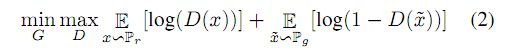1.Conditional Generative Adversarial Netwoks
Describe GAN: Generative adversarial nets were recently introduced as a novel way to train a generative model.
They consists of two ‘adversarial’ models: a generative model G that captures the data distribution,
and a discriminative model D that estimates the probability that a sample came from the training
data rather than G. Both G and D could be a non-linear mapping function, such as a multi-layer
perceptron.(多层的感知机)
GAN两个模型对抗的实质:对于G来说等价于最小化log(1-D(G(z)))期望;对于D来说,等价于最大logD(x)的期望,类似于一个minimax的游戏。由此可以得到GAN的目标函数V(G,D):
解决什么问题:图像标注、图像分类和图像生成过程中,存在两类问题:其一、输出图像的label比较多,成千上万类别;其二、对于一个输入x,对应合适输出y(label)的类别multi-modal(多个),怎么样选择一个合适类别是个问题。CGAN尝试在生成器G和判别器端加入额外的条件信息(additional information)来指导GAN两个模型的训练。
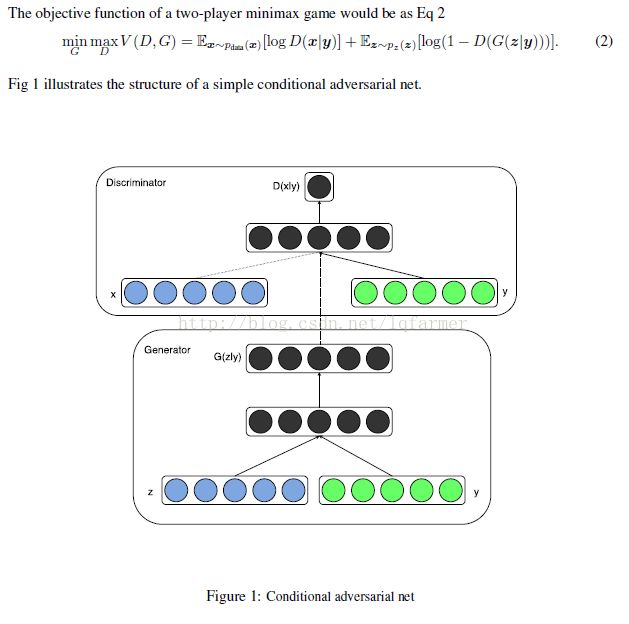
怎么做:条件化(conditional)GAN做法就是直接把额外的信息(y)直接添加到生成器G和判别器D的的目标函数中,与输入Z和X中构成条件概率,如下图所示:
用于指导G和D训练的额外信息可以是各种类型(multi-modal)的数据,已图像分类为例,可以是label标签,也可以是关于图像类别或其他信息的text文本描述。
WGAN:
WGAN:Wasserstein GAN.Martin Arjovsky, Soumith Chintala, and Lon Bottou.2017.03.09
Improved Training of Wasserstein GANs.Ishaan Gulrajani1, Faruk Ahmed1, Martin Arjovsky2.2017.03.31
解决什么问题:GAN在训练很麻烦,需要精心设计生成器G和判别器D的网络结构,调整很多的超参数,经常不收敛。为了解决这个问题,让GAN训练起来更容易,本文提出了Wasserstein GAN(WGAN)。
怎么做:深入分析由GAN所优化的值函数(value function)的收敛特性,指出传统GAN不稳定是因为其基于Jensen-Shannon 差异(divergence)构造的值函数在某一地方不可导,导致生成器G训练不稳定。因此,提出了Earth-Mover距离,又称Wasserstein-1 距离W(q,p),基于Wasserstein distance来构造值函数,代替传统GAN中基于Jensen-Shannon 差异(divergence)的值函数。Wasserstein distance具有更好的特性,Jensen-Shannon divergence可能不连续,在不连续的地方不能提供稳定的梯度用于生成器G的参数优化;相比之下,Earth-Mover距离处处连续,处处可导。
Jensen-Shannon距离与Wassertein距离对比: