把AFNetworking的源码读了一遍,关于详细的源码解析的文章网上已经有很多,便不再赘述。我尝试从源码里寻找以下问题的答案:
- 用户发起一次网络请求后,AFN都做了些什么?
- UIImageView+AFNetworking怎么实现图片的下载与缓存?
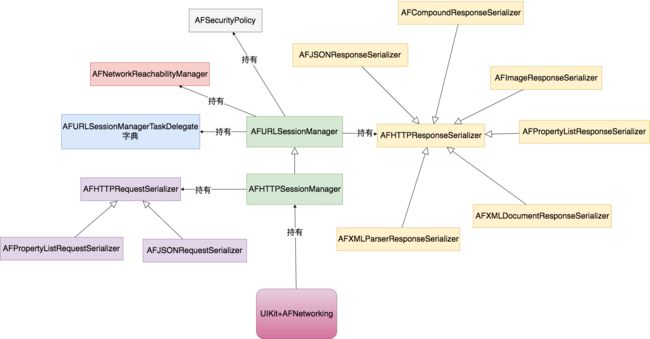
先来个整体的架构:
最核心的两个类是AFURLSessionManager和AFHTTPSessionManager,他们的职责简单来说就是:
- 提供一组API给客户端发起网络请求
- 协调系统各个其他组件,类似于控制器的角色
- 调用
AFHTTPRequestSerializer加工网络请求 - 调用
AFHTTPResponseSerializer解析返回数据 - 调用
AFNetworkReachabilityManager判断网络状态 - 调用
AFSecurityPolicy验证HTTPS请求证书的有效性 - 内部利用
AFURLSessionManagerTaskDelegate处理部分NSURLSessionTaskDelegate回调
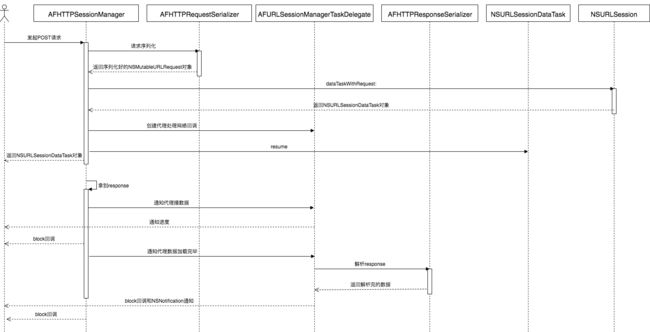
用户发起一次网络请求后,AFN都做了些什么?
假设用户发起一次POST请求:
[self.manager
POST:@"post"
parameters:@{@"key":@"value"}
progress:nil
success:nil
failure:nil];
来个顺序图会比较清楚一些:
UIImageView+AFNetworking怎么实现图片的下载与缓存?
先来看下调setImageWithURLRequest:placeholderImage:success:failure:后AFN都做了些什么,直接贴代码了:
- (void)setImageWithURLRequest:(NSURLRequest *)urlRequest
placeholderImage:(UIImage *)placeholderImage
success:(void (^)(NSURLRequest *request, NSHTTPURLResponse * _Nullable response, UIImage *image))success
failure:(void (^)(NSURLRequest *request, NSHTTPURLResponse * _Nullable response, NSError *error))failure
{
if ([urlRequest URL] == nil) {
[self cancelImageDownloadTask];
self.image = placeholderImage;
return;
}
if ([self isActiveTaskURLEqualToURLRequest:urlRequest]){
return;
}
[self cancelImageDownloadTask];
AFImageDownloader *downloader = [[self class] sharedImageDownloader];
id imageCache = downloader.imageCache;
//Use the image from the image cache if it exists
UIImage *cachedImage = [imageCache imageforRequest:urlRequest withAdditionalIdentifier:nil];
if (cachedImage) {
if (success) {
success(urlRequest, nil, cachedImage);
} else {
self.image = cachedImage;
}
[self clearActiveDownloadInformation];
} else {
if (placeholderImage) {
self.image = placeholderImage;
}
__weak __typeof(self)weakSelf = self;
NSUUID *downloadID = [NSUUID UUID];
AFImageDownloadReceipt *receipt;
receipt = [downloader
downloadImageForURLRequest:urlRequest
withReceiptID:downloadID
success:^(NSURLRequest * _Nonnull request, NSHTTPURLResponse * _Nullable response, UIImage * _Nonnull responseObject) {
__strong __typeof(weakSelf)strongSelf = weakSelf;
if ([strongSelf.af_activeImageDownloadReceipt.receiptID isEqual:downloadID]) {
if (success) {
success(request, response, responseObject);
} else if(responseObject) {
strongSelf.image = responseObject;
}
[strongSelf clearActiveDownloadInformation];
}
}
failure:^(NSURLRequest * _Nonnull request, NSHTTPURLResponse * _Nullable response, NSError * _Nonnull error) {
__strong __typeof(weakSelf)strongSelf = weakSelf;
if ([strongSelf.af_activeImageDownloadReceipt.receiptID isEqual:downloadID]) {
if (failure) {
failure(request, response, error);
}
[strongSelf clearActiveDownloadInformation];
}
}];
self.af_activeImageDownloadReceipt = receipt;
}
}
主要做了:
- 做一些保护,判空,排重
- 起一个
AFImageDownloader单例来完成真正的下载任务 - 先找cache,有直接返回,没有的话用
AFImageDownloader开启下载 - 用一个叫
AFImageDownloadReceipt的对象来记录每一次下载,可以理解为一个下载收据,用[NSUUID UUID]作为它的ID,每个UIImageView实例对应了唯一个正在下载的收据,用af_activeImageDownloadReceipt持有
