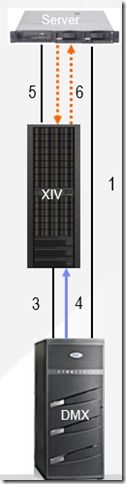
和大多数存储系统一样,XIV也提供多地容灾的解决方案。XIV Data Recovery Protection (XDRP)有三种实现方式, Synchronous Mirroring; ASynchronous Mirroring; Data Migration。除此之外,当然也支持Flashcopy,VolumeCopy
一、Synchronous Mirroring
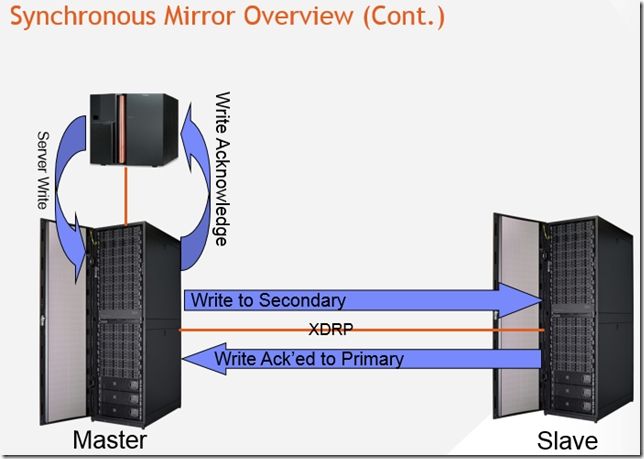
XDRP是在两个或多个XIV系统之间做real-time copy,支持 Fiber Channel 或iSCSI links【考虑到长距离灾备时的可靠性和带宽,大多数使用FC】。有Master system和Slave system。如下图描述了两个XIV系统是如何运作的。
三种状态:
–Initialization -正在做Sync,数据正从Master copy到Slave
–Synchronized - 完成Sync,两端数据一致
–Unsynchronized – Remote Mirror出现问题
那一旦remote mirror出问题了,比如链路段了,Master会对tracking它上面Source Vol的change.
–当链路恢复后,所有tracking的change会被立刻copy到Slave上,这部分数据叫做 “Uncommitted Data”。当Vol resynced时系统在Slave Master上自动创建的一个Special Snapshot,这个Snapshot叫做""Last consistent snapshot”。它是系统Snapshot,用户不能手动删除,会在Fully resynced之后自动删除,它不会考虑大小限制,如果有需要,会占据磁盘所有剩余空间。
Consistency Groups--同时对一组voume做snapshot,比如数据库应用,数据库文件和Log文件不在同一个volume上,为了确保一致性,必须味数据库文件volume和log文件volume创建一个consistency group,然后基于consistency group做flashcopy。
You can switch the role of the entire consistency group
–This will change the Master/Slave location of all member volumes in the consistency group
Both the Master and the Slave system must be configured with an empty CG that is configured for mirroring
After the CG mirror is created and synchronized you can start adding volumes to it
–All volumes must be at a synchronized state and of the same sync type
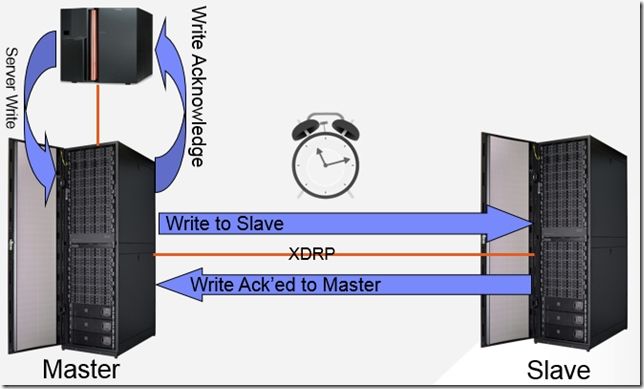
二、Asynchronous Mirroring
只会发送改变的数据块给Slave,可以按事先定义的间隔时间段Sync,比如20s (min_interval), 30s, 1m, 2m, 5m, 10m, 15m, 30m, 1h, 2h, 3h, 6h, 8h, 12h
Mirroring是以Initialization开始,支持(Online Initialization和Offline Initialization,具体解释如下)
–一旦Initialization完成,Master会决定Synchronization的范围
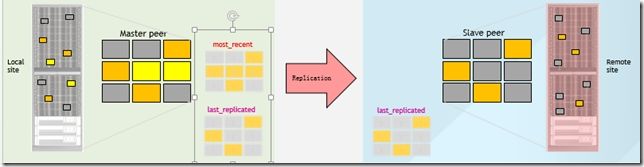
当Define了新的Mirror之后,Master会在Mirror开始之前对系统生成一个Snapshot来代表初始状态
XIV系统使用特殊的Snapshot来决定Sync的范围
Two snapshots are maintained on the Master:
–The most_recent snapshot denotes the most recent mirroring-related snapshot of the Master
–The last_replicated snapshot reflects the most recent state of the Master which has a consistent replica on the Slave
One snapshot is maintained on the Slave
–The last_replicated snapshot reflects the most recent state of the Master which has a consistent replica on the Slave
Offline initialization
-Offline Initialization (previously dubbed ‘Truck‘ initialization) enables initialization of a remote mirror peer (the ‘Slave’) without being required to replicate the contents of the local peer (the ‘Master’) over the link (a.k.a. online initialization)
