使用SpringBoot开启微服务之旅(详细步骤)
https://www.tuicool.com/articles/YJZ3amq
本文要点
- 微服务可以使你的代码解耦
- 微服务可以使不同的团队专注于更小范围的工作职责、使用独立的技术、更安全更频繁地部署
- SpringBoot支持各种REST API的实现方式
- 服务发现和服务调用是独立于服务平台的
- Swagger生成稳健的API文档和调用接口
如果还没有准备好使用微服务,那你肯定落后于学习曲线中的早期接受者阶段了,而且是时候开启微服务之旅了。本文中,我们将演示创建REST风格微服务所必需的各种组件,使用Consul服务注册中心和Spring Boot搭建各种脚手架、进行依赖注入和依赖管理,使用Maven进行构建,使用Spring REST和Jersey/JaxRS创建Java REST风格API。
在过去的二十年里,企业使用SDLC流程变得非常敏捷,但是应用程序仍然相当庞大而且耦合在一起,包含大量支持各种版本的各种各样API的jar包。但是,如今有一种趋势朝着更精简的DevOps范的流程推进,功能也变得“无服务器化”。进行微服务重构可以解耦代码和资源,让构建流程更小,让发布更安全,让API更稳定。
本文中,我们将构建一个简易的股票市场投资组合管理应用程序。在这个应用中,客户可以通过服务调用,为他们的股票投资组合(股票代码和数量)进行定价。投资组合微服务将检索用户的投资组合,将它发送给定价微服务来应用最新的定价,然后返回完全定价和分类汇总过的投资组合,通过一个REST调用将所有这些信息展示给客户。
在我们开始创建微服务之前,需要安装Consul来准备我们的环境。
下载Consul服务注册中心
我们将使用Hashicorp Consul来实现服务发现,所以请前往 https://www.consul.io/downloads.html 下载Consul,有Windows版、Linux版和Mac版等。这个链接将会提供一个可执行程序,你需要将这个程序添加到你的path环境变量中。
启动Consul
从一个脚本弹出框以dev模式启动Consul:
consul agent -dev
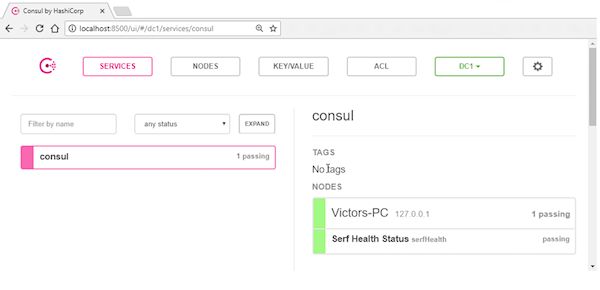
为了验证它确实已经在运行,可以打开浏览器,访问consul UI http://localhost:8500 。如果一切正常,consul应该会报告它的运行状态良好。点击(在左边的)consul服务,会(在右边)提供更多信息。
如果这个地方有什么问题,请确保你已经将consul添加到执行路径中而且8500和8600端口是可用的。
创建SpringBoot应用程序
我们将使用集成在主流IDE中的 Spring Initializr ,来创建我们的SpringBoot应用程序的脚手架。下面的截屏使用的是IntelliJ IDEA。
选择File/New Project,来打开新建项目模板弹出框,然后选择Spring Initializr。
事实上,你可以无需IDE就安装脚手架。通过SpringBoot Initializr网站 https://start.spring.io完成一个在线web表格,会产出一个可以下载的包含你的空项目的zip文件。
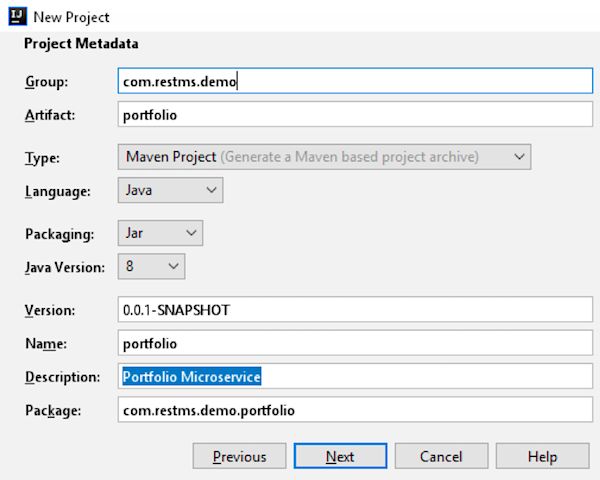
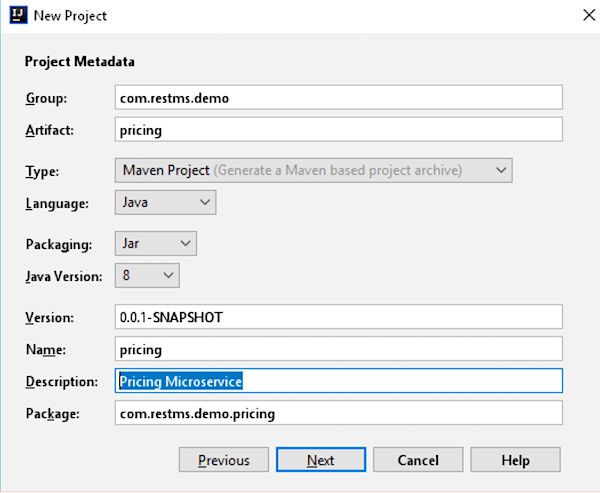
点击“Next”按钮,填写所有的项目元数据。使用下面的配置:
点击“Next”按钮来选择依赖,然后在依赖搜索栏输入Jersey和Consul Discovery。添加那些依赖:
点击“Next“按钮来指定你的项目名字和存放位置。使用在web表单中配置的默认名字“portfolio”,指定你希望存放项目的地址,然后点击“Finish”来生成并打开项目:
(点击图片放大)
你可以使用生成的application.properties文件,但是SpringBoot也接受YAML文件格式,YAML格式看起来更直观,因此可以将这个文件重命名为application.yml。
我们将这个微服务命名为“portfolio-service”。我们可以指定一个端口或者使用端口0来让应用程序使用一个可用的端口。在我们的例子中,我们使用端口57116。如果你将这个服务作为一个Docker container部署,你可以将它映射到任何你选中的端口。让我们通过添加如下配置到applicatin.yml文件,来为应用程序命名并指定端口:
spring:
application:
name: portfolio-service
server:
port: 57116
为了让我们的服务可以被发现,需要为SpringBoot的application类添加注解。打开PortfolioApplication,在这个类声明的上方添加@EnableDiscoveryClient。
接受imports。这个class看起来会是这样:
package com.restms.demo.portfolio;
import org.springframework.cloud.client.discovery.EnableDiscoveryClient;
. . .
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableDiscoveryClient
public class PortfolioApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(PortfolioApplication.class, args);
}
}(为了演示如何由各种独立的平台组合微服务,我们将为这个服务使用Jersey,然后为下一服务使用Spring REST)。
为了安装Jersey REST风格Web Service,我们需要指定一个ResourceConfig Configuration类。增加JerseyConfig类(本例中,我们会把它放在相同的package下作为我们的application类。)它应该看起来像这样,加上适当的package和imports:
@Configuration
@ApplicationPath("portfolios")
public class JerseyConfig extends ResourceConfig {
public JerseyConfig()
{
register(PortfolioImpl.class);
}
}
需要注意的是,它继承了ResourceConfig来表明它是一个Jersey的配置类。@ApplicationPath("portfolios")属性指定了调用的上下文,意味着调用路径应该以“portfolios”开头。(如果你没有指定,上下文默认为“/”。)
PortfolioImpl类将服务两种请求,其中portfolios/customer/{customer-id}返回所有的portfolios,而portfolios/customer/{customer-id}/portfolio/{portfolio-id}返回一个portfolio。一个portfolio包括一组股票代码和相应的持有份额。
(本例中,有3个客户,id分别为0、1、2,而且每一个客户都有3个portfolio,id分别为0、1、2)。
你的IDE会让你创建PortfolioImpl,照着做就行了。本例中,将它添加在相同的package。输入如下代码并接受所有imports:
@Component
@Path("/portfolios")
public class PortfolioImpl implements InitializingBean {
private Object[][][][] clientPortfolios;
@GET
@Path("customer/{customer-id}")
@Produces(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON)
// a portfolio consists of an array of arrays, each containing an array of
// stock ticker and associated shares
public Object[][][] getPortfolios(@PathParam("customer-id") int customerId)
{
return clientPortfolios[customerId];
}
@GET
@Path("customer/{customer-id}/portfolio/{portfolio-id}")
@Produces(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON)
public Object[][] getPortfolio(@PathParam("customer-id") int customerId,
@PathParam("portfolio-id") int portfolioId) {
return getPortfolios(customerId)[portfolioId];
}
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
Object[][][][] clientPortfolios =
{
{
// 3 customers, 3 portfolios each
{new Object[]{"JPM", 10201}, new Object[]{"GE", 20400}, new Object[]{"UTX", 38892}},
{new Object[]{"KO", 12449}, new Object[]{"JPM", 23454}, new Object[]{"MRK", 45344}},
{new Object[]{"WMT", 39583}, new Object[]{"DIS", 95867}, new Object[]{"TRV", 384756}},
}, {
{new Object[]{"GE", 38475}, new Object[]{"MCD", 12395}, new Object[]{"IBM", 91234}},
{new Object[]{"VZ", 22342}, new Object[]{"AXP", 385432}, new Object[]{"UTX", 23432}},
{new Object[]{"IBM", 18343}, new Object[]{"DIS", 45673}, new Object[]{"AAPL", 23456}},
}, {
{new Object[]{"AXP", 34543}, new Object[]{"TRV", 55322}, new Object[]{"NKE", 45642}},
{new Object[]{"CVX", 44332}, new Object[]{"JPM", 12453}, new Object[]{"JNJ", 45433}},
{new Object[]{"MRK", 32346}, new Object[]{"UTX", 46532}, new Object[]{"TRV", 45663}},
}
};
this.clientPortfolios = clientPortfolios;
