径(弱化版)-洛谷|计算机科学教育新生态(luogu.com.cn)【模板】单源最短路径(标准版)P4779【模板
2048
不绝_7647
题目链接:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=2048思路:该题运用了错排公式,即D(n)=(n-1)*(D(n-1)+D(n-2))。计算出n张字条错排给n个人的可能性(每个人得到的都非自己的字条),再除以n张字条给n个人的所有可能性,就能得出结果。做法:建立数组a,并给a[0],a[1].a[2],a[3]分别赋值0,0,1,2.(其中1和2对应
杭电Oj第二周
J_4d20
做题有个习惯,就是没通过一道题之后都会找下答案,对比一下我的代码还有没有可以在优化的地方,使他更简便链接:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=2016我的代码是:#includeintmain(){intn,a[100],t,i,b;while(scanf("%d",&n)!=EOF){if(na[j]){t=a[j];min=j;}for(i=1;
Smiles to the death(3)
KevinZucker
Oneday,a60-year-oldmanexperiencedchestpainandshortnessofbreathduetoexcessiveactivity.Hiswife,whoismorethan10yearshisjunior,wasalarmedatthesightofherhusbandandrushedtomassagehiminanattempttoincreasehis
任意IOS16系统iPad/Iphone开启台前调度
zxfBdd
工作效率ipadiphoneios
方法来自GitHub:GitHub-khanhduytran0/TrollPad:TrollSpringBoardintothinkingit'srunningoniPadOS注意操作前iPad/iPhone上需要安装巨魔手机助手和Filza,关于这两个软件的安装自行百度方法。备注一个巨魔手机助手的下载地址ReleaseTrollStar1.2·34306/TrollStar·GitHub原文内容
K8S之运用节点选择器指定Pod运行的节点
sissie喵~
kuberneteskubernetes容器云原生
node节点选择器的使用使用场景实践使用nodeName使用nodeSelectornodeName和nodeSelector混合使用1、设置了nodeName和设置Node上都不存在的标签。看调度情况2、设置nodeName为node1和设置node2上才有的标签。看调度情况实践总结使用场景默认情况,在创建Pod资源的时候,会根据schduler进行节点调度,默认会随机调度一个工作节点。如果想要
HDU 5159 Card 一次中出现两个也叫一次
DBWG
HDU算法
Problem-5159set暴力超时:intans=0,si=0;intx,b;voiddfs(setcur,intt){if(t==0){for(autox:cur)ans+=x;si++;return;}for(inti=1;i>x>>b;for(inti=1;is;s.insert(i);dfs(s,b-1);}cout>t;for(inti=1;i总次数减去未出现的次数就是出现次数//(
iOS逆向之腾讯视频广告篇
暴躁键盘侠
本文章主要是实现在非越狱机上去掉腾讯视频广告的一个功能,仅供学习交流!!!一、获取褪壳app首先我们需要一个去壳的ipa文件,以前在PP助手可以下载。但是后来PP助手不能用了,也没找到其他地方下载,只能自己动手了。下面推荐三种去壳的方式:Clutchdumpdecryptedfrida-ios-dump。过程在此不多做赘述,下面是我的使用心得。Clutch:失败率比较高,对几个小app砸壳成功,对
java string sscanf_hdu1106 字符串水题strtok()&&strchr()&&sscanf()+atoi()使用
LTT卍
javastringsscanf
字符串的题目用库函数往往能大大简化代码量以hdu1106为例函数介绍strtok()原型:char*strtok(chars[],constchar*delim);功能:分解字符串为一组字符串。s为要分解的字符串,delim为分隔符字符串。例如:strtok("abc,def,ghi",","),最后可以分割成为abcdefghi.尤其在点分十进制的IP中提取应用较多。(注意delim里面的不能看
容斥原理基础例题(HDU 2204, HDU 3208, HDU 1796)
王大凤
ACM
HDU2204题目求[1,N](1≤N≤1018)(1\leN\le10^{18})(1≤N≤1018)之间能被表示成mkm^kmk的数的数量。容斥思想1018约等于26410^{18}约等于2^{64}1018约等于264预处理质数:intprime[20]={2,3,5,7,11,13,17,19,23,29,31,37,41,43,47,53,59};因为合数的话肯定已经包括在所在质因子的部
C语言题目:HDU - 1408 盐水的故事
