HaProxy简介
HaProxy是什么?
HAProxy是一个免费的负载均衡软件,可以运行于大部分主流的Linux操作系统上。
HAProxy提供了L4(TCP)和L7(HTTP)两种负载均衡能力,具备丰富的功能。HAProxy的社区非常活跃,版本更新快速。最关键的是,HAProxy具备媲美商用负载均衡器的性能和稳定性。
因为HAProxy的上述优点,它当前是免费负载均衡软件的首选
HaProxy的核心功能
# 负载均衡:L4和L7两种模式,支持RR/静态RR/LC/IP Hash/URI Hash/URL_PARAM Hash/HTTP_HEADER Hash等丰富的负载均衡算法
# 健康检查:支持TCP和HTTP两种健康检查模式
# 会话保持:对于未实现会话共享的应用集群,可通过Insert Cookie/Rewrite Cookie/Prefix Cookie,以及上述的多种Hash方式实现会话保持
# SSL:HAProxy可以解析HTTPS协议,并能够将请求解密为HTTP后向后端传输
# HTTP请求重写与重定向
# 监控与统计:HAProxy提供了基于Web的统计信息页面,展现健康状态和流量数据。基于此功能,使用者可以开发监控程序来监控HAProxy的状态
HaProxy的关键特性
性能
1 . 采用单线程、事件驱动、非阻塞模型,减少上下文切换的消耗,能在1ms内处理数百个请求。并且每个会话只占用数KB的内存。
2 . 大量精细的性能优化,如O(1)复杂度的事件检查器、延迟更新技术、Single-buffereing、Zero-copy forwarding等等,这些技术使得HAProxy在中等负载下只占用极低的CPU资源。
3 . HAProxy大量利用操作系统本身的功能特性,使得其在处理请求时能发挥极高的性能,通常情况下,HAProxy自身只占用15%的处理时间,剩余的85%都是在系统内核层完成的。
4 . HAProxy作者在8年前(2009)年使用1.4版本进行了一次测试,单个HAProxy进程的处理能力突破了10万请求/秒,并轻松占满了10Gbps的网络带宽。
稳定性
作为建议以单进程模式运行的程序,HAProxy对稳定性的要求是十分严苛的。按照作者的说法,HAProxy在13年间从未出现过一个会导致其崩溃的BUG,HAProxy一旦成功启动,除非操作系统或硬件故障,否则就不会崩溃(我觉得可能多少还是有夸大的成分)。
在上文中提到过,HAProxy的大部分工作都是在操作系统内核完成的,所以HAProxy的稳定性主要依赖于操作系统,作者建议使用2.6或3.x的Linux内核,对sysctls参数进行精细的优化,并且确保主机有足够的内存。这样HAProxy就能够持续满负载稳定运行数年之久。
个人建议
1 . 使用3.x内核的Linux操作系统运行HAProxy
2 . 运行HAProxy的主机上不要部署其他的应用,确保HAProxy独占资源,同时避免其他应用引发操作系统或主机的故障
3 . 至少为HAProxy配备一台备机,以应对主机硬件故障、断电等突发情况(搭建双活HAProxy的方法在后文中有描述)
4 . sysctl的建议配置(并不是万用配置,仍然需要针对具体情况进行更精细的调整,但可以作为首次使用HAProxy的初始配置使用)
net.ipv4.tcp_tw_reuse = 1
net.ipv4.ip_local_port_range = 1024 65023
net.ipv4.tcp_max_syn_backlog = 10240
net.ipv4.tcp_max_tw_buckets = 400000
net.ipv4.tcp_max_orphans = 60000
net.ipv4.tcp_synack_retries = 3
net.core.somaxconn = 10000
HaProxy的部署
下载并解压
为HAProxy创建用户和用户组,此例中用户和用户组都是"ha"。注意,如果想要让HAProxy监听1024以下的端口,则需要以root用户来启动
http://www.haproxy.org/download/1.8/src/haproxy-1.8.12.tar.gz
tar xvf haproxy-1.8.12.tar.gz
编译并安装
# 创建用户组
useradd ha -s /sbin/nologin
yum -y install gcc
make PREFIX=/home/ha/haproxy TARGET=linux3100
make install PREFIX=/home/ha/haproxy
# PREFIX为指定的安装路径, TARGET则根据当前操作系统内核版本指定: uname -a查看
- linux22 for Linux 2.2
- linux24 for Linux 2.4 and above (default)
- linux24e for Linux 2.4 with support for a working epoll (> 0.21)
- linux26 for Linux 2.6 and above
- linux2628 for Linux 2.6.28, 3.x, and above (enables splice and tproxy)
创建HAProxy配置文件
mkdir -p /home/ha/haproxy/conf
vi /home/ha/haproxy/conf/haproxy.cfg
# 我们先创建一个简单的配置文件
global #全局属性
daemon #以daemon方式在后台运行
maxconn 256 #最大同时256连接
pidfile /home/ha/haproxy/conf/haproxy.pid #指定保存HAProxy进程号的文件
defaults #默认参数
mode http #http模式
timeout connect 5000ms #连接server端超时5s
timeout client 50000ms #客户端响应超时50s
timeout server 50000ms #server端响应超时50s
frontend http-in #前端服务http-in
bind *:8080 #监听8080端口
default_backend servers #请求转发至名为"servers"的后端服务
