tomcat8 源码 之单例模式
前言
tomcat8源码中应用了很多设计模式,通过探究源码,get到了这些优秀的设计模式如何在成熟的软件产品中被淋漓尽致的使用,下面先聊聊当中的单例模式
1、背景概述
**
tomcat中有一套完善的异常信息管理机制,在每个需要异常管理的工程包下都有相应的 properties 文件,文件中主要定义了各自pacakage下的类的各种异常信息,极大的方便了对异常信息的维护
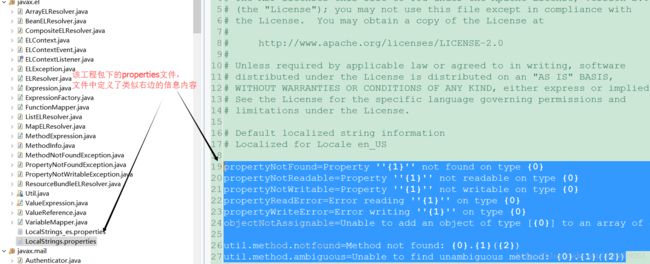
其中,采用org.apache.tomcat.util.res.StringManager来完成对信息的操作,考虑到异常信息的频繁操作,为避免浪费内存资源,避免创建过多的StringManager实例,该类对象用单例模式创建
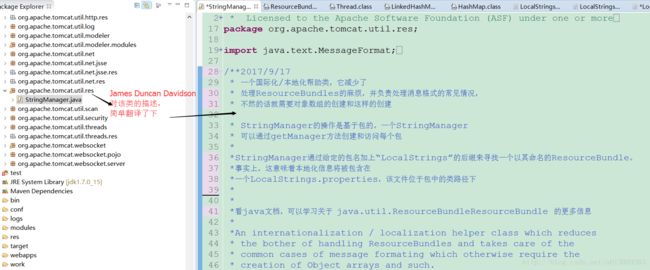
看下作者对该类的描述:
2、StringManager源码学习
public class StringManager {
// **Locale的缓存个数**
private static int LOCALE_CACHE_SIZE = 10;
/**java.util.ResourceBundle 用于读取properties文件
* The ResourceBundle for this StringManager.
*/
private final ResourceBundle bundle;
//一个 Locale对象代表一个特定的地理、政治或文化区
private final Locale locale;
/**
* 私有的构造函数
* 传入包名和Locale
*/
private StringManager(String packageName, Locale locale) {
String bundleName = packageName + ".LocalStrings";
ResourceBundle bnd = null;
try {
bnd = ResourceBundle.getBundle(bundleName, locale);
} catch (MissingResourceException ex) {
// Try from the current loader (that's the case for trusted apps)
// Should only be required if using a TC5 style classloader structure
// where common != shared != server
ClassLoader cl = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader();
if (cl != null) {
try {
bnd = ResourceBundle.getBundle(bundleName, locale, cl);
} catch (MissingResourceException ex2) {
// Ignore
}
}
}
bundle = bnd;
//获取实际的语言环境,这可能与所请求的语言环境不同
// Get the actual locale, which may be different from the requested one
if (bundle != null) {
Locale bundleLocale = bundle.getLocale();
if (bundleLocale.equals(Locale.ROOT)) {
this.locale = Locale.ENGLISH;
} else {
this.locale = bundleLocale;
}
} else {
this.locale = null;
}
}
/**
*通过properties中的key获取对应信息
*/
public String getString(String key) {
if (key == null){
String msg = "key may not have a null value";
throw new IllegalArgumentException(msg);
}
String str = null;
try {
// Avoid NPE if bundle is null and treat it like an MRE
if (bundle != null) {
str = bundle.getString(key);
}
} catch (MissingResourceException mre) {
**在此学习作者一个异常处理的思路**
//坏方式bad: shouldn't mask an exception the following way:
// str = "[cannot find message associated with key '" + key +
// "' due to " + mre + "]";
// because it hides the fact that the String was missing
// from the calling code.