这里要注意的是
AFImageDownloader是个单例,AFN所有UIKit分类中需要用到下载图片的地方都用了同一个downloader.
真正干活的是AFImageDownloader,我们来看一下它的实现。
先来看下初始化函数:
- (instancetype)init {
NSURLSessionConfiguration *defaultConfiguration = [self.class defaultURLSessionConfiguration];
AFHTTPSessionManager *sessionManager = [[AFHTTPSessionManager alloc] initWithSessionConfiguration:defaultConfiguration];
sessionManager.responseSerializer = [AFImageResponseSerializer serializer];
return [self initWithSessionManager:sessionManager
downloadPrioritization:AFImageDownloadPrioritizationFIFO
maximumActiveDownloads:4
imageCache:[[AFAutoPurgingImageCache alloc] init]];
}
实例化了一个AFHTTPSessionManager,给它配了个sessionConfiguration和AFImageResponseSerializer类型的responseSerializer,然后设置它的下载优先级为FIFO(先来先下载,合情合理),最大同时下载数为4(这个必须得控制下),cache类型为AFAutoPurgingImageCache。
先来看下sessionConfiguration:
+ (NSURLCache *)defaultURLCache {
// It's been discovered that a crash will occur on certain versions
// of iOS if you customize the cache.
//
// More info can be found here: https://devforums.apple.com/message/1102182#1102182
//
// When iOS 7 support is dropped, this should be modified to use
// NSProcessInfo methods instead.
if ([[[UIDevice currentDevice] systemVersion] compare:@"8.2" options:NSNumericSearch] == NSOrderedAscending) {
return [NSURLCache sharedURLCache];
}
return [[NSURLCache alloc] initWithMemoryCapacity:20 * 1024 * 1024
diskCapacity:150 * 1024 * 1024
diskPath:@"com.alamofire.imagedownloader"];
}
+ (NSURLSessionConfiguration *)defaultURLSessionConfiguration {
NSURLSessionConfiguration *configuration = [NSURLSessionConfiguration defaultSessionConfiguration];
//TODO set the default HTTP headers
configuration.HTTPShouldSetCookies = YES;
configuration.HTTPShouldUsePipelining = NO;
configuration.requestCachePolicy = NSURLRequestUseProtocolCachePolicy;
configuration.allowsCellularAccess = YES;
configuration.timeoutIntervalForRequest = 60.0;
configuration.URLCache = [AFImageDownloader defaultURLCache];
return configuration;
}
-
NSURLRequestUseProtocolCachePolicy是默认缓存策略, 其策略如下:
详情见:https://developer.apple.com/reference/foundation/nsurlrequestcachepolicy -
allowsCellularAccess = YES,允许非wifi下下载图片,这是当然 -
URLCache允许20MB的内存空间和150MB的磁盘空间。当应用不在前台跑的时候,如果系统磁盘空间不够了,磁盘上的图片缓存会被清理。
切入正题,来看下图片是怎么下载的:
- (nullable AFImageDownloadReceipt *)downloadImageForURLRequest:(NSURLRequest *)request
withReceiptID:(nonnull NSUUID *)receiptID
success:(nullable void (^)(NSURLRequest *request, NSHTTPURLResponse * _Nullable response, UIImage *responseObject))success
failure:(nullable void (^)(NSURLRequest *request, NSHTTPURLResponse * _Nullable response, NSError *error))failure {
__block NSURLSessionDataTask *task = nil;
dispatch_sync(self.synchronizationQueue, ^{
NSString *URLIdentifier = request.URL.absoluteString;
if (URLIdentifier == nil) {
if (failure) {
NSError *error = [NSError errorWithDomain:NSURLErrorDomain code:NSURLErrorBadURL userInfo:nil];
dispatch_async(dispatch_get_main_queue(), ^{
failure(request, nil, error);
});
}
return;
}