guuuuug
蓝桥杯c语言蓝桥杯算法c#
题目描述挂盐水的时候,如果滴起来有规律,先是滴一滴,停一下;然后滴二滴,停一下;再滴三滴,停一下...,现在有一个问题:这瓶盐水一共有VUL毫升,每一滴是D毫升,每一滴的速度是一秒(假设最后一滴不到D毫升,则花费的时间也算一秒),停一下的时间也是一秒这瓶水什么时候能挂完呢?输入输入数据占一行,由VUL和D组成,其中0<D<VUL<5000。输出
HDUOJ 4738 Caocao‘s Bridges 题解 桥 割边 Tarjan
kaiserqzyue
算法题目c++算法图论
题目链接:HDUOJ4738Caocao’sBridges题目描述:给定一个无向图,你可以选择最多删除一条边,删除边的代价是边的边权(特殊地,删除一条边权为0的边的代价是1),问最小代价使得图不连通。如果无论如何图都是连通的,那么则输出-1。题解:题目也就是需要我们求一条桥边,这个桥边所拥有的边权最小。我们只需要求出所有的桥边,然后对边权取一个最小值即可(需要注意边权为0的边我们要将其变成边权为1
HDU1677 矩阵嵌套 DP 记忆化搜索 图 最长上升序列
JUNLONG2
矩阵嵌套题有两种解法第一种是用图,然后记忆化搜索若矩形i能被嵌入矩形j则G[i][j]为1,状态转移方程:dp(i)=max{dp(i),dp(j)+1}这题如果我用图来解会显示超时第二种排序,然后求最长上升序列按面积递减排序
【2022杭电多校1】2022“杭电杯”中国大学生算法设计超级联赛(1)
andyc_03
算法acm
2022“杭电杯”中国大学生算法设计超级联赛(1)hdu7138-71491001String利用exkmp把s的每个后缀与s的lcp求出来设后缀[i,n][i,n][i,n]和sss的lcplcplcp长度为xxx那么只有当i≤xi\lexi≤x时,会产生贡献,中间重合部分为kkk的倍数的时候有贡献找到第一个和最后一个kkk的倍数的位置,把贡献差分一下即可#includeusingnamespa
杭电2055
NiRAutomata
题目链接:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=2055image.png思路:不难发现,这里a,b,c.....z呈现递增趋势分别对应相应的数字,而不是无规律的对应数字,那么我们就可以用ASCII码的加减转换,通过循环得到对应的所有值,再进行运算代码如下#includeintmain(void){intn,i,m,sum;chary;scanf("%
杭电HDU 3974Assign the task dfs出父包子的数组->知道管辖范围,线段树
DBWG
HDU深度优先算法
题目链接:Problem-3974(hdu.edu.cn)别的题解那对数的输入有点复杂,而且不用。。本题不讲线段树原理,会线段树后来看即可。思路:我们建好树,对树dfs。就题目样例吧:(建树网站:CSAcademy)每个节点进的时候记录,出的时候也记录,dfs完是这个效果节点//2344113552下标//12345678910比如start数组记录该点左下标start[2]=1end数组记录右下
iOS之removeFromSuperview遇到的坑:第二次执行animateWithDuration动画,没有动画效果
CoderZb
直接先附上有问题的效果101.175515.gif原因:我懒加载创建的view,而removeFromSuperview不是真正的移除view,所以view还存在,只是被隐藏了。因此第二次并不会再次懒加载创建view。所以第二次没有动画是因为,第一次最后停留的位置BBB,和第二次的位置是一模一样的。所以第二次移动之前,利用代码AAA更新一下frame就可以了(将view更新到屏幕底部)详情代码//
hdu(2680) 最短路径技巧
不给赞就别想跑哼
选择最佳路线时间限制:2000/1000MS(Java/Others)内存限制:32768/32768K(Java/Others)总提交内容:18613接受提交内容:6025问题描述有一天,琪琪想去拜访她的一个朋友。由于她很容易晕车,她想尽快到她朋友家。现在给你一张城市交通路线的地图,以及靠近Kiki家的车站,以便她可以乘坐。您可以认为Kiki可以在任何车站更换公交车。请找出Kiki需要花费的最少
【论文复现】DCFace: Synthetic Face Generation with Dual Condition Diffusion Model
李加号pluuuus
python人工智能机器学习
DCFace:用双条件扩散模型生成合成人脸。CVPR2023.4code:mk-minchul/dcface(github.com)paper:[2304.07060]DCFace:SyntheticFaceGenerationwithDualConditionDiffusionModel(arxiv.org)论文介绍应用:生成用于训练人脸识别模型的合成数据集。背景:生成合成数据集需要考虑多个因素
hdu 4734 F(x)
吵闹的人群保持笑容多冷静
算法c++动态规划