backend servers
# 后端服务servers
server server1 127.0.0.1:8000 maxconn 32 # backend servers中只有一个后端服务,名字叫server1,起在本机的8000端口,HAProxy同时最多向这个服务发起32个连接
# 注意:HAProxy要求系统的ulimit -n参数大于[maxconn*2+18],在设置较大的maxconn时,注意检查并修改ulimit -n参数
HAProxy关键配置详解
HAProxy的配置文件共有5个域
# global:用于配置全局参数
# default:用于配置所有frontend和backend的默认属性
# frontend:用于配置前端服务(即HAProxy自身提供的服务)实例
# backend:用于配置后端服务(即HAProxy后面接的服务)实例组
# listen:frontend+backend的组合配置,可以理解成更简洁的配置方法
Global域的关键配置
# daemon:指定HAProxy以后台模式运行,通常情况下都应该使用这一配置
# user [username] :指定HAProxy进程所属的用户
# group [groupname] :指定HAProxy进程所属的用户组
# log [address] [device] [maxlevel] [minlevel]:日志输出配置,如log 127.0.0.1 local0 info warning,即向本机rsyslog或syslog的local0输出info到warning级别的日志。其中[minlevel]可以省略。HAProxy的日志共有8个级别,从高到低为emerg/alert/crit/err/warning/notice/info/debug
# pidfile :指定记录HAProxy进程号的文件绝对路径。主要用于HAProxy进程的停止和重启动作。
# maxconn :HAProxy进程同时处理的连接数,当连接数达到这一数值时,HAProxy将停止接收连接请求
frontend域的关键配置
# acl [name] [criterion] [flags] [operator] [value]:定义一条ACL,ACL是根据数据包的指定属性以指定表达式计算出的true/false值。如"acl url_ms1 path_beg -i /ms1/"定义了名为url_ms1的ACL,该ACL在请求uri以/ms1/开头(忽略大小写)时为true
# bind [ip]:[port]:frontend服务监听的端口
# default_backend [name]:frontend对应的默认backend
# disabled:禁用此frontend
# http-request [operation] [condition]:对所有到达此frontend的HTTP请求应用的策略,例如可以拒绝、要求认证、添加header、替换header、定义ACL等等。
# http-response [operation] [condition]:对所有从此frontend返回的HTTP响应应用的策略,大体同上
# log:同global域的log配置,仅应用于此frontend。如果要沿用global域的log配置,则此处配置为log global
# maxconn:同global域的maxconn,仅应用于此frontend
# mode:此frontend的工作模式,主要有http和tcp两种,对应L7和L4两种负载均衡模式
# option forwardfor:在请求中添加X-Forwarded-For Header,记录客户端ip
# option http-keep-alive:以KeepAlive模式提供服务
# option httpclose:与http-keep-alive对应,关闭KeepAlive模式,如果HAProxy主要提供的是接口类型的服务,可以考虑采用httpclose模式,以节省连接数资源。但如果这样做了,接口的调用端将不能使用HTTP连接池
# option httplog:开启httplog,HAProxy将会以类似Apache HTTP或Nginx的格式来记录请求日志
# option tcplog:开启tcplog,HAProxy将会在日志中记录数据包在传输层的更多属性
# stats uri [uri]:在此frontend上开启监控页面,通过[uri]访问
# stats refresh [time]:监控数据刷新周期
# stats auth [user]:[password]:监控页面的认证用户名密码
# timeout client [time]:指连接创建后,客户端持续不发送数据的超时时间
# timeout http-request [time]:指连接创建后,客户端没能发送完整HTTP请求的超时时间,主要用于防止DoS类攻击,即创建连接后,以非常缓慢的速度发送请求包,导致HAProxy连接被长时间占用
# use_backend [backend] if|unless [acl]:与ACL搭配使用,在满足/不满足ACL时转发至指定的backend
backend域的关键配置
# acl:同frontend域
# balance [algorithm]:在此backend下所有server间的负载均衡算法,常用的有roundrobin和source,完整的算法说明见官方文档configuration.html#4.2-balance
# cookie:在backend server间启用基于cookie的会话保持策略,最常用的是insert方式,如cookie HA_STICKY_ms1 insert indirect nocache,指HAProxy将在响应中插入名为HA_STICKY_ms1的cookie,其值为对应的server定义中指定的值,并根据请求中此cookie的值决定转发至哪个server。indirect代表如果请求中已经带有合法的HA_STICK_ms1 cookie,则HAProxy不会在响应中再次插入此cookie,nocache则代表禁止链路上的所有网关和缓存服务器缓存带有Set-Cookie头的响应。
# default-server:用于指定此backend下所有server的默认设置。具体见下面的server配置。
# disabled:禁用此backend
# http-request/http-response:同frontend域
# log:同frontend域
# mode:同frontend域
# option forwardfor:同frontend域
# option http-keep-alive:同frontend域
# option httpclose:同frontend域
# option httpchk [METHOD] [URL] [VERSION]:# 定义以http方式进行的健康检查策略。如option httpchk GET /healthCheck.html HTTP/1.1
# option httplog:同frontend域
# option tcplog:同frontend域
# server [name] [ip]:[port] [params]: # 定义backend中的一个后端server,[params]用于指定这个server的参数,常用的包括有:
# check:指定此参数时,HAProxy将会对此server执行健康检查,检查方法在option httpchk中配置。同时还可以在check后指定inter, rise, fall三个参数,分别代表健康检查的周期、连续几次成功认为server UP,连续几次失败认为server DOWN,默认值是inter 2000ms rise 2 fall 3
# cookie [value]:用于配合基于cookie的会话保持,如cookie ms1.srv1代表交由此server处理的请求会在响应中写入值为ms1.srv1的cookie(具体的cookie名则在backend域中的cookie设置中指定)
# maxconn:指HAProxy最多同时向此server发起的连接数,当连接数到达maxconn后,向此server发起的新连接会进入等待队列。默认为0,即无限
# maxqueue:等待队列的长度,当队列已满后,后续请求将会发至此backend下的其他server,默认为0,即无限
# weight:server的权重,0-256,权重越大,分给这个server的请求就越多。weight为0的server将不会被分配任何新的连接。所有server默认weight为1
# timeout connect [time]:指HAProxy尝试与backend server创建连接的超时时间
# timeout check [time]:默认情况下,健康检查的连接+响应超时时间为server命令中指定的inter值,如果配置了timeout check,HAProxy会以inter作为健康检查请求的连接超时时间,并以timeout check的值作为健康检查请求的响应超时时间
# timeout server [time]:指backend server响应HAProxy请求的超时时间
defalut域名
# 上文所属的frontend和backend域关键配置中,除acl、bind、http-request、http-response、use_backend外,其余的均可以配置在default域中。default域中配置了的项目,如果在frontend或backend域中没有配置,将会使用default域中的配置。
listen域
# listen域是frontend域和backend域的组合,frontend域和backend域中所有的配置都可以配置在listen域下
HAProxy的配置项非常多,支持非常丰富的功能,上文只列出了作为L7负载均衡器使用HAProxy时的一些关键参数。完整的参数说明请参见官方文档 configuration.html
注册为系统服务
在/etc/init.d目录下添加HAProxy服务的启停脚本
cat /etc/init.d/haproxy
#! /bin/sh
set -e
PATH=/sbin:/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/home/ha/haproxy/sbin
PROGDIR=/home/ha/haproxy
PROGNAME=haproxy
DAEMON=$PROGDIR/sbin/$PROGNAME
CONFIG=$PROGDIR/conf/$PROGNAME.cfg
PIDFILE=$PROGDIR/conf/$PROGNAME.pid
DESC="HAProxy daemon"
SCRIPTNAME=/etc/init.d/$PROGNAME
# Gracefully exit if the package has been removed.
test -x $DAEMON || exit 0
start()
{
echo -e "Starting $DESC: $PROGNAME\n"
$DAEMON -f $CONFIG
echo "."
}
stop()
{
echo -e "Stopping $DESC: $PROGNAME\n"
haproxy_pid="$(cat $PIDFILE)"
kill $haproxy_pid
echo "."
}
restart()
{
echo -e "Restarting $DESC: $PROGNAME\n"
$DAEMON -f $CONFIG -p $PIDFILE -sf $(cat $PIDFILE)
echo "."
}
case "$1" in
start)
start
;;
stop)
stop
;;
restart)
restart
;;
*)
echo "Usage: $SCRIPTNAME {start|stop|restart}" >&2
exit 1
;;
esac
exit 0
# 给脚本一个执行权限
chmod +x /etc/init.d/haproxy
# 启动
service haproxy start
添加日志
HAProxy不会直接输出文件日志,所以我们要借助Linux的rsyslog来让HAProxy输出日志
1 . 修改haproxy.cfg
global
...
log 127.0.0.1 local0 info
log 127.0.0.1 local1 warning
...
defaults
...
log global
...