// 1) Append the success and failure blocks to a pre-existing request if it already exists
AFImageDownloaderMergedTask *existingMergedTask = self.mergedTasks[URLIdentifier];
if (existingMergedTask != nil) {
AFImageDownloaderResponseHandler *handler = [[AFImageDownloaderResponseHandler alloc] initWithUUID:receiptID success:success failure:failure];
[existingMergedTask addResponseHandler:handler];
task = existingMergedTask.task;
return;
}
// 2) Attempt to load the image from the image cache if the cache policy allows it
switch (request.cachePolicy) {
case NSURLRequestUseProtocolCachePolicy:
case NSURLRequestReturnCacheDataElseLoad:
case NSURLRequestReturnCacheDataDontLoad: {
UIImage *cachedImage = [self.imageCache imageforRequest:request withAdditionalIdentifier:nil];
if (cachedImage != nil) {
if (success) {
dispatch_async(dispatch_get_main_queue(), ^{
success(request, nil, cachedImage);
});
}
return;
}
break;
}
default:
break;
}
// 3) Create the request and set up authentication, validation and response serialization
NSUUID *mergedTaskIdentifier = [NSUUID UUID];
NSURLSessionDataTask *createdTask;
__weak __typeof__(self) weakSelf = self;
createdTask = [self.sessionManager
dataTaskWithRequest:request
uploadProgress:nil
downloadProgress:nil
completionHandler:^(NSURLResponse * _Nonnull response, id _Nullable responseObject, NSError * _Nullable error) {
dispatch_async(self.responseQueue, ^{
__strong __typeof__(weakSelf) strongSelf = weakSelf;
AFImageDownloaderMergedTask *mergedTask = self.mergedTasks[URLIdentifier];
if ([mergedTask.identifier isEqual:mergedTaskIdentifier]) {
mergedTask = [strongSelf safelyRemoveMergedTaskWithURLIdentifier:URLIdentifier];
if (error) {
for (AFImageDownloaderResponseHandler *handler in mergedTask.responseHandlers) {
if (handler.failureBlock) {
dispatch_async(dispatch_get_main_queue(), ^{
handler.failureBlock(request, (NSHTTPURLResponse*)response, error);
});
}
}
} else {
[strongSelf.imageCache addImage:responseObject forRequest:request withAdditionalIdentifier:nil];
for (AFImageDownloaderResponseHandler *handler in mergedTask.responseHandlers) {
if (handler.successBlock) {
dispatch_async(dispatch_get_main_queue(), ^{
handler.successBlock(request, (NSHTTPURLResponse*)response, responseObject);
});
}
}
}
}
[strongSelf safelyDecrementActiveTaskCount];
[strongSelf safelyStartNextTaskIfNecessary];
});
}];
// 4) Store the response handler for use when the request completes
AFImageDownloaderResponseHandler *handler = [[AFImageDownloaderResponseHandler alloc] initWithUUID:receiptID
success:success
failure:failure];
AFImageDownloaderMergedTask *mergedTask = [[AFImageDownloaderMergedTask alloc]
initWithURLIdentifier:URLIdentifier
identifier:mergedTaskIdentifier
task:createdTask];
[mergedTask addResponseHandler:handler];
self.mergedTasks[URLIdentifier] = mergedTask;
// 5) Either start the request or enqueue it depending on the current active request count
if ([self isActiveRequestCountBelowMaximumLimit]) {
[self startMergedTask:mergedTask];
} else {
[self enqueueMergedTask:mergedTask];