F(x)题意定义一个十进制数的权重:F(x)=xn⋅2n−1+xn−1⋅2n−2+...+x1⋅20F(x)=x_n\cdot2^{n-1}+x_{n-1}\cdot2^{n-2}+...+x_1\cdot2^0F(x)=xn⋅2n−1+xn−1⋅2n−2+...+x1⋅20给定两个数A,BA,BA,B,求出[0,B][0,B][0,B]中有多少个数的权重不大于AAA的权重思路可以发现权重最大为9
iOS动画中的枚举UIViewAnimationOptions
香橙柚子
首先这个枚举属于UIViewAnimation。我们经常使用的函数是[UIViewanimateWithDuration:animations:^{}completion:^(BOOLfinished){}];和[UIViewanimateWithDuration:animations:^{}];如果动画稍微复杂点,例如需要组合等等就可能用到这个函数:[UIViewanimateWithDurat
What made me change my mind about studying chemistry?
淑华_6c8b
Whatmademechangemymindaboutstudyingchemistry?WhydidIdecidetolearnandteachEnglishduringcollege?Inmyopinion,theyareaquestion,asamequestion.Ilikemakingdream.Butchemistryisnotaboutadream.It'sabouttruth,re
HttpClient 4.3与4.3版本以下版本比较
spjich
javahttpclient
网上利用java发送http请求的代码很多,一搜一大把,有的利用的是java.net.*下的HttpURLConnection,有的用httpclient,而且发送的代码也分门别类。今天我们主要来说的是利用httpclient发送请求。
httpclient又可分为
httpclient3.x
httpclient4.x到httpclient4.3以下
httpclient4.3
Essential Studio Enterprise Edition 2015 v1新功能体验
Axiba
.net
概述:Essential Studio已全线升级至2015 v1版本了!新版本为JavaScript和ASP.NET MVC添加了新的文件资源管理器控件,还有其他一些控件功能升级,精彩不容错过,让我们一起来看看吧!
syncfusion公司是世界领先的Windows开发组件提供商,该公司正式对外发布Essential Studio Enterprise Edition 2015 v1版本。新版本
[宇宙与天文]微波背景辐射值与地球温度
comsci
背景
宇宙这个庞大,无边无际的空间是否存在某种确定的,变化的温度呢?
如果宇宙微波背景辐射值是表示宇宙空间温度的参数之一,那么测量这些数值,并观测周围的恒星能量输出值,我们是否获得地球的长期气候变化的情况呢?
&nbs
lvs-server
男人50
server
#!/bin/bash
#
# LVS script for VS/DR
#
#./etc/rc.d/init.d/functions
#
VIP=10.10.6.252
RIP1=10.10.6.101
RIP2=10.10.6.13
PORT=80
case $1 in
start)
/sbin/ifconfig eth2:0 $VIP broadca
java的WebCollector爬虫框架
oloz
爬虫
WebCollector主页:
https://github.com/CrawlScript/WebCollector
下载:webcollector-版本号-bin.zip将解压后文件夹中的所有jar包添加到工程既可。
接下来看demo
package org.spider.myspider;
import cn.edu.hfut.dmic.webcollector.cra
jQuery append 与 after 的区别
小猪猪08
1、after函数
定义和用法:
after() 方法在被选元素后插入指定的内容。
语法:
$(selector).after(content)
实例:
<html>
<head>
<script type="text/javascript" src="/jquery/jquery.js"></scr
mysql知识充电
香水浓
mysql
索引
索引是在存储引擎中实现的,因此每种存储引擎的索引都不一定完全相同,并且每种存储引擎也不一定支持所有索引类型。
根据存储引擎定义每个表的最大索引数和最大索引长度。所有存储引擎支持每个表至少16个索引,总索引长度至少为256字节。
大多数存储引擎有更高的限制。MYSQL中索引的存储类型有两种:BTREE和HASH,具体和表的存储引擎相关;
MYISAM和InnoDB存储引擎
我的架构经验系列文章索引
agevs
架构
下面是一些个人架构上的总结,本来想只在公司内部进行共享的,因此内容写的口语化一点,也没什么图示,所有内容没有查任何资料是脑子里面的东西吐出来的因此可能会不准确不全,希望抛砖引玉,大家互相讨论。
要注意,我这些文章是一个总体的架构经验不针对具体的语言和平台,因此也不一定是适用所有的语言和平台的。
(内容是前几天写的,现附上索引)
前端架构 http://www.