意思是将info级(及以上)的日志推送到rsyslog的local0接口,将warn级(及以上)的日志推送到rsyslog的local1接口,并且所有frontend都默认使用global中的日志配置。
注:info级的日志会打印HAProxy处理的每一条请求,会占用很大的磁盘空间,在生产环境中,建议将日志级别调整为notice
2 . 为rsyslog添加HAproxy日志的配置
vim /etc/rsyslog.d/haproxy.conf
$ModLoad imudp
$UDPServerRun 514
$FileCreateMode 0644 #日志文件的权限
$FileOwner ha #日志文件的owner
local0.* /var/log/haproxy.log #local0接口对应的日志输出文件
local1.* /var/log/haproxy_warn.log #local1接口对应的日志输出文件
3 . 修改rsyslog的启动参数
vim /etc/sysconfig/rsyslog
# Options for rsyslogd
# Syslogd options are deprecated since rsyslog v3.
# If you want to use them, switch to compatibility mode 2 by "-c 2"
# See rsyslogd(8) for more details
SYSLOGD_OPTIONS="-c 2 -r -m 0"
4 . 重启rsyslog和HAProxy
service haproxy restart
5 . 用logrotate进行日志切分
通过rsyslog输出的日志是不会切分的,所以需要依靠Linux提供的logrotate来进行切分工作,使用root用户创建haproxy日志切分配置文件
mkdir /root/logrotate
vim /root/logrotate/haproxy
# 创建日志切割规则
cat /root/logrotate/haproxy
/var/log/haproxy.log /var/log/haproxy_warn.log { #切分的两个文件名
daily #按天切分
rotate 7 #保留7份
create 0644 ha ha #创建新文件的权限、用户、用户组
compress #压缩旧日志
delaycompress #延迟一天压缩
missingok #忽略文件不存在的错误
dateext #旧日志加上日志后缀
sharedscripts #切分后的重启脚本只运行一次
postrotate #切分后运行脚本重载rsyslog,让rsyslog向新的日志文件中输出日志
/bin/kill -HUP $(/bin/cat /var/run/syslogd.pid 2>/dev/null) &>/dev/null
endscript
}
# 配置在crontab运行
0 0 * * * /usr/sbin/logrotate /root/logrotate/haproxy
使用HAProxy搭建L7负载均衡器
使用HAProxy搭建一个L7负载均衡器,应用如下功能:
# 负载均衡
# 会话保持
# 健康检查
# 根据URI前缀向不同的后端集群转发
# 监控页面
# 架构中共有6个后端服务,划分为3组,每组中2个服务:
# ms1:服务URI前缀为ms1/的请求
# ms2:服务URI前缀为ms2/的请求
# def:服务其他请求
搭建后端服务
部署6个后端服务,可以使用任意的Web服务,如Nginx、Apache HTTPD、Tomcat、Jetty等
| 节点名 | IP | 软件版本 | 硬件 | 网络 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| haproxy1 | 192.168.171.129(vip为192.168.171.250) | keepalived-1.3.5 | 2C4G | Nat,内网 | 测试环境 |
| haproxy2 | 192.168.171.130(vip为192.168.171.250) | keepalived-1.3.5 | 2C4G | Nat,内网 | 测试环境 |
| nginx-1 | 192.168.171.133:81 | nginx1.16 | 2C4G | Nat,内网 | 测试环境 |
| nginx-2 | 192.168.171.133:82 | nginx1.16 | 2C4G | Nat,内网 | 测试环境 |
| nginx-3 | 192.168.171.133:83 | nginx1.16 | 2C4G | Nat,内网 | 测试环境 |
| nginx-4 | 192.168.171.145:84 | nginx1.16 | 2C4G | Nat,内网 | 测试环境 |
| nginx-5 | 192.168.171.145:85 | nginx1.16 | 2C4G | Nat,内网 | 测试环境 |
| nginx-6 | 192.168.171.145:86 | nginx1.16 | 2C4G | Nat,内网 | 测试环境 |
此处我们用nginx多实例
yum -y install nginx
cat nginx8*
server{
listen 81;
server_name 192.168.171.133;
location / {
root /test/nginx81;
index index.html;
}
}
server{
listen 82;
server_name 192.168.171.133;
location / {
root /test/nginx82;
index index.html;
}
}
server{
listen 83;
server_name 192.168.171.133;
location / {
root /test/nginx83;
index index.html;
}
}
cat nginx8*.conf
server{
listen 84;
server_name 192.168.171.145;
location / {
root /test/nginx84;
index index.html;
}
}
server{
listen 85;
server_name 192.168.171.145;
location / {
root /test/nginx85;
index index.html;
}
}
server{
listen 86;
server_name 192.168.171.145;
location / {
root /test/nginx86;
index index.html;
}
}
mkdir /test/nginx{81..86} -p
echo nginx81 > /test/nginx81/index.html
echo nginx82 > /test/nginx82/index.html
echo nginx83 > /test/nginx83/index.html
echo nginx84 > /test/nginx84/index.html
echo nginx85 > /test/nginx85/index.html
echo nginx86 > /test/nginx86/index.html
搭建HAProxy
在192.168.171.129,192.168.171.130两台机器安装HAProxy,安装和配置步骤参考上文
HAProxy配置文件
cat conf/haproxy.cfg
global
daemon
maxconn 30000 #ulimit -n至少为60018
user ha
pidfile /home/ha/haproxy/conf/haproxy.pid
log 127.0.0.1 local0 info
log 127.0.0.1 local1 warning
defaults
mode http
log global
option http-keep-alive #使用keepAlive连接
option forwardfor #记录客户端IP在X-Forwarded-For头域中
option httplog #开启httplog,HAProxy会记录更丰富的请求信息
timeout connect 5000ms
timeout client 10000ms
timeout server 50000ms
timeout http-request 20000ms #从连接创建开始到从客户端读取完整HTTP请求的超时时间,用于避免类DoS攻击
option httpchk GET /healthCheck.html
frontend http
mode http
bind *:80
acl url_ms1 path_beg -i /ms1/ #定义ACL,当uri以/ms1/开头时,ACL[url_ms1]为true
acl url_ms2 path_beg -i /ms2/
use_backend ms1 if url_ms1 #当[url_ms1]为true时,定向到后端服务群ms1中
use_backend ms2 if url_ms2
default_backend default_servers #其他情况时,定向到后端服务群default_servers中
backend ms1
balance roundrobin #使用RR负载均衡算法
cookie HA_STICKY_ms1 insert indirect nocache #会话保持策略,insert名为"HA_STICKY_ms1"的cookie
#定义后端server[ms1.srv1],请求定向到该server时会在响应中写入cookie值[ms1.srv1]
#针对此server的maxconn设置为300
#应用默认健康检查策略,健康检查间隔和超时时间为2000ms,两次成功视为节点UP,三次失败视为节点DOWN
server ms1.srv1 192.168.171.133:81 cookie ms1.srv1 maxconn 300 check inter 2000ms rise 2 fall 3
#同上,inter 2000ms rise 2 fall 3是默认值,可以省略
server ms1.srv2 192.168.171.133:82 check maxconn 2000
backend ms2
balance roundrobin
server ms2.srv1 192.168.171.133:83 check maxconn 2000
server ms2.srv2 192.168.171.145:84 check maxconn 2000
backend default_servers
balance roundrobin
server srv1 192.168.171.145:85 check maxconn 2000
server srv2 192.168.171.145:86 check maxconn 2000
listen stats #定义监控页面
bind *:1080 #绑定端口1080
stats refresh 30s #每30秒更新监控数据
stats uri /stats #访问监控页面的uri
stats realm HAProxy\ Stats #监控页面的认证提示
stats auth admin:admin #监控页面的用户名和密码
测试
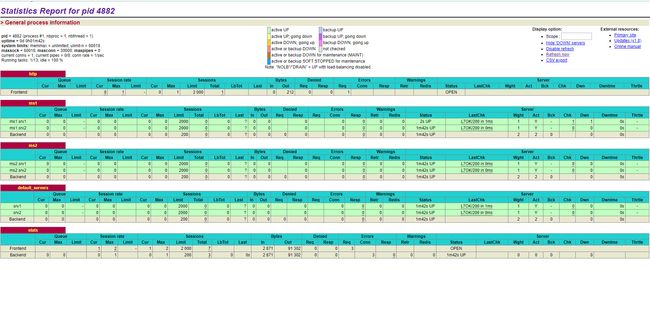
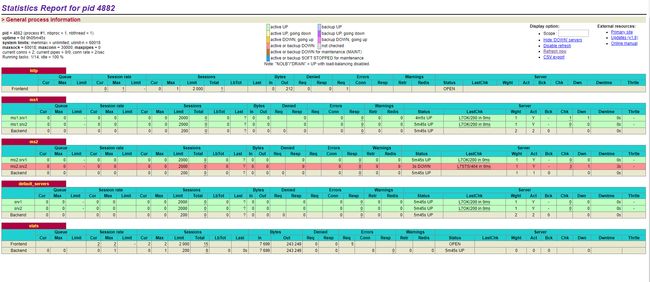
访问一下监控页面,就能看到下面监控页面
1 . 健康检查
从监控页面中就可以直接看出健康检查配置的是否正确,上图中可以看到,http ms1、ms2、default_servers下属的6个后端服务的Status都是五六分钟 UP,代表健康状态已持续了五六分钟分钟,而LastChk显示L7OK/200 in 1ms则代表在1ms前进行了L7的健康检查(即HTTP请求方式的健康检查),返回码为200
我们去修改一个Nginx实例的测试Html名字
mv /test/nginx84/healthCheck.html /test/nginx84/healthCheck.html.bak
使用HAProxy搭建L4负载均衡器
HAProxy作为L4负载均衡器工作时,不会去解析任何与HTTP协议相关的内容,只在传输层对数据包进行处理。也就是说,以L4模式运行的HAProxy,无法实现根据URL向不同后端转发、通过cookie实现会话保持等功能。
同时,在L4模式下工作的HAProxy也无法提供监控页面。
但作为L4负载均衡器的HAProxy能够提供更高的性能,适合于基于套接字的服务(如数据库、消息队列、RPC、邮件服务、Redis等),或不需要逻辑规则判断,并已实现了会话共享的HTTP服务。
修改haproxy以L4方式来代理两个HTTP服务,不提供会话保持
cat haproxy.cfg
global
daemon
maxconn 30000 #ulimit -n至少为60018
user ha
pidfile /home/ha/haproxy/conf/haproxy.pid
log 127.0.0.1 local0 info
log 127.0.0.1 local1 warning
defaults
mode tcp
log global
option tcplog #开启tcplog
timeout connect 5000ms
timeout client 10000ms
timeout server 10000ms #TCP模式下,应将timeout client和timeout server设置为一样的值,以防止出现问题
option httpchk GET /healthCheck.html #定义默认的健康检查策略
frontend http-in
bind *:9002
maxconn 30000 #定义此端口上的maxconn
default_backend default_servers #请求定向至后端服务群default_servers
backend default_servers #定义后端服务群default_servers
balance roundrobin
server def.srv1 192.168.171.133:81 maxconn 300 check
server def.srv2 192.168.171.133:82 maxconn 300 check
server def.srv3 192.168.171.133:83 maxconn 300 check
service haproxy restart
[root@haproxy1 haproxy]# curl 192.168.171.129:9002
nginx83
[root@haproxy1 haproxy]# curl 192.168.171.129:9002
ms1_Nginx_81
[root@haproxy1 haproxy]# curl 192.168.171.129:9002
nginx82
[root@haproxy1 haproxy]# curl 192.168.171.129:9002