}
}
@Component注解表明这是一个Spring组件类,将它暴露为一个端点。正如我们从方法的注解中看到的那样,@Path注解声明这个类可以通过“portfolios”路径访问到,两个支持的api调用可以通过portfolios/customer/{customer-id}和portfolios/customer/{customer-id}/portfolio/{portfolio-id}。这些方法通过@GET注解表明它服务HTTP GET请求,这个方法声明返回一个数组并注解为返回Json,因此它会返回一个Json数组。注意如何在方法声明中使用@PathParam注解来从request中提取映射的参数。
(本例中,我们返回硬编码的值。当然,在实际应用中,实现的服务在这里会查询数据库或其它一些服务或者数据源。)
现在构建这个项目,然后运行。如果你是在使用IntelliJ,它会创建一个默认的可运行程序,你只需点击绿色的“运行”箭头。你还可以使用
mvn spring-boot:run
或者,你可以运行一次maven install,然后使用java -jar并指定target目录下生成的jar文件来运行这个应用程序:
java -jar target\portfolio-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar
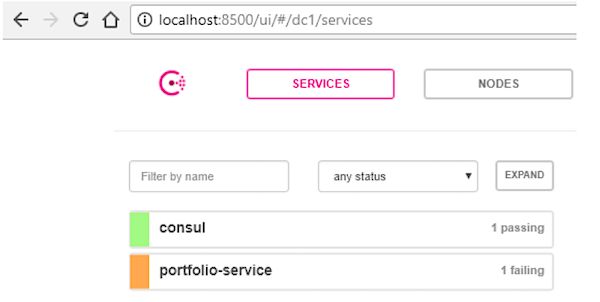
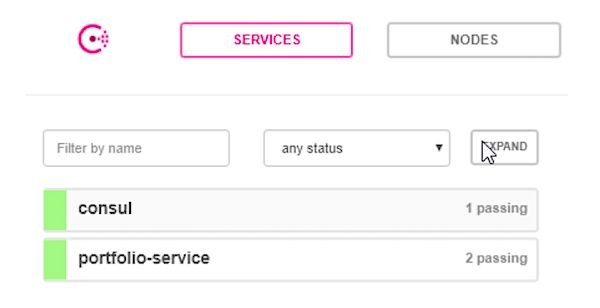
我们现在应该可以在Consul中查看这个服务,所以返回浏览器,打开 http://localhost:8500/ui/#/dc1/services (如果你已经打开了这个地址,刷新就可以了)。
我们看到我们的portfolio-service在那里了,但是显示为failing(失败)。那是因为Consol在等待从我们的服务发送一个“健康”的心跳请求。
为了生成心跳请求,我们在应用程序的pom文件中增加SpringBoot “Actuator”服务 的依赖。
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuatorartifactId>
dependency>
在pom文件中,请注意,Jersey版本在consul-starter和jersey-starter中有一个版本冲突。为了解决这个冲突,将jersey starter移为第一个依赖。
你的pom文件现在应该包含如下依赖:
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-jerseyartifactId>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloudgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-consul-discoveryartifactId>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuatorartifactId>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-testartifactId>
<scope>testscope>
dependency>
dependencies>
重启Consul,然后portfolio-service会显示正常:
现在在portfolio-service下有两个通过的节点,其中一个是我们实现的portfolio服务,另外一个是心跳服务。
检查分配的端口。你可以在应用程序输出台看到:
INFO 19792 --- [ main] s.b.c.e.t.TomcatEmbeddedServletContainer : Tomcat started on port(s): 57116 (http)
你也可以直接在consul UI中查看这个端口。点击portfolio-service,然后选择“Service 'portfolio-service'”链接,会显示该服务的端口,本例中为57116。
调用 http://localhost:57116/portfolios/customer/1/portfolio/2 ,然后你会看到json数组 [["IBM",18343],["DIS",45673],["AAPL",23456]]。
我们第一个微服务就正式开放了!
定价服务
接下来,我们会创建定价服务,这一次使用Spring RestController而不是Jersey。
定价服务会接受客户端id和portfolio id作为参数,然后会使用一个RestTemplate查询portfolio服务来获取股票代码和份额,随后返回当前的价格。(这些都是假数据,所以不要用这些数据来做交易决策!)
使用如下信息创建一个新项目:
这次选择Web、Consul Discovery和Actuator依赖:
(点击图片放大)
将项目命名为“pricing”,在你选中的目录中生成项目。
这次我们会使用application.properties而不是application.yml。
在application.properties中设置名字和端口如下:
spring.application.name=pricing
server.port=57216用@EnableDiscoveryClient给PricingApplication注解。这个类应该看起来像这样,加上package和imports。
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableDiscoveryClient
public class PricingApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(PricingApplication.class, args);
}
}
接下来,我们会创建PricingEndpoint类。这个类有一点冗长,因为它演示了一些重要的功能,包括服务发现(查找portfolio service)和使用RestTemplate来创建一个查询:
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/pricing")
public class PricingEndpoint implements InitializingBean {
@Autowired
DiscoveryClient client;
Map pricingMap = new HashMap<>();
RestTemplate restTemplate = new RestTemplate();
@GetMapping("/customer/{customer-id}/portfolio/{portfolio-id}")
public List getPricedPortfolio(
@PathVariable("customer-id") Integer customerId,
@PathVariable("portfolio-id") Integer portfolioId)
{
List instances
= client.getInstances("portfolio-service");
ServiceInstance instance
= instances.stream()
.findFirst()
.orElseThrow(() -> new RuntimeException("not found"));
String url = String.format("%s/portfolios/customer/%d/portfolio/%d",
instance.getUri(), customerId, portfolioId);
// query for the portfolios, returned as an array of List
// of size 2, containing a ticker and a position (# of shares)
Object[] portfolio = restTemplate.getForObject(url, Object[].class);
// Look up the share prices, and return a list of Strings, formatted as
// ticker, shares, price, total
List<String> collect = Arrays.stream(portfolio).map(position -> {
String ticker = ((List) position).get(0);
int shares = ((List) position).get(1);
double price = getPrice(ticker);
double total = shares * price;
return String.format("%s %d %f %f", ticker, shares, price, total);
}) .collect(Collectors.toList());
return collect;
}
private double getPrice(String ticker)
{
return pricingMap.get(ticker);
}
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
pricingMap.put("MMM",201.81);
pricingMap.put("AXP",85.11);
pricingMap.put("AAPL",161.04);
pricingMap.put("BA",236.32);
pricingMap.put("CAT",118.02);
pricingMap.put("CVX",111.31);
pricingMap.put("CSCO",31.7);
pricingMap.put("KO",46.00);
pricingMap.put("DIS",101.92);
pricingMap.put("XOM",78.7);
pricingMap.put("GE",24.9);
pricingMap.put("GS",217.62);
pricingMap.put("HD",155.82);
pricingMap.put("IBM",144.29);
pricingMap.put("INTC",35.66);
pricingMap.put("JNJ",130.8);
pricingMap.put("JPM",89.75);
pricingMap.put("MCD",159.81);
pricingMap.put("MRK",63.89);
pricingMap.put("MSFT",73.65);
pricingMap.put("NKE",52.78);
pricingMap.put("PFE",33.92);
pricingMap.put("PG",92.79);
pricingMap.put("TRV",117.00);
pricingMap.put("UTX",110.12);
pricingMap.put("UNH",198.00);