Android so lib库远程http下载和动态注册
aijuans
andorid
一、背景
在开发Android应用程序的实现,有时候需要引入第三方so lib库,但第三方so库比较大,例如开源第三方播放组件ffmpeg库, 如果直接打包的apk包里面, 整个应用程序会大很多.经过查阅资料和实验,发现通过远程下载so文件,然后再动态注册so文件时可行的。主要需要解决下载so文件存放位置以及文件读写权限问题。
二、主要
linux中svn配置出错 conf/svnserve.conf:12: Option expected 解决方法
baalwolf
option
在客户端访问subversion版本库时出现这个错误:
svnserve.conf:12: Option expected
为什么会出现这个错误呢,就是因为subversion读取配置文件svnserve.conf时,无法识别有前置空格的配置文件,如### This file controls the configuration of the svnserve daemon, if you##
MongoDB的连接池和连接管理
BigCat2013
mongodb
在关系型数据库中,我们总是需要关闭使用的数据库连接,不然大量的创建连接会导致资源的浪费甚至于数据库宕机。这篇文章主要想解释一下mongoDB的连接池以及连接管理机制,如果正对此有疑惑的朋友可以看一下。
通常我们习惯于new 一个connection并且通常在finally语句中调用connection的close()方法将其关闭。正巧,mongoDB中当我们new一个Mongo的时候,会发现它也
AngularJS使用Socket.IO
bijian1013
JavaScriptAngularJSSocket.IO
目前,web应用普遍被要求是实时web应用,即服务端的数据更新之后,应用能立即更新。以前使用的技术(例如polling)存在一些局限性,而且有时我们需要在客户端打开一个socket,然后进行通信。
Socket.IO(http://socket.io/)是一个非常优秀的库,它可以帮你实
[Maven学习笔记四]Maven依赖特性
bit1129
maven
三个模块
为了说明问题,以用户登陆小web应用为例。通常一个web应用分为三个模块,模型和数据持久化层user-core, 业务逻辑层user-service以及web展现层user-web,
user-service依赖于user-core
user-web依赖于user-core和user-service
依赖作用范围
Maven的dependency定义
【Akka一】Akka入门
bit1129
akka
什么是Akka
Message-Driven Runtime is the Foundation to Reactive Applications
In Akka, your business logic is driven through message-based communication patterns that are independent of physical locatio
zabbix_api之perl语言写法
ronin47
zabbix_api之perl
zabbix_api网上比较多的写法是python或curl。上次我用java--http://bossr.iteye.com/blog/2195679,这次用perl。for example: #!/usr/bin/perl
use 5.010 ;
use strict ;
use warnings ;
use JSON :: RPC :: Client ;
use
比优衣库跟牛掰的视频流出了,兄弟连Linux运维工程师课堂实录,更加刺激,更加实在!
brotherlamp
linux运维工程师linux运维工程师教程linux运维工程师视频linux运维工程师资料linux运维工程师自学
比优衣库跟牛掰的视频流出了,兄弟连Linux运维工程师课堂实录,更加刺激,更加实在!