nginx83
[root@haproxy1 haproxy]# curl 192.168.171.129:9002
ms1_Nginx_81
L4模式下的会话保持
虽然TCP模式下的HAProxy无法通过HTTP Cookie实现会话保持,但可以很方便的实现基于客户端IP的会话保持。只需将
balance roundrobin
# 更改为
balance source
service haproxy restart
# 测试
[root@haproxy1 haproxy]# curl 192.168.171.129:9002
nginx82
[root@haproxy1 haproxy]# curl 192.168.171.129:9002
nginx82
[root@haproxy1 haproxy]# curl 192.168.171.129:9002
nginx82
[root@haproxy1 haproxy]# curl 192.168.171.129:9002
nginx82
[root@haproxy1 haproxy]# curl 192.168.171.129:9002
nginx82
# 此外,HAProxy提供了强大的stick-table功能,HAProxy可以从传输层的数据包中采样出大量的属性,并将这些属性作为会话保持的策略写入stick-table中。
HaProxy+Keepalive结合使用
环境延用之前的,nginx实例不变,改下haproxy配置文件,安装keepalived和修改下相应配置文件即可
尽管HAProxy非常稳定,但仍然无法规避操作系统故障、主机硬件故障、网络故障甚至断电带来的风险。所以必须对HAProxy实施高可用方案。
原理
在两台HAProxy的主机上分别运行着一个Keepalived实例,这两个Keepalived争抢同一个虚IP地址,两个HAProxy也尝试去绑定这同一个虚IP地址上的端口。
显然,同时只能有一个Keepalived抢到这个虚IP,抢到了这个虚IP的Keepalived主机上的HAProxy便是当前的MASTER。
Keepalived内部维护一个权重值,权重值最高的Keepalived实例能够抢到虚IP。同时Keepalived会定期check本主机上的HAProxy状态,状态OK时权重值增加。
搭建HAProxy主备集群
在两台机器上安装HAProxy安装haproxy,跟上面环境一致,改下配置文件即可
haproxy配置文件
cat /home/ha/haproxy/conf/haproxy.cfg
global
daemon
maxconn 30000 #ulimit -n至少为60018
user ha
pidfile /home/ha/haproxy/conf/haproxy.pid
log 127.0.0.1 local0 info
log 127.0.0.1 local1 warning
defaults
mode tcp
log global
option tcplog #开启tcplog
timeout connect 5000ms
timeout client 10000ms
timeout server 10000ms #TCP模式下,应将timeout client和timeout server设置为一样的值,以防止出现问题
option httpchk GET /healthCheck.html #定义默认的健康检查策略
frontend http-in
bind *:9002
maxconn 30000 #定义此端口上的maxconn
default_backend default_servers #请求定向至后端服务群default_servers
backend default_servers #定义后端服务群default_servers
balance source
server def.srv1 192.168.171.133:81 maxconn 300 check
server def.srv2 192.168.171.133:82 maxconn 300 check
server def.srv3 192.168.171.133:83 maxconn 300 check
安装配置keepalived
yum -y install keepalived
主keepalived
cat keepalived.conf
! Configuration File for keepalived
global_defs {
router_id nginx
}
vrrp_script nginx_check {
script "/etc/keepalived/chk_haproxy.sh"
interval 5
}
vrrp_instance VI_1 {
state BACKUP
interface ens32
virtual_router_id 51
priority 120
advert_int 1
authentication {
auth_type PASS
auth_pass admin123
}
track_script {
chk_haproxy
}
virtual_ipaddress {
192.168.171.250
}
}
从keepalived
cat /etc/keepalived/keepalived.conf
! Configuration File for keepalived
global_defs {
router_id nginx
}
vrrp_script nginx_check {
script "/etc/keepalived/chk_haproxy.sh"
interval 5
}
vrrp_instance VI_1 {
state BACKUP
interface ens32
virtual_router_id 51
priority 100
advert_int 1
authentication {
auth_type PASS
auth_pass admin123
}
track_script {
chk_haproxy
}
virtual_ipaddress {
192.168.171.250
}
}
监测脚本
cat chk_haproxy.sh
#!/bin/bash
curl -I http://localhost:9002 &>/dev/null
if [ $? -ne 0 ];then
systemctl stop keepalived
fi
cat chk_haproxy.sh
#!/bin/bash
curl -I http://localhost:9002 &>/dev/null
if [ $? -ne 0 ];then
systemctl stop keepalived
fi
chmod a+x /etc/keepalived/chk_haproxy.sh
chown ha:ha /etc/keepalived/chk_haproxy.sh
service haproxy restart
systemctl restart keepalived
检测
我们模拟一台haproxy宕机,然后浏览器同时访问
service haproxy stop
Stopping HAProxy daemon: haproxy
[root@haproxy1 keepalived]# ss -tnl
State Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address:Port Peer Address:Port
LISTEN 0 128 *:22 *:*