}
task = mergedTask.task;
});
if (task) {
return [[AFImageDownloadReceipt alloc] initWithReceiptID:receiptID task:task];
} else {
return nil;
}
}
作者注释中已经写的很清楚了,分为5步:
- 如果是重复请求,将成功和失败的block回调存入之前已存在的任务中
- 如果缓存策略允许,尝试从缓存中取图片
- 创建请求,response序列化对象
- 将成功失败的block存起来备用
- 根据当前活跃请求数,直接开启下载任务或者加入下载队列
可以看到,这些步骤都被放入了一个串行队列synchronizationQueue中,并用dispatch_sync的方式调用,保证了线程安全性。
在图片下载成功的回调中,将当前活跃任务数-1,并在下载队列里拿一个任务出来下载:
[strongSelf safelyDecrementActiveTaskCount];
[strongSelf safelyStartNextTaskIfNecessary];
接着来看下图片的缓存,这里用了AFAutoPurgingImageCache这个类来做。
这是个实现了AFImageRequestCache协议的类:
@protocol AFImageRequestCache
- (void)addImage:(UIImage *)image forRequest:(NSURLRequest *)request withAdditionalIdentifier:(nullable NSString *)identifier;
- (BOOL)removeImageforRequest:(NSURLRequest *)request withAdditionalIdentifier:(nullable NSString *)identifier;
- (nullable UIImage *)imageforRequest:(NSURLRequest *)request withAdditionalIdentifier:(nullable NSString *)identifier;
@end
如果它的缓存实现不满足你的要求,也可以自己实现一套。
记得以前老版本的AFN用了NSCache来做图片缓存,现在的版本在AFAutoPurgingImageCache里用了NSDictionary自己实现了一套,作者应该是觉得系统的NSCache不太好定制化需求,比如想更精准的控制缓存清理的时间用NSCache就做不到。不过NSCache是线程安全的,用了NSDictionary必须自己来保证。代码里用了dispatch_barrier_async来保证线程安全:
- (void)addImage:(UIImage *)image withIdentifier:(NSString *)identifier {
dispatch_barrier_async(self.synchronizationQueue, ^{
AFCachedImage *cacheImage = [[AFCachedImage alloc] initWithImage:image identifier:identifier];
AFCachedImage *previousCachedImage = self.cachedImages[identifier];
if (previousCachedImage != nil) {
self.currentMemoryUsage -= previousCachedImage.totalBytes;
}
self.cachedImages[identifier] = cacheImage;
self.currentMemoryUsage += cacheImage.totalBytes;
});
dispatch_barrier_async(self.synchronizationQueue, ^{
if (self.currentMemoryUsage > self.memoryCapacity) {
UInt64 bytesToPurge = self.currentMemoryUsage - self.preferredMemoryUsageAfterPurge;
NSMutableArray *sortedImages = [NSMutableArray arrayWithArray:self.cachedImages.allValues];
NSSortDescriptor *sortDescriptor = [[NSSortDescriptor alloc] initWithKey:@"lastAccessDate"
ascending:YES];
[sortedImages sortUsingDescriptors:@[sortDescriptor]];
UInt64 bytesPurged = 0;
for (AFCachedImage *cachedImage in sortedImages) {
[self.cachedImages removeObjectForKey:cachedImage.identifier];
bytesPurged += cachedImage.totalBytes;
if (bytesPurged >= bytesToPurge) {
break ;
}
}
self.currentMemoryUsage -= bytesPurged;
}
});
}
- (nullable UIImage *)imageWithIdentifier:(NSString *)identifier {
__block UIImage *image = nil;
dispatch_sync(self.synchronizationQueue, ^{
AFCachedImage *cachedImage = self.cachedImages[identifier];
image = [cachedImage accessImage];
});
return image;
}
- (UIImage*)accessImage {
self.lastAccessDate = [NSDate date];
return self.image;
}
- 每次命中缓存都会更新cache的最后访问时间
lastAccessDate - 如果有新图加入缓存了以后,缓存占用内存超出了容量,会清理部分缓存的图片
- 从最久没被使用的图开始清理,直到所占内存达标
默认的内存容量为100M,每次清理后默认会降到60M以下:
- (instancetype)init {
return [self initWithMemoryCapacity:100 * 1024 * 1024 preferredMemoryCapacity:60 * 1024 * 1024];
}
大致先分析到这里。