-----------------------------------------------------
兄弟连Linux运维工程师课堂实录-计算机基础-1-课程体系介绍1
链接:http://pan.baidu.com/s/1i3GQtGL 密码:bl65
兄弟连Lin
bitmap求哈密顿距离-给定N(1<=N<=100000)个五维的点A(x1,x2,x3,x4,x5),求两个点X(x1,x2,x3,x4,x5)和Y(
bylijinnan
java
import java.util.Random;
/**
* 题目:
* 给定N(1<=N<=100000)个五维的点A(x1,x2,x3,x4,x5),求两个点X(x1,x2,x3,x4,x5)和Y(y1,y2,y3,y4,y5),
* 使得他们的哈密顿距离(d=|x1-y1| + |x2-y2| + |x3-y3| + |x4-y4| + |x5-y5|)最大
map的三种遍历方法
chicony
map
package com.test;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
public class TestMap {
public static v
Linux安装mysql的一些坑
chenchao051
linux
1、mysql不建议在root用户下运行
2、出现服务启动不了,111错误,注意要用chown来赋予权限, 我在root用户下装的mysql,我就把usr/share/mysql/mysql.server复制到/etc/init.d/mysqld, (同时把my-huge.cnf复制/etc/my.cnf)
chown -R cc /etc/init.d/mysql
Sublime Text 3 配置
daizj
配置Sublime Text
Sublime Text 3 配置解释(默认){// 设置主题文件“color_scheme”: “Packages/Color Scheme – Default/Monokai.tmTheme”,// 设置字体和大小“font_face”: “Consolas”,“font_size”: 12,// 字体选项:no_bold不显示粗体字,no_italic不显示斜体字,no_antialias和
MySQL server has gone away 问题的解决方法
dcj3sjt126com
SQL Server
MySQL server has gone away 问题解决方法,需要的朋友可以参考下。
应用程序(比如PHP)长时间的执行批量的MYSQL语句。执行一个SQL,但SQL语句过大或者语句中含有BLOB或者longblob字段。比如,图片数据的处理。都容易引起MySQL server has gone away。 今天遇到类似的情景,MySQL只是冷冷的说:MySQL server h
javascript/dom:固定居中效果
dcj3sjt126com
JavaScript
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd">
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml&
使用 Spring 2.5 注释驱动的 IoC 功能
e200702084
springbean配置管理IOCOffice
使用 Spring 2.5 注释驱动的 IoC 功能
developerWorks
文档选项
将打印机的版面设置成横向打印模式
打印本页
将此页作为电子邮件发送
将此页作为电子邮件发送
级别: 初级
陈 雄华 (
[email protected]), 技术总监, 宝宝淘网络科技有限公司
2008 年 2 月 28 日
&nb
1. 基本操作
db.AddUser(username,password) 添加用户
db.auth(usrename,password) 设置数据库连接验证
db.cloneDataBase(fromhost)
php写守护进程(Daemon)
hongtoushizi
PHP
转载自: http://blog.csdn.net/tengzhaorong/article/details/9764655
守护进程(Daemon)是运行在后台的一种特殊进程。它独立于控制终端并且周期性地执行某种任务或等待处理某些发生的事件。守护进程是一种很有用的进程。php也可以实现守护进程的功能。
1、基本概念
&nbs
spring整合mybatis,关于注入Dao对象出错问题
jonsvien
DAOspringbeanmybatisprototype
今天在公司测试功能时发现一问题:
先进行代码说明:
1,controller配置了Scope="prototype"(表明每一次请求都是原子型)
@resource/@autowired service对象都可以(两种注解都可以)。
2,service 配置了Scope="prototype"(表明每一次请求都是原子型)
对象关系行为模式之标识映射
home198979
PHP架构企业应用对象关系标识映射
HELLO!架构
一、概念
identity Map:通过在映射中保存每个已经加载的对象,确保每个对象只加载一次,当要访问对象的时候,通过映射来查找它们。其实在数据源架构模式之数据映射器代码中有提及到标识映射,Mapper类的getFromMap方法就是实现标识映射的实现。
二、为什么要使用标识映射?
在数据源架构模式之数据映射器中
//c
Linux下hosts文件详解
pda158
linux
1、主机名: 无论在局域网还是INTERNET上,每台主机都有一个IP地址,是为了区分此台主机和彼台主机,也就是说IP地址就是主机的门牌号。 公网:IP地址不方便记忆,所以又有了域名。域名只是在公网(INtERNET)中存在,每个域名都对应一个IP地址,但一个IP地址可有对应多个域名。 局域网:每台机器都有一个主机名,用于主机与主机之间的便于区分,就可以为每台机器设置主机
nginx配置文件粗解
spjich
javanginx
#运行用户#user nobody;#启动进程,通常设置成和cpu的数量相等worker_processes 2;#全局错误日志及PID文件#error_log logs/error.log;#error_log logs/error.log notice;#error_log logs/error.log inf
数学函数
w54653520
java
public
class
S {
// 传入两个整数,进行比较,返回两个数中的最大值的方法。
public
int
get(
int
num1,
int
nu