LISTEN 0 128 :::22 :::*
# 我们可以发现还是可以访问的
[root@haproxy1 keepalived]# curl http://192.168.171.250:9002
nginx82
[root@haproxy1 keepalived]# curl http://192.168.171.250:9002
nginx82
# 我们查看下宕机过后的haproxy日志
tail -f /var/log/haproxy_warn.log
# 我们可以看到我们一停止haproxy就会产生keepalived停止日志
May 28 21:24:36 haproxy2 Keepalived_vrrp[5423]: VRRP_Instance(VI_1) sent 0 priority
May 28 21:24:36 haproxy2 Keepalived_vrrp[5423]: VRRP_Instance(VI_1) removing protocol VIPs.
May 28 21:24:37 haproxy2 Keepalived_vrrp[5423]: Stopped
# 同时IP也会自动切换过去,而我们直管访问vip即可
[root@haproxy1 keepalived]# ip a
1: lo: mtu 65536 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN qlen 1
link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00
inet 127.0.0.1/8 scope host lo
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
2: ens32: mtu 1500 qdisc pfifo_fast state UP qlen 1000
link/ether 00:0c:29:9c:70:c3 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
inet 192.168.171.130/24 brd 192.168.171.255 scope global dynamic ens32
valid_lft 1513sec preferred_lft 1513sec
inet 192.168.171.250/32 scope global ens32
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet6 fe80::67c7:461b:a607:5b36/64 scope link
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
HAProxy+Nginx(https)+Tomcat
| 节点名 | 软件版本 | IP | 硬件 | 网络 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| haproxy1 | haproxy1.8.12,nginx1.14 | 39.108.140.0 | 2C4G | Nat,内网 | 公有云 |
| tomcat | tomcat8.5 | 2C4G | Nat,内网 | 测试环境 |
安装haproxy和nginx
# haproxy安装请看上面,只用修改下配置文件即可
cat conf/haproxy.cfg
global
log 127.0.0.1 local0 info
log 127.0.0.1 local1 warning
daemon
maxconn 256
pidfile /home/ha/haproxy/conf/haproxy.pid
defaults
log global
mode tcp
log global
option tcplog
timeout connect 5000ms
timeout client 50000ms
timeout server 50000ms
option httpchk GET /healthCheck.html
listen admin_status
bind 0.0.0.0:1080
mode http
stats refresh 5s
stats uri /haproxy?stats
stats realm Haproxy Manager
stats auth admin:admin
stats hide-version
stats admin if TRUE
frontend http-in
log global
bind *:80
default_backend servers
backend servers
server server1 39.108.140.0:801 maxconn 32
./sbin/haproxy -f conf/haproxy.cfg
安装Nginx
#!/usr/bin/env bash
# Author: ZhouJian
# Mail: [email protected]
# Time: 2019-9-3
# Describe: CentOS 7 Install Nginx Source Code Script
version="nginx-1.14.2.tar.gz"
user="nginx"
nginx=${version%.tar*}
path=/usr/local/src/$nginx
echo $path
if ! ping -c2 www.baidu.com &>/dev/null
then
echo "网络不通,无法安装"
exit
fi
yum install -y gcc gcc-c++ openssl-devel pcre-devel make zlib-devel wget psmisc
if [ ! -e $version ];then
wget http://nginx.org/download/$version
fi
if ! id $user &>/dev/null
then
useradd $user -M -s /sbin/nologin
fi
if [ ! -d /var/tmp/nginx ];then
mkdir -p /var/tmp/nginx/{client,proxy,fastcgi,uwsgi,scgi}
fi
tar xf $version -C /usr/local/src
cd $path
./configure \
--prefix=/usr/local/nginx \
--user=nginx \
--group=nginx \
--with-http_ssl_module \
--with-http_flv_module \
--with-http_stub_status_module \
--with-http_sub_module \
--with-http_gzip_static_module \
--with-http_auth_request_module \
--with-http_random_index_module \
--with-http_realip_module \
--http-client-body-temp-path=/var/tmp/nginx/client \
--http-proxy-temp-path=/var/tmp/nginx/proxy \
--http-fastcgi-temp-path=/var/tmp/nginx/fastcgi \
--http-uwsgi-temp-path=/var/tmp/nginx/uwsgi \