-The feature applies to asynchronous mirroring, and entails validation of the replica data prior to ongoing mirroring 只适用于异步Mirror这种方式,减少带宽占用,节省Initialization的时间,在Mirror之前会对“运输”过来的replica做check
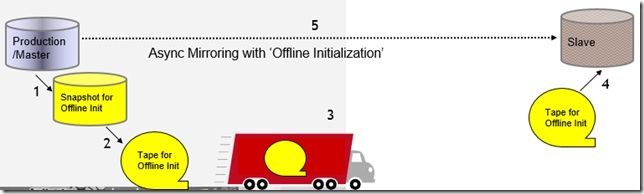
Asynchronous Replication Offline Initialization (“Truck” Mode) process
1.Create Snapshot of future Master volume
2.Backup Snapshot to transportable media (e.g. tape)
3.Transport media to remote site
4.Restore future Slave volume from transported media
5.Create async mirror specifying ‘offline initialization’
6.Activate async mirror
–Offline initialization will begin
- Checksum exchange on 64K boundaries
- Reduces bandwidth and time required for initialization
三、Data Migration
XIV DM可以通过FC或者iscsi将其他任何存储上的数据迁移到XIV上且不需要停机,实现生产环境下在线迁移。(这个其实是有点不准确的,中间会停机一段时间,即下面的DM Process的Step2)
在迁移数据过程中,XIV还是会继续处理主机发过来的IO
–所有读操作会根据目前数据在哪里来处理:
如果数据已经写到XIV了,那就从XIV读
如果数据还没写到XIV,那从host发给XIV的读操作就从legacy storage中读取并返还给主机
–XIV处理所有主机发过来的写操作:
处理写请求时,有两种方式,这是在你定义data migration时就选择了Source Updating还是No Source Updating
Source Updating
--- 两套Storage(legacy Storage和XIV)上都写数据,即Source Storage在migration过程中是keep updated的,就像XDRP,是既写到XIV,也写到legacy Storage后,才会给Host发送Acknowledge。如果migration过程中和legacy Storage的通信断了,那么XIV也会将这个写操作置为Fail
No Source Updating
--- Migration过程中legacy Storage是不写任何数据的,即两套存储上数据是不同步的
XIV Data Migration Process
1.Server is connected to legacy system & accessing legacy luns 2.Unmap LUNs and disconnect server from legacy system
–Remove any proprietary device drivers from server
–Prepare server to use native multipathing (MPIO)
3.Connect XIV to legacy system
–Define XIV as a Linux ‘host’ to legacy system
–Map legacy LUNs to XIV ‘host’
4.Start XIV data migration
–“Keep Source Updated” is recommended
–XIV reads LUN sequentially
5.Connect server to XIV
–Map new XIV LUN to server
6.Production resumes and continues during migration
7.Disconnect legacy storage from XIV after migration is complete
8.Discard or repurpose legacy storage
附:
XIV_1300023>>target_list
Name SCSI Type Connected
XIV_1310138 FC yes
XIV_1300023>>target_connectivity_list
Target Name Remote Port FC Port IP Interface Active Up
XIV_1310138 50017380279A0152 1:FC_Port:7:2 yes yes
更多关于Copy Service和Data Migration的内容可以参考这本书《SG24-7759-02,IBM XIV Storage System:Copy Services and Migration》。BTW,所有的IBM redbook都可以到这里找http://www.redbooks.ibm.com/,非常好用,工程师必备。
-------------------------
至此XIV到此就告一段落,讲的非常简单,知道个皮毛而已,如果以后的工作涉及到XIV会更加详细地研究下。