pricingMap.put("VZ",47.05);
pricingMap.put("V",103.34);
pricingMap.put("WMT", 80.05);
}
}
为了发现portfolio服务,我们需要访问一个DiscoveryClient。这可以通过Spring的@Autowired注解轻松实现
@Autowired
DiscoveryClient client;
然后在服务调用中,用这个DiscoveryClient实例来寻址我们的服务:
List instances = client.getInstances("portfolio-service");
ServiceInstance instance = instances.stream().findFirst().orElseThrow(() -> new RuntimeException("not found"));
一旦寻址到这个服务,我们可以用它来执行我们的请求。这个请求是我们根据在portflo-service中创建的api调用组合而成的。
String url = String.format("%s/portfolios/customer/%d/portfolio/%d", instance.getUri(), customerId, portfolioId);
最终,我们使用一个RestTemplate来执行我们的GET请求。
Object[] portfolio = restTemplate.getForObject(url, Object[].class);需要注意的是,对于RestControllers(和SpringMVC RequestController一样),路径变量可以从@PathVariable注解中提取,而不像Jersey那样从@PathParam中提取。
这里使用一个Spring RestController来将定价服务发布出去。
文档
我们已经克服所有困难创建了我们的微服务,但是如果不让世界知道如何使用它们,它们就不会产生任何价值。
为此,我们使用了一个称作 Swagger 的工具。Swagger是一个简单易用的工具,不仅为我们的API调用生成文档,还提供了一个可以援引这些文档的易用的web客户端。
首先,让我们在pom文件中指定Swagger:
<dependency>
<groupId>io.springfoxgroupId>
<artifactId>springfox-swagger2artifactId>
<version>2.7.0version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.springfoxgroupId>
<artifactId>springfox-swagger-uiartifactId>
<version>2.7.0version>
dependency>
接下来,我们需要告诉Swagger想要为哪些类生成文档。我们需要引入一个称为SwaggerConfig的新类,它包含Swagger的各种配置。
@Configuration
@EnableSwagger2
public class SwaggerConfig {
@Bean
public Docket api() {
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2)
.select()
.apis(RequestHandlerSelectors.any())
.paths(PathSelectors.regex("/pricing.*"))
.build();
}
}
我们可以看下这个类做了什么。首先,我们用@EnableSwagger2注解表明它是一个Swagger配置。
接下来,我们创建了一个Docket bean,告诉Swagger要暴露哪些API。在上面的例子中,我们告诉Swagger暴露所有以“/pricing”开头的路径。还可以选择指定class文件而不是路径来生成文档:
.apis(RequestHandlerSelectors.basePackage("com.restms.demo"))
.paths(PathSelectors.any())重启定价微服务,然后在浏览器上调用 http://localhost:57216/swagger-ui.html 。
点击“List Operations”按钮来查看详细的服务操作。
点击“Expand Opeartions”来创建一个基于form的查询调用。提供一些参数,点击“Try it out!”,然后等待响应结果:
(点击图片放大)
你可以通过给方法增加Swagger注解来增加更多的颜色。
例如,使用@ApiOperation注解来装饰已有的方法PricingImpl.getPricedPortfolio:
@ApiOperation(value = "Retrieves a fully priced portfolio",
notes = "Retrieves fully priced portfolio given customer id and portfolio id")
@GetMapping("/customer/{customer-id}/portfolio/{portfolio-id}")
public List getPricedPortfolio(@PathVariable("customer-id") Integer customerId, @PathVariable("portfolio-id") Integer portfolioId)
重启并刷新swagger-ui,查看新创建的文档:
你还可以用Swagger做许多事情,更多详情请查看它的文档。