--http-scgi-temp-path=/var/tmp/nginx/scgi \
--with-pcre \
--with-file-aio \
--with-http_secure_link_module && make && make install
if [ $? -ne 0 ];then
echo "nginx未安装成功"
exit
fi
killall nginx
/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx
#echo "/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx" >> /etc/rc.local
#chmod +x /etc/rc.local
#systemctl start rc-local
#systemctl enable rc-local
ss -antp |grep nginx
配置Nginx
cat /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
worker_processes 1;
events {
worker_connections 1024;
}
http {
include mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
#log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" '
# '$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" '
# '"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';
#access_log logs/access.log main;
sendfile on;
#tcp_nopush on;
keepalive_timeout 65;
#gzip on;
server {
listen 801;
server_name zcj.net.cn;
# 此处域名需要自己购买并备案,此处就不详细介绍了
#charset koi8-r;
#access_log logs/host.access.log main;
location / {
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = /50x.html {
root html;
}
}
}
# 我们访问这个域名默认是访问80端口, 经过haproxy的四层转发,然后反代到nginxd 801端口
配置https的nginx通过haproxy反代
我们需要先有一个域名和申请好的证书,此处不详细介绍,具体看我Nginx标签文章
# 我们下载好证书后有两个文件
ls 3913786_www.zcj.net.cn*
3913786_www.zcj.net.cn.key 3913786_www.zcj.net.cn_nginx.zip 3913786_www.zcj.net.cn.pem
# 以.pem为后缀或文件类型的是证书文件
# 以.key位后缀或文件类型的是密钥文件
# 我们到nginx下面目录创建一个cert目录
mkdir /usr/local/nginx/cert
# 将我们的证书换个容易识别的名字
mv 3913786_www.zcj.net.cn.key /usr/local/nginx/cert/www.zcj.net.cn.key
mv 3913786_www.zcj.net.cn.pem /usr/local/nginx/cert/www.zcj.net.cn.pem
配置nginx
cat /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
worker_processes 1;
events {
worker_connections 1024;
}
http {
include mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
sendfile on;
keepalive_timeout 65;
server {
listen 80;
server_name zcj.net.cn www.zcj.net.cn;
return 301 https://www.zcj.net.cn$request_uri;
location / {
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
}
server {
listen 443 ssl;
ssl on;
ssl_certificate_key /usr/local/nginx/cert/www.zcj.net.cn.key;
ssl_certificate /usr/local/nginx/cert/www.zcj.net.cn.pem;
location / {
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
}
}
/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -s reload
curl www.zcj.net.cn -I
HTTP/1.1 301 Moved Permanently
Server: nginx/1.14.2
Date: Tue, 02 Jun 2020 08:58:39 GMT
Content-Type: text/html
Content-Length: 185
Connection: keep-alive
Location: https://www.zcj.net.cn/
配置HaProxy反代Nginx
cat conf/haproxy.cfg
global
log 127.0.0.1 local0 info
log 127.0.0.1 local1 warning
daemon
maxconn 256
pidfile /home/ha/haproxy/conf/haproxy.pid
defaults
log global
mode tcp
log global
option tcplog
timeout connect 5000ms
timeout client 50000ms
timeout server 50000ms
option httpchk GET /healthCheck.html
listen admin_status
bind 0.0.0.0:1080
mode http
stats refresh 5s
stats uri /haproxy?stats
stats realm Haproxy Manager
stats auth admin:admin
stats hide-version
stats admin if TRUE
listen 192_168_3_37-80
bind 0.0.0.0:80
mode tcp
log global
option tcplog
balance roundrobin
server nginx_test 39.108.140.0:80
listen 192_168_3_37-443
bind 0.0.0.0:443
mode tcp
log global
option tcplog
balance roundrobin
server nginx_test 39.108.140.0:443
./sbin/haproxy -f conf/haproxy.cfg