//好方式good: could just throw the exception (or wrap it in another)
// but that would probably cause much havoc on existing
// code.
//更好方式better: consistent with container pattern to
// simply return null. Calling code can then do
// a null check.
str = null;
}
return str;
}
/**
* Get a string from the underlying resource bundle and format
* it with the given set of arguments.
*
* @param key The key for the required message
* @param args The values to insert into the message
*
* @return The request string formatted with the provided arguments or the
* key if the key was not found.
*/
public String getString(final String key, final Object... args) {
String value = getString(key);
if (value == null) {
value = key;
}
MessageFormat mf = new MessageFormat(value);
mf.setLocale(locale);
return mf.format(args, new StringBuffer(), null).toString();
}
/**
* Identify the Locale this StringManager is associated with.
*
* @return The Locale associated with the StringManager
*/
public Locale getLocale() {
return locale;
}
// --------------------------------------------------------------
// STATIC SUPPORT METHODS
// --------------------------------------------------------------
========
/**
通过hashtable 维护 各自package下的StringManager实例
因为hashtable线程安全
*/
private static final Map> managers =
new Hashtable>();
public static final StringManager getManager(Class clazz) {
return getManager(clazz.getPackage().getName());
}
public static final StringManager getManager(String packageName) {
return getManager(packageName, Locale.getDefault());
}
/**通过synchronized 锁机制,
*获取一个特定包和场所的StringManager。如果对于一个包/场所组合manager已经存在,它将被重用,
*否则将创建一个新的StringManager,并返回
* Get the StringManager for a particular package and Locale. If a manager
* for a package/Locale combination already exists, it will be reused, else
* a new StringManager will be created and returned.
*
* @param packageName The package name
* @param locale The Locale
*
* @return The instance associated with the given package and Locale
*/
public static final synchronized StringManager getManager(String packageName, Locale locale) {
Map map = managers.get(packageName);
if (map == null) {
/*get这个维护map容量的新技能
*
* 不要希望将HashMap扩展到localecachesize(10个元素)之外。当大小()超过容量时,扩展就会发生。因此,保持map大小或低于容量。
*removeEldestEntry()在插入之后执行,即put方法,超过10个元 素,会移除其中最老的元素
*
* Don't want the HashMap to be expanded beyond LOCALE_CACHE_SIZE.
* Expansion occurs when size() exceeds capacity. Therefore keep
* size at or below capacity.
* removeEldestEntry() executes after insertion therefore the test
* for removal needs to use one less than the maximum desired size
*
*/
map = new LinkedHashMap(LOCALE_CACHE_SIZE, 1, true) {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
@Override
protected boolean removeEldestEntry(
Map.Entry eldest) {
if (size() > (LOCALE_CACHE_SIZE - 1)) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
};
//放入map
managers.put(packageName, map);
}
//获取存在的单例
StringManager mgr = map.get(locale);
if (mgr == null) {
mgr = new StringManager(packageName, locale);
map.put(locale, mgr);
}
return mgr;
}
/**
*/
public static StringManager getManager(String packageName,
Enumeration requestedLocales) {
while (requestedLocales.hasMoreElements()) {
Locale locale = requestedLocales.nextElement();
StringManager result = getManager(packageName, locale);
if (result.getLocale().equals(locale)) {
return result;
}
}
// Return the default
return getManager(packageName);
}
/**
*测试removeEldestEntry的移除特性
*/
private static final int MAX_ENTRIES = 5;
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedHashMap lhm = new LinkedHashMap(MAX_ENTRIES + 1, .75F, false) {
protected boolean removeEldestEntry(Map.Entry eldest) {
return size() > MAX_ENTRIES;
}
};
lhm.put(0, "H");
lhm.put(1, "E");
lhm.put(2, "L");
lhm.put(3, "L");
lhm.put(4, "O");
/*加入后,超过5个元素容量,
*H 作为最老元素,将被移除
*/
lhm.put(5, "O");//
System.out.println("" + lhm);
}
} 3、单例模式小结
1)意图:保证一个类仅有一个实例,并提供一个访问它的全局访问点。
2)主要解决:一个全局使用的类频繁地创建与销毁。
3)何时使用:当您想控制实例数目,节省系统资源的时候。
4)如何解决:判断系统是否已经有这个单例,如果有则返回,如果没有则创建。(多个实例:多线程环境下使用锁机制+线程安全的容器)
5)关键代码:构造函数是私有的。
优点:
1、减少了内存的开销,尤其是频繁的创建和销毁实例
2、避免对资源的多重占用(比如写文件操作)。
缺点:没有接口,不能继承,与单一职责原则冲突,一个类应该只关心内部逻辑,而不关心外面怎么样来实例化。
使用场景: 1、要求生产唯一序列号。 2、WEB 中的计数器,不用每次刷新都在数据库里加一次,用单例先缓存起来。 3、创建的一个对象需要消耗的资源过多,比如 I/O 与数据库的连接等。
4、拓展学习
1、懒汉式,线程安全
是否 Lazy 初始化:是
是否多线程安全:是
描述:这种方式具备很好的 lazy loading,能够在多线程中很好的工作,但是,效率很低,99% 情况下不需要同步。
优点:第一次调用才初始化,避免内存浪费。
缺点:必须加锁 synchronized 才能保证单例,但加锁会影响效率。
getInstance() 的性能对应用程序不是很关键(该方法使用不太频繁)
public class Singleton {
private static Singleton instance;
private Singleton (){}
public static synchronized Singleton getInstance() {
if (instance == null) {
instance = new Singleton();
}
return instance;
}
} 2、双检锁/双重校验锁(DCL,即 double-checked locking)
JDK 版本:JDK1.5 起
是否 Lazy 初始化:是
是否多线程安全:是
描述:这种方式采用双锁机制,安全且在多线程情况下能保持高性能。
getInstance() 的性能对应用程序很关键。
public class Singleton {
private volatile static Singleton singleton;
private Singleton (){}
public static Singleton getSingleton() {
if (singleton == null) {
synchronized (Singleton.class) {
if (singleton == null) {
singleton = new Singleton();
}
}
}
return singleton;
}
} 3、静态内部类
是否 Lazy 初始化:是
是否多线程安全:是
描述:这种方式能达到双检锁方式一样的功效,但实现更简单。对静态域使用延迟初始化,应使用这种方式而不是双检锁方式。这种方式只适用于静态域的情况,双检锁方式可在实例域需要延迟初始化时使用。
这种方式同样利用了 classloder 机制来保证初始化 instance 时只有一个线程,这种方式是 Singleton 类被装载了,instance 不一定被初始化。因为 SingletonHolder 类没有被主动使用,只有显示通过调用 getInstance 方法时,才会显示装载 SingletonHolder 类,从而实例化 instance。想象一下,如果实例化 instance 很消耗资源,所以想让它延迟加载,另外一方面,又不希望在 Singleton 类加载时就实例化,因为不能确保 Singleton 类还可能在其他的地方被主动使用从而被加载,那么这个时候实例化 instance 显然是不合适的。这个时候,可以采用饿汉式
public class Singleton {
private static class SingletonHolder {
private static final Singleton INSTANCE = new Singleton();
}
private Singleton (){}
public static final Singleton getInstance() {
return SingletonHolder.INSTANCE;
}
}
4、枚举
DK 版本:JDK1.5 起
是否 Lazy 初始化:否
是否多线程安全:是
描述:这种实现方式还没有被广泛采用,但这是实现单例模式的最佳方法。它更简洁,自动支持序列化机制,绝对防止多次实例化。
这种方式是 Effective Java 作者 Josh Bloch 提倡的方式,它不仅能避免多线程同步问题,而且还自动支持序列化机制,防止反序列化重新创建新的对象,绝对防止多次实例化。不过,由于 JDK1.5 之后才加入 enum 特性,用这种方式写不免让人感觉生疏,在实际工作中,也很少用。
不能通过 reflection attack 来调用私有构造方法
public enum Singleton {
INSTANCE;
public void whateverMethod() {
}
}